Nội dung toàn văn Circular No. 21/2015/TT-BCT pricing method for electric power systems ancillary services
|
MINISTRY
OF INDUSTRY AND TRADE |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 21/2015/TT-BCT |
Hanoi, 23 June 2015 |
CIRCULAR
ON REGULATING THE PRICING METHOD FOR ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM'S ANCILLARY SERVICES AND THE PROCEDURE FOR SCRUTINIZING A CONTRACT FOR PROVISION OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM’S ANCILLARY SERVICES
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 95/2012/NĐ-CP dated 12 November 2012 on regulating the functions, missions, authority and organizational structure of the Ministry of Industry and Trade;
Pursuant to the Law on electricity dated 03 December 2004 and the Law on amendments to the Law on electricity dated 20 November 2012;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 137/2013/NĐ-CP dated 21 October 2013 on detailing the enforcement of certain articles of the Law on electricity and the Law on amendments to the Law on electricity;
At the request of the Head of the Electricity Regulatory Authority of Vietnam,
Minister of Industry and Trade issues the Circular on regulating the pricing method for electric power system’s ancillary services and the procedures for scrutinizing a contract for provision of electric power system’s ancillary services.
Chapter I
GENERAL
Article 1. Scope of regulation and regulated entities
1. This Circular regulates the procedure for an entity's calculation, assessment and endorsement of electric power system’s ancillary service price at discretion and the procedure for scrutinizing a contract for provision of electric power system’s ancillary services.
2. This Circular is applicable to Vietnam Electricity Corporation, electricity trading companies, the operator of electric power system and market, and providers of electric power system’s ancillary services.
3. This Circular amends Article 68 of the Circular No. 30/2014/TT-BCT dated 02 October 2014 by Ministry of Industry and Trade on regulating the operation of the competitive power generation market.
Article 2. Terminology
In this Circular, the following terms are construed as follows:
1. Scheduled available output of an electric generator is the anticipated maximum output gained during the electric generator's continuous and stable generation of electric power for at least 8 hours.
2. Ancillary services refer to services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve, mandatory maintenance of electrical system security during power generation, frequency control and spinning reserves as demanded in dispatching orders by the operator of electric power system and market, in order to uphold operational standards, maintain reliability and security of the electric power system.
3. Provider of ancillary services is a power generation enterprise that owns one or several power plants and is mobilized to provide ancillary services as per dispatching orders. For the services providing fast boot or cold boot reserve, mandatory maintenance of electric power system security during power generation, the providers of ancillary services from Electricity Regulatory Authority's list shall engage in contracts for provision of ancillary services with Vietnam Electricity Corporation. Fees for provision of ancillary services as parts of power generation costs are settled as per current regulations.
4. The operator of electric power system and market governs and controls the generation, transmission and distribution of electric power through national power grids while managing transactions in the electric power market.
5. A dispatching order is an order for real-time governing and control of the electric power system.
6. The limit of forced outage hours due to unexpected factors refers to the total annual sum of forced outage due to unexpected factors subject to particular characteristics of each generator and power plant. It includes the amount of outage hours originating from errors or repairs or maintenance of equipment outside the plans approved.
7. Year N refers to the year when ancillary service pricing takes effect, from the 1st of January to 31st of December.
8. Year N-1 immediately precedes year N.
9. Year N-2 precedes year N-1
Chapter II
METHOD FOR PRICING OF ANCILLARY SERVICES
Title 1. PRINCIPLES FOR PRICING OF ANCILLARY SERVICES
Article 3. Principles for pricing of ancillary services
1. The pricing of services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security during power generation adopts the principles of adequately compensating for reasonable and valid actual expenses and generating rational annual profit for thermal power plants providing ancillary services. Price is exclusive of value added tax and environmental protection fee levied on solid waste. The price of ancillary service for the said entity consists of:
a) Fixed price for ancillary service providers' recovering of total fixed cost of the provision of ancillary services in the year when such price takes effect;
b) Variable price for ancillary service providers’ recovering of fuel and material costs for production of electricity as per a dispatching order by the operator of electric power system and market;
c) Generator booting price for the recovery of the power generator's costs of fuel and electricity consumed when a generator in hot, warm or cold shutdown condition is switched on to produce electricity as per a dispatching order by the operator of electric power system and market.
2. For frequency control service, the principles for mobilization and pricing are:
a) The operator of electric power system and market mobilizes strategic multi-target hydroelectric plants of Vietnam Electricity Corporation to provide frequency control service. Reasonable and valid actual costs for providing frequency control service are posted into the electricity production and trading costs of strategic multi-target hydroelectric plants;
b) For the plants participating directly in the electric power market, the frequency control service provision cost is settled as per the regulation of the operation of competitive power market as issued by the Ministry of Industry and Trade, and relevant regulations.
3. For spinning reserve service, the providers of spinning reserve service are power plants participating directly in the power market. The method for pricing of spinning reserve service is governed by Title 3 of this Chapter.
Title 2. METHOD FOR PRICING OF ANCILLARY SERVICES FOR FAST BOOT RESERVE, COLD BOOT RESERVE AND MANDATORY MAINTENANCE OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM SECURITY
Article 4. Fixed pricing method
1. Fix priced (gcd) for a provider of ancillary services is calculated by the following formula:
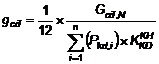
Including:
|
gcd |
Fixed price (VND/(kW.month)); |
|
Gcd,N: |
The ancillary service provider’s total fixed income (in VND) in the year N; |
|
|
Planned annual coefficient of availability of the provider of ancillary services is determined as per section 2 of this Article; |
|
Pkd,i |
Scheduled available output of generator i in the year N (kW); |
|
n: |
Quantity of power generators of the provider of ancillary services. |
The provider of ancillary services are responsible for defining the scheduled available output of a generator in the year N, which shall be negotiated and stipulated in the contract for provision of ancillary services with Vietnam Electricity Corporation. Such parameter is a factor for the calculation of the fixed price for the provider of ancillary services.
2. Planned annual coefficient of availability of the provider of ancillary services is calculated by the following formula:
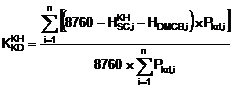
Including:
|
|
The number of hours for repairs of the generator i according to the repair plan in the year N (hour); |
|
HDMCB,i |
The limit of hours of forced outage of the generator i due to unexpected factors in the year N (hour), according to the parties' negotiations; |
|
n: |
The quantity of generators of the provider of ancillary services. |
Article 5. Method for calculation of total fixed income
Total fixed income in the year N (Gcd,N) of the provider of ancillary services is determined by the following formula:
Gcd,N = CKH + COM,N + CLVDH + LNN
Including:
|
CKH: |
Total fixed asset depreciation cost of the provider of ancillary services in the year N is calculated according to section 1 of this Article (VND); |
|
COM,N: |
Total fixed operational cost in the year N is ascertained according to Section 2 of this Article (VND); |
|
CLVDH: |
Total sum of interest cost and lending fees payable in the year N for the ancillary service provider's investments in assets (VND); |
|
LNN: |
Rated profit in the year N (VND). |
1. Total fixed asset depreciation cost (CKH) of the provider of ancillary services in the year N is determined subject to the depreciation method and service time of fixed assets as per the Circular No. 45/2013/TT-BTC dated 25 April 2013 by the Ministry of Finance on issue the regulations on the management, use and depreciation of fixed assets and written amendments.
2. Total fixed operational cost (COM,N) of the provider of ancillary services in the year N is calculated by the following formula:
COM,N = CVLcđ + CTL + CSCL + CMN + CK
In which:
|
CVLcd: |
Total fixed material cost in the year N (VND); |
|
CTL: |
Total salary cost in the year N (VND): |
|
CSCL: |
Total major repair cost in the year N (VND); |
|
CMN: |
Total outsourced service cost in the year N (VND); |
|
CK: |
Total sum of other costs in monetary unit in the year N (VND). |
a) Method for calculation of total material cost (CVLcd)
Total fixed material cost (CVLcd) of the provider of ancillary services in the year N is determined subject to the provider’s audited fixed material cost in the year N-2, exclusive of unusually variable costs, at the slippage rate of 2.5% per year.
b) Method for calculation of total salary cost (CTL)
Total salary cost in the year N (CTL) is composed of total salary cost and salary-related costs such as expenses for medical insurance, social insurance and unemployment insurance and labor union's expenditure, according to relevant laws.
c) Method for calculation of major repair cost (CSCL)
The parties negotiate total major repair cost (CSCL) subject to the values approved by competent authorities. If a year's repair schedule, due to objective reasons, is delayed to the following year, the parties adjust the following year's major repair cost to have the cycle-based major repair cost unchanged or slightly changed.
d) Method for calculation of total outsourced service cost (CMN)
Total outsourced service cost in the year N (CMN) includes all payables for outsourced entities' services on request, such as water, telephone, outsourced electricity, hiring of audit advisor and other service expenses for the ancillary service provider's managerial and operational activities in the year N.
Total outsourced service cost in the year N is determined subject to the provider’s audited outsourced service cost in the year N-2, exclusive of unusually variable costs, at the slippage rate of 2.5% per year.
dd) Method for calculating total sum of other costs in monetary unit (CK)
Total sum of other costs in the year N (CK) includes expenses for business trips, travel on leave, meetings, guests, trainings, scientific research, initiatives, meal break, self-defense militia, guards, recovery from aftermaths of flood or storm, fire fighting, labor protection, work clothing, labor safety, industrial and environmental sanitation, water at work, material incentive for night shift, hazard allowance, first aid for work accidents, ordinary medicine, workers' physical rehabilitation, unemployment aid, recruitment, land tax, and exchange differences and other costs in monetary unit in the year N according to current regulations.
Total sum of other costs in the year N (exclusive of land tax and exchange differences) is determined subject to the provider’s total sum of other audited costs in monetary unit in the year N-2 (in case the figures in the year N-1 have been audited, the data in the year N-1 is used), exclusive of unusually variable costs, at the slippage rate of 2.5% per year.
3. The interest cost and lending fees (CLVDH): As per the capital loan contracts or legal documents between the Investor and lending credit institutions and banks.
4. The profit in the year N (LNN) is determined by the following formula:
LNN = ROE x VCSH
In which:
|
ROE: |
The ancillary service provider’s return on equity in the year N is determined subject to the general return rate of Vietnam Electricity Corporation in the electrical power retail plan currently in force. For the ancillary service providers capitalized prior to the effect of this Circular, the parties negotiate the return rate subject to power plants' commitments towards shareholders in the former's capitalization plan previously approved by competent authorities; |
|
VCSH: |
The equity of the provider of ancillary services is determined subject to equity investments in power plants, to the 31st of December of the year N-2, according the audited financial statement (VND). |
Article 6. Variable pricing method
1. The following formula determines the variable price for the provider of ancillary services supplying supporting services at the request of the operator of electric power system and market:
![]()
In which:
|
|
The variable price of the generator i at its maximum output j (VND/kWh); |
|
bi,j |
Refined fuel consumption rate of the generator i at the power j is determined subject to the fuel consumption characteristics of the generator (kg/kWh or BTU/kWh); |
|
Gnl: |
The price of fuel for production of electricity (VND/kg or VND/BTU); |
|
CvIp,i: |
Auxiliary material cost rate for the generator i to produce 01 kWh of electricity (VND/kWh); |
|
i: |
Generator i of the provider of ancillary services. |
2. Ancillary service providers are responsible for establishing fuel consumption characteristics of the generators and auxiliary material cost rate for production of electricity, which shall be negotiated and stipulated in the contracts for provision of ancillary services with Vietnam Electricity Corporation. Such parameters are factors for the calculation of the generators’ variable prices. Characteristics and rates in the year N-1 can be utilized for the year N, if necessary.
Article 7. Method for start-up pricing
1. The booting price of the generator, defined for every start of the generator at each booting mode, is calculated by the following formula:
![]()
Including:
|
|
The booting price of the generator i at the booting mode j (VND); |
|
Mi,j: |
Fuel consumption rate for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j (kg or BTU); |
|
Gnlkd: |
The cost of fuel consumed to start the generator (VND/kg or VND/BTU); |
|
|
The rate of electric power internally consumed to start the generator i at the booting mode j (kWh); |
|
gkd: |
The price of electric power purchased by the provider of ancillary services for the starting the generator, which is determined subject to the electric power retail price (a week's average hourly charge) currently imposed on customers generating electricity at the voltage level for generators' internal consumption of power (VND/kWh); |
|
|
The rate of auxiliary fuel consumption for starting the generator i at the booting mode j in a coal-fired thermal power plant (kg); |
|
gnlp: |
The price of auxiliary fuel consumed to start generators in coal-fired thermal power plants (VND/kg); |
|
|
The cost of auxiliary materials used to start the generator i at the booting mode j in a coal-fired thermal power plant (VND); |
|
j: |
The booting mode of the generator (hot, warm or cold); |
|
i: |
The generator i of the provider of ancillary services. |
2. Providers of ancillary services are responsible for establishing the consumption rates for fuel and auxiliary materials and the rate of electric power internally consumed for hot boot, warm boot and cold boot of each generator, which shall be negotiated and stipulated in the contracts for provision of ancillary services with Vietnam Electricity Corporation. Such parameters are factors for the calculation of generators' booting price. The rates established in the year N-1 can be used for the year N, if necessary.
Title 3. METHOD FOR PRICING OF SPINNING RESERVE SERVICE
Article 8. Method for pricing of spinning reserve power
1. The spinning reserve power price (SRi) compensates for the power maintained at reserve level by thermal power plants directly participating in the market to be available for the electric power system, if necessary. This price is formulated as follows:
SRj = Max [SMPi, bid] - bid
In which:
|
SRi: |
The price for 01 kW of spinning reserve power produced by the generator G in the trading cycle i (VND/kW); |
|
SMPi: |
The price of electricity in the power market during the trading cycle i (VND/kWh); |
|
bid: |
The highest bid price for the generator providing spinning reserve service in the power market during the trading cycle i (VND/kWh). |
2. The spinning reserve power determines the payables in the trading cycle i, which the operator of electric power system and market examines, compiles and announces according to the Ministry of Industry and Trade's Regulation on the operation of the competitive power market. Only the power contributing to the spinning reserve service is remunerated.
Chapter III
THE PROCEDURE FOR CALCULATION, ASSESSMENT AND APPROVAL OF ANCILLARY SERVICE PRICE
Article 9. The procedure for calculation, assessment and approval of ancillary service price
1. Prior to the 1st of November of the year N-1, Vietnam Electricity Corporation is responsible for pricing the services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve, mandatory maintenance of electric power system security for the providers of ancillary services on power grids according to Article 4, Article 5, Article 6 and Article 7 of this Circular. Later, prices are reported to Electricity Regulatory Authority, which present the figures to the Minister of Industry and Trade for approval.
2. Before the 15th of December of the year N-1, the Ministry of Industry and Trade ratifies the prices of ancillary services in the year N for the providers of services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security.
Article 10. Documents for ratification of ancillary service pricing
The following documents shall be presented to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for assessment and transfer of such to the Ministry of Industry and Trade for ratification of prices of services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security:
1. The application for ratification of ancillary service prices.
2. 05 (five) copies of the written description for the calculation of ancillary service prices, including these essential particulars:
a) The report on power plants' past and planned enforcement of economic-technical norms to the 30th of September and 31st of December of the year N-1, respectively;
b) The report on the amount of electricity delivered and average fuel consumption rate in the year N-1;
- The report on business and production results, such as power plants' revenues and costs to the 30th of September and their anticipated revenues, costs and profits to the 31st of December in the year N-1/
b) The description and calculation of ancillary service prices in the year N consist of:
The detailed description and calculation sheet of the business plan, including depreciation cost, interest cost, salary cost, auxiliary material cost, major repair cost, outsourced service cost, other costs in monetary unit, drying cost, exchange differences, rated profit. Such parameters are factors for the determination of power plants’ fixed costs and price in the year N.
c) Documents enclosed:
- The general financial statement for the year N-2 and the cost price report, audited by an independent auditing entity (if available), in consonance with each factor of the production of electricity in the year N-2;
- The plan for major repairs of generators of the provider of ancillary services in the year N;
- The ancillary service provider's registration of electricity generators’ available output anticipated in the year N;
- The fuel consumption characteristics of the ancillary service provider's generators;
- The ancillary service provider’s auxiliary material rate for production of electricity;
- The rate of consumption of fuel and electronics for booting generators at hot and cold start modes;
- The rate of electric power for drying generators in standby shutdown condition;
- The anticipated price of fuel and materials in the year N for production of electricity and regular repairs.
Chapter IV
CONTRACT FOR PROVISION OF ANCILLARY SERVICES
Article 11. Sample contract for provision of ancillary services
1. The sample contract, as stipulated in the appendix of this Circular, is applicable to the provision of ancillary services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve, mandatory maintenance of electric power system security for generation of electricity, between the designated provider of ancillary services and Vietnam Electricity Corporation.
2. The parties, on annual basis, are responsible for unanimously executing amendments to the clauses on ancillary service pricing in their contracts, according to the decisions by Ministry of Industry and Trade. The amended contract shall be submitted to the Electricity Regulatory Authority.
Article 12. Procedures for inspection of a contract for provision of ancillary services
1. In 05 working days' time upon the parties' affixture of their initial signatures on the contract for provision of ancillary services, Vietnam Electricity Corporation is responsible for send the draft contract to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for the latter’s inspection.
2. In 15 working days’ time upon the receipt of the draft contract, the Electricity Regulatory Authority is responsible for inspecting the contract for provision of ancillary services and consulting.
3. Vietnam Electricity Corporation, no later than 30 working days upon the official signing of a contract for provision of ancillary services, is responsible for submitting 01 copy of the contract to the contract to the Electricity Regulatory Authority.
Chapter V
ENFORCEMENT
Article 13. Amendments to Article 68 of Circular No. 30/2014/TT-BCT
The following amendments redress Article 68 of Circular No. 30/2014/TT-BCT dated 02 October 2014 by Ministry of Industry and Trade regulates the operation of the competitive power generation market:
Article 68. Calculation of electric power output billed for payables
1. The principles for determining the electric power output billed for each trading cycle’s payables
a) In each cycle, the pricing of market output is scheduled for the generators producing electricity to the market, except for slow generators in reserve shutdown condition and those in forced outage condition;
b) For the generators not providing spinning reserve and frequency control services, their billed output equals their output of electricity at measuring points during trading cycles;
c) For the generators providing spinning reserve and frequency control services, the generators' electricity output at measuring points (at delivery locations) in trading cycles and output for spinning reserve and frequency control, calculated according to Section 2 and Section 3 of this Article, are billed for payables.
2. The spinning reserve output billed for payables in the trading cycle i is formulated as follows:
Qdpq = Min [{Min[(Qdd,i (QĐ) + Qdpqcb), Qcb] - Qmq}, Qdpqcb]
Including:
|
Qdpq: |
The generator’s spinning reserve output in the trading cycle i at measuring points (kW); |
|
Qdđ i (QĐ) |
The output demanded as per a dispatching order and interpreted to that at measuring points in the trading cycle i (kWh); |
|
Qdpqcb: |
The generators’ spinning reserve output announced for successive days and interpreted to that at measuring points in the trading cycle i (kW); |
|
Qcb: |
The generator’s output announced in its schedule offer and interpreted to that at measuring points of the trading cycle i (kW); |
|
Qmq: |
The generator’s electricity output measured in the trading cycle i (kWh). |
3. The following formula determines the frequency control output for calculation of payables in the trading cycle i:
Qđt = Min [{Min[(Qdd,i (QĐ) + Qđtcb), Qcb] - Qmq}, Qđtcb]
Including:
|
Qđt: |
The generator’s frequency control output billed in the trading cycle i, interpreted to that at measuring points (kW); |
|
Qdd,i (QĐ): |
The output demanded as per a dispatching order, interpreted to that at measuring points of the trading cycle i (kWh); |
|
Qđtcb: |
The generator’s frequency control output announced for successive days, interpreted to that at measuring points of the trading cycle i (kW); |
|
Qcb: |
The generator’s output announced in its schedule offer, interpreted to that at measuring points of the trading cycle i (kW); |
|
Qmq: |
The generator’s electricity output measured in the trading cycle i (kWh). |
4. By 9 o'clock on the day D+2, the operator of electric power system and market is responsible for announcing each generator's output billed for payables in trading cycles of the former day D.
Article 14. Enforcement
1. Electricity Regulatory Authority is responsible for:
a) Issuing the list of power plants providing services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security by the 15th of December of each year;
b) Inspecting and presenting the pricing of ancillary services provided by power plants to the Minister of Industry and Trade for approval;
c) Inspect contracts for provision of ancillary services;
d) Guide and inspect the enforcement of this Circular and settle relevant disputes.
2. Vietnam Electricity Corporation is responsible for:
a) Listing power plants providing services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve, mandatory maintenance of electric power system security, and providing the list to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for ratification and release on annual basis;
b) Negotiating and setting prices of ancillary services with the providers of such;
c) Negotiating and entering contracts or authorizing power trading companies to negotiate and engage in ancillary service contracts with the providers; and presenting contracts to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for contract inspection;
d) Presenting ancillary service prices in providers’ agreements to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for assessment, which submits such data to Ministry of Industry and Trade for approval.
3. The providers of services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security are responsible for:
a) Negotiating and entering contracts for provision of ancillary services;
b) Providing sufficient information, assuming liabilities and maintaining accuracy, logic and validity of data and documents submitted to relevant entities and authorities during negotiation and inspection of contracts for provision of ancillary services.
Article 15. Effect
1. This Circular comes into force as of 07 August 2015.
2. It amends Article 68 of Circular No. 30/2014/TT-BCT dated 02 October 2014 by Ministry of Industry and Trade on the operation of the competitive power generation market.
3. Vietnam Electricity Corporation and the providers of services for services for fast boot reserve, cold boot reserve and mandatory maintenance of electric power system security shall negotiate and setting ancillary service prices in 2015 according to the methods in this Circular. Upon the effect of this Circular, such prices shall be presented to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for assessment before transferred to Ministry of Industry and Trade for approval.
4. Relevant entities must submit their inquiries on difficulties to the Electricity Regulatory Authority that provides solutions under its jurisdiction or reports to Ministry of Industry and Trade for settlement of matters./.
|
|
pp.
MINISTER |
APPENDIX
SAMPLE CONTRACT FOR PROVISION OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM’S
ANCILLARY SERVICES
(Enclosed to the Circular No. 21/2015/TT-BCT date 23 June 2015 by Minister
of Industry and Trade)
SOCIALIST
REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM
Independence – Freedom – Happiness
ANCILLARY SERVICE CONTRACT
POWER PLANT OF …
Between
COMPANY [Name of the company]
(VENDOR)
- and -
VIETNAM ELECTRICITY CORPORATION
(BUYER)
CONTRACT NO. …/20…/DVPT/[Company’s name]-[EVN]
Hanoi, … [month] / 20 …
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Article 1. Definitions
Article 2. Effect and term of contract
Article 3. Sale and purchase of ancillary services
Article 4. Commitments
Article 5. Responsibilities for establishing connections and electricity measurement system
Article 6. Power plant dispatch and operation
Article 7. Invoicing and payment for electricity
Article 8. Events affecting the Contract and legal remedies
Article 9. Termination and postponement of contract
Article 10. Compensation for damages
Article 11. Indemnity
Article 12. Settlement of disputes
Article 13. Restructuring of electricity sector and transfer of rights and duties
Article 14. Document retention and provision of information
Article 15. Other expenses
Article 16. Authorized representative and exchange of information
Article 17. Confidentiality
Article 18. Other stipulations
Appendix 1. MAIN PARAMETERS OF THE POWER PLANT
Appendix 2. MEASUREMENT SYSTEM AND COLLECTION OF DATA
Article 3. AGREEMENT ON OPERATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
Appendix 4. INFORMATION REQUIRED BY SCADA/EMS SYTEM
Appendix 5. PRICE AND PAYMENT FOR ANCILLARY SERVICES
SOCIALIST
REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM
Independence – Freedom – Happiness
ANCILLARY SERVICE CONTRACT
Pursuant to the Law on electricity dated 03 December 2004 and the Law on amendments to Electricity Law dated 20 November 2012;
Pursuant to the Commercial Law dated 14 June 2005;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 137/2013/NĐ-CP dated 21 October 2013 on detailing the enforcement of certain articles of the Law on electricity and the Law of amendments to Electricity Law.
Pursuant to the Circular No. 21/2015/TT-BCT dated 23 June 2015 by Minister of Industry and Trade on regulating the pricing method for electric power system's ancillary services and the procedure for inspection of contracts for electric power system's ancillary services;
As per the parties' demands for sale and purchase of ancillary services,
As of … , at …
The parties include:
Vendor: ___________________________________________________________________
Address: ___________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _____________________________ Fax:________________________________
Tax code:__________________________________________________________________
Account: _____________________________ Bank: ________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Represented by: ____________________________________________________________
Position: __________________________________ as authorized by __________
____________________________________________ according to the letter of authorization
no_______________________________, dated ________
Buyer: Vietnam Electricity Corporation
Address: ___________________________________________________________________
Telephone: _____________________________ Fax: _______________________________
Tax code: __________________________________________________________________
Account: _____________________________ Bank:________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Represented by: ____________________________________________________________
Position: __________________________________ as authorized by __________ _______
__________________________________________ according to the letter of authorization
no_______________________________, dated ________
The parties agree to enter the Ancillary service contract on the following terms:
Article 1. Definitions
In this contract, the following terms are construed as follows:
1. Vendor refers to … [Company] that owns the Power plant of …
2. Buyer refers to Vietnam Electricity Corporation.
3. The available output announced by the Vendor is the readily attainable output of a generator or power plant at a definite point of time.
4. Ancillary service(s) provide (fast boot reserve), (cold boot reserve), (mandatory maintenance of electric power system security), as supplied by the Vendor at the Buyer’s request, for maintaining operational standards, reliability and electric power system security.
5. Connection point is a site for the Vendor's connection of equipment, power grids and power plant's facilities to the National power system.
6. Point of electricity delivery is a site for the measurement of the amount of Vendor's electricity sold to the Buyer.
7. National power system consists of electric power generation equipment, power grids and ancillary equipment jointly connected and unanimously controlled on nation-wide scale.
8. Primary measurement system is composed of measurement equipment (meters, measurement current transformers, measurement transformers) and secondary circuits connected to the said equipment. The system is installed at the parties' agreed locations to set firm basis for the calculation of the amount of electricity delivered.
9. Backup measurement system comprises every measurement equipment (meters, measurement current transformers, measurement transformers) and secondary circuits connected to the said equipment. The system is installed at the parties’ agreed locations for testing and backing up the primary measurement system.
10. Contract refers to this ancillary service contract and its appendices and amendments.
11. Dispatching order is an order for real-time steering and control of electric power system’s operations.
12. Day refers to a day in Gregorian calendar.
13. Power plant refers to the Power plant [name of Power plant] with the maximum established output of … MW, including … generators at [power plant's location], each of which has an output of … MW.
14. The electricity sector’s technical regulations and standards include obligatory technical regulations issued by Vietnam's competent authorities and rules, standards and practices observed by international organizations and enforced by other nations in correspondence in line with the laws of Vietnam.
15. Connection equipment refers to power transmission lines, measurement equipment system, control devices, protective relay, circuit breakers, information and communication system and buildings synchronized for power plants' linkage with points of connection.
16. Competitive power generation market is the first-level electricity market as defined in Article 18 of the Electricity Law and operates according to the Ministry of Industry and Trade’s regulation on the operation of the competitive power generation market.
Article 2. Effect and term of contract
1. Effect of Contract
This contract comes into force upon the parties’ authorized representatives’ official signing of the contract or according to the parties' stipulation in this contract.
2. Term of Contract
The contract, unless extended or terminated according to Article 9 of this contract, takes effect from its effective date to the closing date of the competitive power market according to competent governmental authorities.
Article 3. Sale and purchase of ancillary services
1. Vendor undertakes to provide ancillary service(s) for (fast boot reserve), (cold boot reserve), (mandatory maintenance of electric power system security) according to the dispatching orders and the Ministry of Industry and Trade’s regulation on power transmission system.
2. Vendor's duty is to maintain the power plant's readiness to provide ancillary services at the Buyer's request according to the standards in Ministry of Industry and Trade's regulation on power transmission system and technical specifications in Appendix 1 and Appendix 3 of the contract.
3. Ancillary service price is defined on annual basis in Appendix 5 of the contract. By the 31st of December each year, Buyer and Vendor share the duty to execute written amendments to the contract’s clause on ancillary service price upon Ministry of Industry and Trade’s decision on approval of electric power system’s ancillary service price.
4. Buyer undertakes to pay for the Vendor's provision of ancillary services on monthly basis according to Article 7 and Appendix 5 of the contract/
Article 4. Commitments
The parties undertake that:
1. Each party's signing and execution of the contract do not violate its corporate regulations, relevant laws or other contracts that it engages in.
2. The parties’ signing and execution of the contract abide by their electrical operating licenses as issued by competent authorities and relevant laws.
3. The parties are not defendants in a lawsuit, whose result may remarkably alter contract parties’ financial capacities or ability to execute their contracted duties or the validity and effect of contract, in a court, commercial arbitration or before a competent governmental authority.
4. The parties undertake to execute precisely the duties and contents in this contract.
Article 5. Responsibilities for establishing connections and electricity measurement system
1. Responsibilities for establishing connections
Vendor is responsible for:
a) Investing, managing and operating the equipment for connection, transmission and delivery of electricity to Buyer at points of delivery according to Ministry of Industry and Trade’s regulation on power transmission system and relevant technical regulations and standards of the electricity sector;
b) Investing, installing, managing, operating and maintaining the power plant’s system equipment for collection, transmission of data and automatic control for the power plant’s connection to SCADA/EMS system of the operator of national electric power system and electricity market. Such connection facilitates the operation of the power plant.
2. Measurement system
a) Vendor is responsible for investing, installing, managing, operating, maintaining and inspecting the equipment of the primary and backup measurement systems on annual basis. Competent or authorized organizations shall inspect the measurement equipment or verify the precision of such equipment. The measurement equipment must be secured with lead seal after the inspection;
b) Each party can request additional or random inspection of measurement equipment and system, if necessary. Vendor is responsible for organizing inspections at Buyer’s request. If random inspection detects measurement equipment’s deviations higher than the permissible limit, Vendor must pay for the random inspection. If deviations fall within the permissible limit, the requesting party incurs inspection fees.
c) Vendor's duty is to inform Buyer of the result of the inspection of measurement equipment. Vendor's duty is to inform Buyer in advance of the inspection of measurement equipment. Buyer is responsible for assigning its witness of the process of seal removal, inspection and lead sealing of the meters;
d) If measurement equipment's deviations exceed the permissible limit according to the Regulation on electricity measurement, Vendor is liable for adjusting or replacing such equipment. If one of the parties considers a meter damaged or not functional, it must promptly inform the other party. Vendor bears the duty of inspection and repair;
dd) The amount of electricity traded by Buyer and Vendor is defined according to the method of delivery in Appendix 2 of the contract.
If the primary measurement system does not function properly or its deviations, as found by an inspection, exceed the regulated precision level, the amount of electricity traded during such events is defined by the backup measurement system. If the backup measurement system fails or generates deviations, during an inspection, higher than the permissible limit, the amount of electricity traded is calculated as follows:
(i) If the primary measurement system functions but generates deviations higher than the regulated precision level, the amount of electricity traded is determined by the primary measurement system and interpreted to an equivalent value of electricity at the deviation rate of 0%. According to the adjusted result of measurement agreed by the parties, Vendor bears the duty to calculate the payables that one of the parties owes to the other. Such payables arise during the measurement system’s inaccurate time.
(ii) If the primary measurement system does not function, the parties consider the problematic conditions and actual deviations of measurement systems according to the inspecting entity’s records and figures approved by the parties to unanimously consent to a method for calculating the amount of electricity to be adjusted during the time of inaccurate measurement. If the parties fail to agree to a method and the amount of electricity trade requires adjustment, the parties are responsible for settling disputes according to Article 12 of the contract.
e) If the measurement equipment burns or breaks down, Vendor is responsible for having it replaced or repaired in the shortest time to make the equipment abide by technical requirements and resume to work. The replacements or repaired equipment, before used, must be inspected according to regulations.
Article 6. Power plant dispatch and operation
1. The duty to register a method of mobilization
Vendor bears the duty to register the method for mobilizing each of the power plant's generators, according to the Electricity Regulatory Authority's procedure for planning the operation of the national power grids, with the operator of the national power system and electricity market. Buyer also receives a written copy of the method. The method shall include:
a) Available output announced, electricity output anticipated and monthly repair plan for the subsequent year;
b) Available output announced, electricity output anticipated and repair plan for the following month;
c) Available output announced, electricity output anticipated and plan of repair and maintenance for the ensuing week;
d) Available output announced on hourly basis and electricity output anticipated for the successive days, by 10 o’clock every day.
2. Operation of Power plant
a) Vendor is responsible for conforming to the regulations on power plant dispatch and operation according to the Ministry of Industry and Trade’s regulations on power transmission system, electricity sector’s technical regulations and standards and relevant documents. Vendor bears the duty to operate the power plant’s generators according to technical specifications in Appendix 1 and Appendix 3 of the contract;
b) Vendor bears the duty to install, operate and maintain the equipment to synchronize the power plant with the national power grids. Vendor is responsible for conforming to the Ministry of Industry and Trade’s regulation on power transmission system, electricity sector’s technical regulations and standards and other dispatch regulations upon the synchronization of the power plant with the national power grids;
c) If the national power grid operation methods bring threats to the power plant's primary equipment, cause injury, fatality or equipment damages, Vendor is allowed to disconnect the generators.
Article 7. Invoicing and payment for electricity
1. Invoicing and payment for electricity
a) By the … [date] of each month, Vendor informs Buyer in writing of the latter’s payables for the former’s provision of ancillary services with the immediate preceding month’s payment documents.
The documents for payment of the immediate preceding month’s ancillary services (referred to as payment documents) include: the confirmation of meter-based amount of electricity, the sheet of available output announced and implemented on daily basis, the request of the confirmation of availability coefficient used and boot times billable, the summary of payables with the detailed calculation sheets of payables as defined in Article 5 of the contract and relevant documents.
b) In 03 working days’ time upon receiving the payment documents, Buyer verifies the accuracy of such documents. Buyer, if detecting errors, informs Vendor in writing for the latter's correction of payment documents. If Buyer does not inform Vendor by the 15th of each month, payment documents shall be deemed unanimously agreed;
c) By the … [day] of each month, Vendor must issue payment invoices to Buyer. Ministry of Finance’s regulations govern the making of such payment invoices;
d) Buyer bears the duty to transfer all amounts invoiced for the immediate preceding month’s ancillary services through banks, no later than the … [day] (payment deadline). Buyer incurs bank transfer fees;
dd) If data for invoicing is insufficient upon the release of a payment invoice, Vendor is allowed to temporarily calculate the payables for its provision of ancillary services by rationally estimating missing figures. The adjusted payables constitute deductibles for the month when official data is available.
2. Payment disputes
a) If Buyer does not consent to parts or all payables invoiced, it must inform in writing of the amounts invoiced and reasons of its disapproval prior to the payment deadline. Buyer bears the duty to settle all undisputed payables by or on the due date of payment;
b) In 15 days’ time upon receiving the notice of payment dispute, Vendor must respond to Buyer officially in writing. If the parties fail to resolve payment disputes, one of the parties can settle disputes according to Article 12 of the contract;
c) If Buyer does not complain in writing about the amounts invoiced before the payment deadline, it is deemed to waive its rights to complain about the payables invoiced. If Vendor does not respond to Buyer official in writing about payment disputes in 15 days’ time upon the former’s receipt of the latter’s notice of payment disputes, the former is deemed to abandon its rights to complain about the payables invoiced.
3. Calculation of interest
Interest is imposed on:
a) The monthly payables for electricity deferred after the deadline according to point d, section 1 of this Article;
b) The payables arising according to a decision on dispute settlement according to Article 12 of the contract;
c) The adjusted payables for monthly electricity according to point dd, section 1 of this Article.
Interest accumulates on monthly basis from the day immediately following the payment deadline to the actual date of payment fulfillment. The rate of such interest equals a 12-month deposit’s accrual interest rate for Vietnamese currency plus an annual interest margin rate of 3%, on the due date of the invoice, as defined by four commercial banks including Vietcombank, Vietinbank, BIDV and Agribank or legitimate successors of such banks.
4. Deductibles
The parties may deduct debts, disputed amounts settled, adjusted amounts and monthly interest from the monthly payables for electricity in the nearest month’s invoice.
Article 8. Events affecting the contract and legal remedies
1. The following events affect Buyer’s execution of the contract.
a) The events related to Vendor’s dissolution or bankruptcy:
(i) Vendor is dissolved (except for pre-merger or pre-consolidation dissolution);
(ii) Vendor fails to settle due debts;
(iii) Vendor transfers or merges its entire entity with the creditors or with another entity for creditors’ benefits;
(iv) A court issues its rulings on the bankruptcy procedure against Vendor.
b) Vendor commits serious violations of its duties as stated in the contract and fails to correct such violations in 90 days upon Buyer's notice of such violations.
c) Vendor is suspended by competent authorities’ decisions.
2. The following events affect Vendor’s execution of the contract
a) The events related to Buyer’s dissolution or bankruptcy:
(i) Buyer is dissolved (except for pre-merger or pre-consolidation dissolution);
(ii) Buyer fails to settle due debts;
(iii) A court issues its decision on the bankruptcy procedure against Buyer.
b) Buyer commits serious violations of its duties as defined in the contract and fails to correct such violations in 90 days upon Vendor’s notice of such violations.
c) Buyer is suspended by competent authorities' decisions.
3. Legal remedies
a) If fundamental violations occur and continue, the affected party has the right to enforce the legal remedies, as stated in Article 9 of this contract, against the violating party;
b) Legal remedies in this contract do not nullify each other or obstruct other remedies.
Article 9. Termination and postponement of contract
1. Termination of contract by agreement
The parties can enter a written agreement on early termination of contract.
2. Unilateral termination of contract
a) If an affecting event, as defined in point a, point b, section 1 or point a, point c, section 2, Article 8 of the contract, occurs, continues and affects one of the contract parties, the affected party is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract 90 days after its delivery of a written notice to the other party;
b) If force majeure affects one party and continues in at least 180 days, the other party is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract 30 days after its delivery of written notice;
c) If an event affecting the party's execution of the contract, as defined in point b, section 1 or point b, section 2, Article 8 of the contract, occurs, the affected party is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract 30 days after its delivery of a written notice.
3. Postponement of contract
Buyer is allowed to postpone the contract, after informing Vendor, if Electricity Regulatory Authority suspends Vendor from participating in the competitive power market or by competent authorities from operating in the power generation sector. Contract postponement time must not exceed the duration of the suspension of participation in the competitive power generation market or operation in the electricity sector.
Article 10. Compensation for damages
1. The violating party is responsible for compensating the affected party for damages caused by the former's violations. Damages include losses, damages or costs that the affected party has incurred while executing its contracted rights and duties. The method for calculation of damages is governed by the Civil Law.
2. The affected party, if claiming for damages, shall promptly inform the violating party in writing of the nature of the events for damage claims. The affected party's deferral of its notices shall not impinge on the violating party’s duties of compensation, unless the violating party suffers from actual damages due to the affected party’s delay.
Article 11. Indemnity
1. The violating party is exempt from liabilities in the following events:
a) An event of indemnity, as agreed by the parties, occurs;
b) One party's faults cause all of the other's violations;
c) One party commits violations when fulfilling a competent governmental authority's decisions, which the parties could not be aware of upon their signing of the contract;
d) Force majeure occurs
Force majeure is unavoidable beyond one party’s control and obstructs or delays that party’s execution of its contracted duties, partly or fully, despite its implementation of rational measures.
Force majeure obstructing or delaying the parties' execution of their contract duties must overwhelm the affected party's reasonable control and derive from none of its faults or negligence. Moreover, the affected party fails to avoid such events despite its implementation of reasonable solutions, practices, procedures and standards. Such events include but are not limited to:
i) A decision by a court or competent authority adversely affecting one party’s execution of its contracted duties;
ii) Natural disasters including fire, explosion, drought, flood, volcanic eruption, earthquake, landslide, tide, storm, tornado, hurricane or similar events;
iii) Riot, demonstration, revolt, insurgency, war activities whether war is declared or not, opposition, terrorism, sabotage, embargo, blockade, quarantine or similar events;
iv) Vendor’s power plants or assets are nationalized, deprived or seized according to competent governmental authorities' decisions;
v) Vendor is not licensed by competent authorities or fails to obtain written approvals necessary despite its fulfillment of all duties according to the laws related to the said licenses and written approvals.
2. Announcement and endorsement of indemnity
a) The violating party must inform the other in writing of exemptions and possible consequences;
b) When indemnity ends, the violating party must immediately inform the other. If the violating party fails or delays its announcements to the other party, it must compensate for damages caused.
c) The violating party bears the duty to evidence its indemnity with the affected party.
3. Indemnity and refusal to execute the contract in force majeure
a) The party committing violations due to force majeure is responsible for regularly reporting to the other party about the former’s implementation of solutions against force majeure or information reasonably requested by the other party. Such reports shall evidence the violating party's adducing of force majeure. The other party must be informed of force majeure' end time in 48 hours from the finis of such events, unless loss of communication occurs;
b) The party affected by force majeure is only excused for its non-execution or delay of contracted duties due to such events after it release notices and executes duties of recovery according to point a of this Article;
c) If force majeure obstructs one party's execution of its contracted duties in at least 180 days, one of the parties is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract.
Article 12. Settlement of disputes
1. If disputes between the contract parties arise, the party provoking disputes must inform the other party in writing of the contents of such disputes. The parties are responsible for discussing solutions against disputes in 60 days upon the date of the notice from the party raising such disputes. The parties are responsible for discussing disputes over payments in 15 days. The parties are allowed to negotiate and execute an extension of dispute settlement time in writing.
2. If the parties fail to settle disputes through discussions within the time limit as per section 1 of this Article, the parties shall agree to forward their disputes to the Electricity Regulatory Authority or other authorities as unanimously selected by the parties to settle disputes according to relevant laws.
Article 13. Restructuring of electricity sector and transfer of rights and duties
1. Restructuring of electricity sector and transfer of Buyer’s rights and duties
The parties agree that Buyer may be reorganized, restructured, dissolved or gradually deprived of its sole capacity of purchasing electricity for the conversion of the electricity sector's model to that of the competitive power market according to the pathway approved by Prime Minister or subsequent written amendments. When a competent governmental authority issues a decision on reorganizing, restructuring or dissolution, Buyer is allowed to assign all or parts of its contracted rights and duties without Vendor's consent to one or many successors, which are defined by the competent governmental authority. Such successors are responsible for executing Buyer’s legal rights and duties according to the laws.
Vendor must approve in writing all of Buyer’s assignment or relegation of its rights and duties from this contract.
2. Transfer of Vendor’s rights and duties
Vendor is only allowed to assign its rights and duties from this contract to successor(s) after obtaining Buyer’s written consent. Buyer cannot reject Vendor’s assignment or relegation without a reason. However, Vendor can relegate or assign parts or all of its contracted rights and duties on financing or financial arrangements for the power plant without Buyer’s agreement. The effect of this contract survives to continue the benefits and duties of Vendor's successors, assignees or relegated entities.
3. Transition to the competitive wholesale market
If the wholesale market or other models as per competent governmental authorities' decisions replace the competitive power market during the term of this contract, the parties are responsible for negotiating changes or replacements of this contract in consonance with the new electricity market structure on the condition that the parties' economic values from the contract remain unaffected.
Article 14. Retention of documents and provision of information
1. Retention of documents
The parties are responsible for retaining documents, data, materials or information evidencing the accuracy of invoices, prices or calculations as per the contract or proving the parties' conformity to the contract.
2. Provision of information
Each party is responsible for providing the other party with figures, materials or papers necessary at reasonable level to evince the accuracy of payment invoices, pricing formulas or calculations as per the contract or verify the parties' abidance by the contract.
Article 15. Other expenses
Each party is responsible for paying taxes and fees or settling debts arising during its execution of the contract. The parties agree that this contract is not inclusive of expenses for power transmission, power distribution, connection or similar expenses. Each party is responsible for covering such expenses according to regulations.
Article 16. Authorized representative and exchange of information
1. Authorized representative
The authorized representatives of the contract parties are:
Vendor: Buyer:
________________________ ________________________
________________________ ________________________
2. Exchange of information
a) Notices, invoices or essential information exchanged during the enforcement of this contract must be executed in writing. Their issue dates and relation to the contract must be clearly specified. The original of a fax must be sent by pre-paid post. Notices, invoices or information must be delivered to the following addresses:
Vendor: _________________________________
________________________________
Buyer: _________________________________
________________________________
b) Notices, invoices or information sent as per point a of this Section are deemed received:
(i) when delivered by hand; or:
(ii) when proof of delivery by guarantee post is signed; or:
(iii) when a fax is actually received and the sender attains a confirmation of no fax delivery errors; or:
(iv) when a regular postage's arrival is confirmed.
Article 17. Confidentiality
Each party bears the duty to maintain confidentiality of information and documents given by the other party as per the contract. Each party shall not disclose, publicize or exploit such information and documents for any purposes save the execution of its contracted duties. Exceptions are:
Documents and information are publicized or exploited according to the laws.
2. Documents and information are demanded by competent authorities.
3. Documents and information are announced or publicized by entities outside the contract.
Article 18. Other stipulations
1. Amendments to the contract
Every amendment to the contract must be executed in writing.
2. Complete contract
This contract is the final complete agreement between the parties and replaces all previous discussions, information and correspondences arising prior to the signing of this contract.
3. Third party
This contract only benefits its parties and does not constitute any benefits or duties for a third party.
4. Constitution of no joint venture
This contract does not constitute a joint venture or association between the parties or impose any legal duty or liability related to a joint venture or association on any of the parties. None of the parties is allowed to engage in or represent the other party to engage in an agent contract or act as a representative to perform duties against the other party.
5. Waiver of rights
One party's relinquishment of its contracted duties must be executed in writing and endorsed by its authorized representative’s signature. One party's non-execution or deferral of its rights from this contract is not construed as its abnegation of such rights.
6. Execution of remaining duties
Termination, closure or expiration of contract does not end the parties’ execution of their remaining duties as per the contract.
7. Governing law
The contract is interpreted and executed as per the laws of Vietnam.
8. Separability of contents
If a part of the contract does not correspond with the laws or becomes void as per a competent government authority’s decision, other parts of the contract sustain effect on the condition that remaining parts constitute sufficient contents without the ineffectual part.
9. Titles
Titles in this contract are for the purpose of convenience without influence on the interpretation of the contract and do not constitute any duties on any of the contract parties.
This contract is executed into 09 equally valid originals. Each party retains 04 originals. Vendor is responsible for sending one original to the Electricity Regulatory Authority.
|
BUYER'S
REPRESENTATIVE |
VENDOR'S
REPRESENTATIVE |
APPENDIX 1
PRIMARY PARAMETERS OF THE POWER PLANT
(Enclosed to the Contract No. ... dated ...)
This includes description, charts and technical specifications of the power plant
1. Turbine
a) Quantity
b) Type
c) Manufacturer
2. Boiler
a) Quantity
b) Boiler maximum continuous rating (BMCR)
c) Steam pressure
d) Temperature of saturated steam in steam drum
dd) Temperature of superheated steam
e) Temperature of water filtered and supplied
g) Boiler's output
h) Fuel consumption
i) Temperature of heated air
k) Temperature of exhaust gases
3. Electric generator
a) Quantity
b) Type
c) Generator’s output (MVA)
d) Output voltage (kV)
dd) Cosj
e) Rotations (per minute)
g) Frequency
h) Supplier
4. Transformer
a) Quantity
b) Output (MVA)
c) Transformer ratio
d) Wiring diagram
dd) Short-circuit voltage Uk
e) Type (Technical description of the transformer)
5. Electricity distributor and breaker
a) Breaker for … kV
- Quantity
- Type
b) Disconnector switch for … kV
- Quantity
- Type
c) Current transformer for … kV
- Quantity
- Type
d) Voltage transformer for … kV
- Quantity
- Type
dd) Lightning arrester for … kV
- Quantity
- Type
e) Capacitor and high-frequency choke
- Quantity
- Type
g) Protective relay and automatic control system, ancillary equipment system
6. Connection to the national power grids
a) Connection line
b) Type of connection line
c) Rated voltage
d) Conductor
dd) Anti-lightning cord
e) Circuit length
APPENDIX 2
MEASUREMENT AND DATA COLLECTION SYSTEM
(Enclosed to the Contract No. … dated …)
I. Measurement points
The parties agree to employ the power plant’s current measurement points as follows:
|
Generator |
Primary measurement system |
Backup measurement system |
|
[...] |
[...] |
[...] |
|
[...] |
[...] |
|
|
[...] |
[...] |
II. Method for the calculation of the amount of electricity delivered
On the 1st of each month, the parties' legal representatives shall record and confirm the meters' indicators at 0 o'clock on the first of the month and the immediate preceding month’s amount of electricity delivered in writing.
a) The following formula defines the amount of electricity delivered by Vendor to Buyer in a billed month:
![]()
Including:
|
AG,i: |
The relevant amount of electricity outward at the measurement point i of the primary measurement system in the month; |
|
AG: |
The amount of electricity that Buyer pays to Vendor in the billed month (kWh). |
b) The following formula defines the amount of electricity that Vendor receives from the national power grids in a billed month:
![]()
Including:
|
AN,i: |
The relevant amount of electricity inward at the measurement point i of the primary measurement system in the month; |
|
AN: |
The amount of electricity that Vendor pays for ... [power corporation] according to the electricity selling price list for industrial customers as per competent governmental authorities’ regulations (kWh). |
c) Vendor and Buyer augment the amount of reactive electricity for generators running in rotary compensation mode.
APPENDIX 3
AGREEMENT ON OPERATIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Enclosed to the Contract No. ... dated ...)
The parties agree to the following main operational characteristics of the power plant:
1. Generator's generative output
a) Minimum generative output: … MW.
b) Maximum generative output: … MW.
2. Time for start and synchronization
The following table defines the time for start and synchronization of generators with the national power grids from generators’ shutdown conditions:
|
Condition |
Shutdown time |
Time from start to synchronization |
|
Cold boot |
From … hours |
... hours |
|
Warm boot |
From … hours to … hours |
... hours |
|
Hot boot |
Less than … hours |
... hours |
3. Load variation speed
a) Average load reducing speed: … MW per minute
b) Average load increasing speed: ... MW per minute
4. Power plant's output power factor, voltage regulation and frequency limit in normal operational conditions.
a) The power plant operates according to the dispatching regulations applicable to the power plant's technical specifications.
b) Voltage regulation: The power plant's operations must maintain a voltage variation rate of ± 5% of the rated voltage at the connection points with the National power grids.
Frequency limit: The power plant operates with the frequency range of 49.8 to 50.2 Hz.
APPENDIX 4
DATA REQUIRED FOR SCADA/EMS SYSTEM
(Enclosed to the Contract No. … dated …)
APPENDIX 5
ANCILLARY SERVICE PRICE AND PAYMENT
(Enclosed to the Contract No. … dated …)
I. Ancillary service price
1. Fixed price gcđ:
Table 1. Output annually announced and fixed price
|
Year |
Output annually announced (kW) |
Fixed
price gcđ |
|||
|
Generator 1 |
.... |
Generator n |
Total |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Variable price gbđ:
The power plant’s variable price (gbđ,i,j) is defined according to each generator's output level through the following formula:
![]()
Including:
|
|
The variable price of the generator i at the output level j (VND/kWh); |
|
bi,j: |
Refined fuel consumption rate of the generator i at the power j is determined subject to the fuel consumption characteristics of the generator (kg/kWh or BTU/kWh) |
|
Gnl: |
The average fuel price in the month (exclusive of value added tax) (VND/kg or VND/BTU); |
|
Cvip,i,j: |
Auxiliary material cost rate for the generator i’s production of 1 kW of electricity per hour at the output level j (VND/kWh); |
|
i: |
The generator i of the power plant. |
Table 2. Refined fuel consumption and auxiliary material cost rate
|
Generator |
Generative output level at the delivery point (kW) |
Refined fuel consumption bi,j (g/kWh) |
Auxiliary material cost cvlp,i (VND/kWh) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Booting price Ckđ
a) The booting price (Ckđ,i,j), calculated when a generator of the power plant is started, is defined by the following formula:
![]()
Including:
|
|
Fuel price for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j (VND); |
|
Mi,j: |
Fuel consumption rate for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j (kg or BTU); |
|
Gnl: |
Average price of fuel consumed in the month m (exclusive of value added tax) (VND/kg or VND/BTU); |
|
|
Auxiliary fuel consumption rate for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j in a coal-fired thermal power station (kg); |
|
gnlp: |
The price of auxiliary fuel consumed to start the coal-fired thermal power station’s generators (VND/kg); |
|
|
The cost of auxiliary materials for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j in a coal-fired thermal power station; |
|
j: |
The booting mode (hot, warm or cold) of the generator; |
|
i: |
The generator i of the provider of ancillary services. |
Table 3. Fuel consumption rate for the start of a generator (kg/time)
|
Generator |
Booting mode |
||
|
Hot boot |
Warm boot |
Cold boot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b) This contract validates generator starts in the following events:
- Generators are started after repaired according to registered plans;
- Generators are started at Buyer’s request;
- Generators are started after an objective issue.
If a generator is started at Buyer’s request but is not connected to the grids then is shut down on request, each start shall be billed through Vendor's sufficient documents specifying dispatching orders that Vendor has received during the start of the generator (start order receipt time, shutdown order receipt time ...) and relevant documents evidencing the activation of the start process (generators marked).
All restarts due to subjective or unplanned issues shall not be billed.
II. Payment for ancillary services:
Buyer makes payments, on monthly basis, for Vendor's provision of ancillary services. The following formulate specifies such payments:
Tm = (Tcđ,m + Tbđ,m + Tkđ,m + Tk,m) x (1+VAT)
Including:
|
Tm: |
Total payment (VND) for ancillary services, which Buyer gives to Vendor in the month m; |
|
Tcđ,m: |
Total fixed price in the month m (VND); |
|
Tbđ,m: |
Total variable cost in the month m (VND); |
|
Tkđ,m: |
Total cost for generator start in the month m (VND); |
|
Tk,m: |
The sum of other payables (VND); |
|
VAT: |
Valued added tax |
1. Total fixed cost
a) The following formulate regulates the total monthly fixed cost (Tcđ,m) that Buyer pays to Vendor:
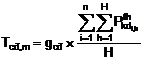
Including:
|
TCđ,m: |
Total fixed cost in the month m (VND); |
|
gcđ: |
The fixed price as defined in section 1, title 1 of this Appendix (VND/(kw.month)); |
|
|
Available output realized by the generator i at the hour h (MW); |
|
H: |
Number of hours in the month m (hours); |
|
n: |
Number of generators in the power plant |
b) The available output realized by the generator I at the hour h in the month m is calculated as follows:
- The available output announced (or the valid adjusted available output announced, if available) when the actual average generative output of the generator i at the hour h equals or exceeds 95% of the output actually demanded at Buyer's request.
- The actual generative output of the generator i at the hour h (or the valid adjusted available output, if available) when the actual generative output of the generator i is lower than 95% of the output actually demanded at Buyer’s request.
2. Total variable cost
The following formula specifies total monthly variable cost (Tbđ,m) that Buyer pays to Vendor:
![]()
Including:
|
Tbđ,m: |
Total variable cost in the month m (VND); |
|
|
The variable price of the generator i at the output level j in the hour h, as defined in section 2, title 1 of this Appendix (VND/kWh); |
|
|
The effective amount of electricity of the generator i at the hour h at the delivery point (VND/kWh); |
|
H: |
Number of hours in the month m; |
|
n: |
Total quantity of the power plant’s generators |
3. Total generator start cost
The following formula regulates total monthly generator start cost (Tkđ,m) that Buyer pays to Vendor:
![]()
Including:
|
Tkđ,m: |
Total generator start cost in the month m (VND). |
|
|
The price for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j is defined in section 3, title 1 of this Appendix (VND); |
|
|
Rate of electricity internally consumed for the start of the generator i at the booting mode j (kWh); |
|
gkđ: |
The price of electricity, purchased by the ancillary service provider from the power system to start the generator, is defined according to the electricity retail price list (hourly average price) for customers producing electricity at the voltage level for internal consumption by generators in the month m (VND/kWh); |
|
k: |
Number of billed starts of the generator i at the booting mode j; |
|
j: |
The generator’s booting mode; |
|
n: |
Number of generators in the power plant |
Table 4. Rate of electricity internally consumed for generator start (kWh/start)
|
Generator |
Booting mode |
||
|
Hot boot |
Warm boot |
Cold boot |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Other payables
The sum of other monthly payables that Buyer pays to Vendor is composed of:
a) Total drying cost (Txs,m) is calculated by the following formula:
![]()
Including:
|
cxs,i: |
Electricity consumption rate for drying the generator I in standby shutdown condition in 1 hour (subject to the duration of standby shutdown) (kWh/hour); |
|
ge,xs: |
The price of electricity, purchased by the ancillary service provider from the power system to dry generators, is defined according to the electricity retail price list (hourly average price) for customers producing electricity at the voltage level for drying generators in the month m (VND/kWh) |
|
Hi: |
Total number of hours, in which the generator i is dried, in the month m (hours) |
b) The amount balancing fuel cost difference due to the use of alternative fuel other than the primary one;
c) The following formulate defines total payables for generators providing reactive electricity Tpk,m (generators only running in rotary compensation mode) at the request of the operator of electric power system and electricity market:
Tpk,m = Tkdpk + Tpkp + Tpkn + Txs,m
Including:
|
Tkdpk: |
Fixed sum of the generator producing reactive electricity in the month m (VND), determined via the following formula: Tkdpk = Qpk x Gpk x Hpk |
|
Tpkp: |
Total variable cost of the generator producing reactive electricity in the month m (VND), as defined by the following formula: |
|
Tpkn: |
Total variable cost of the generator receiving reactive electricity in the month m (VND), through the following formula:
|
|
Txs,m: |
Total drying cost of the generator producing reactive electricity in the month m (VND), through the following formula:
|
|
Qpk: |
Total reactive output, as announced, of generators producing reactive electricity in the month m (kVar); |
|
Gpk: |
Fixed price subject to available reactive output (VND/kVAr/th), as negotiated according to actual contract value; |
|
Hpk: |
Coefficient of availability of generators producing reactive electricity in the month m; |
|
AGpkp,i,j: |
The amount of reactive electricity generated by the generator i at the hour h in the month m at the point of delivery (kVarh); |
|
Gpkp,i,j: |
The price of reactive electricity generated by the generator i (VND/kVArh), as defined by the following formula: Gpkp,ij - cvlp,i + cep,i,j x ge |
|
cvlpi: |
The cost of auxiliary materials for the generation or receipt of 01 kVArh by the generator i providing reactive electricity (VND); |
|
cep,i,j: |
Electricity consumption for the generation of 01 kVArh by the generator i providing reactive electricity at the output level j (kWh/kVArh); |
|
ge: |
The price of electricity, purchased by the ancillary service provider from the power system to generate or receive reactive power, is defined according to the electricity retail price list (price in normal hours) for customers producing electricity at the voltage level for internal consumption by generators in the month m (VND/kWh) |
|
AGpkn,i,j: |
The amount of reactive electricity that the generator i receives at the hour h at the point of delivery (kVArh); |
|
Gpkn,i,j: |
The price of reactive electricity that the generator i receives (VND/kVarh), as determined by the following formula: Gpkn,i,j = cvlp,i + cen,i,j x ge |
|
cen,i,j: |
Electricity consumption for the rotary compensation generator to receive 01 kVarh at the output level j (kWh/kVArh); |
|
cxs,i: |
Electricity consumption rate for drying the reactive output generator i in standby shutdown condition in 1 hour (kWh/hour); |
|
ge,xs: |
The price of electricity, purchased by the ancillary service provider from the power system to dry reactive output generators, is defined according to the electricity retail price list (price in normal hours) for customers producing electricity at the voltage level for drying generators in the month m (VND/kWh); |
|
Hi: |
Total number of hours, at which the generator I is dried, in the month m (hours). |
d) The cost of generators for ancillary services running on no load at the request of the operator of electric power system and electricity market;
dd) Taxes and other payables according to current regulations and the contract (if any);
e) Parts of the previous year’s balanced or audited interest cost from reserve fuel purchase loans for electricity production, carried forward to the billed month.








