Nội dung toàn văn Circular No. 32/2010/TT-BCT regulations on distribution power system
|
MINISTRY OF
INDUSTRY AND TRADE |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 32/2010/TT-BCT |
Hanoi, July 30, 2010 |
CIRCULAR
REGULATIONS ON DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
Pursuant to Decree No. 189/2007/ND-CP dated December 27, 2007 of the Government defining the functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Industry and Trade;
Pursuant to the Electricity Law dated December 3, 2004;
Pursuant to Decree No. 105/2005/ND-CP dated August 17, 2005 of the Government detailing and guiding the implementation of some provisions of the Electricity Law;Pursuant to Decision No. 26/2006/QD-TTg dated January 26, 2006 by the Prime Minister on approval of roadmap and the formation and development conditions of levels of electricity market in Vietnam;
The Ministry of Industry and Trade provides for the distribution power system as follows:
Chapter I
GENERAL REGULATIONS
Article 1. Scope of adjustment
This Circular provides for:
1. Operational standards of distribution power system.
2. Investment and development of distribution power grid.
3. Forecasting of electrical load demand;
4. Conditions and procedures for connection to the distribution power grid.
5. Dispatch and operation of distribution power system;
6. Metering of power at the point of delivery between the distribution power grid and power plants connected to the distribution power grid not involved in competitive electrical generation markets and customers using the distribution power grid.
Article 2. Subjects of application
This Circular applies to the following subjects:
1. Power distribution units;
2. Customers using the distribution power grid;
3. Vietnam Electricity Group.
Article 3. Explanation of terms
In this Circular, the terms below are construed as follows:
1. Voltage level is one of the values of the nominal voltage used in the power system, including:
a) Lower voltage is the nominal voltage of below 1000V;
b) Medium voltage is the nominal voltage from 1000v to 35kV;
c) High voltage is the nominal voltage from 35kV to 220kV;
d) Ultra high voltage is the nominal voltage of over 220kV;
2. Current transformer (CT) is the current transformation equipment expanding the scope of current measurement and power for the metering system.
3. Voltage transformer (VT) is voltage transformation equipment, expanding range of voltage and power measurement for the metering system.
4. Available power of generating unit is the actual maximum generation output of generating units which may generate power stably and continuously in a defined period.
5. Voltage oscillation is the change of voltage amplitude compared with the nominal voltage during the time longer than one (01) minute;
6. Point of connection is the point connecting the equipment, power grid and power plant of customers using the distribution power grid or other power distribution units into the distribution power grid;
7. Power distribution unit is the power unit issued with the power operation permit in the field of power distribution and receives the power directly from the electric transmission grid to sell power to power user or other power distributing and retailing units;
8. Power distributing and retailing unit is the electricity unit issued with the power operation permit in the field of power distribution and retailing or wholesaling purchase from the power distribution unit for retail sale to power user;
9. Power transmission unit is a power unit licensed to operate the electricity in the field of transmission and is responsible for managing the operation of the national transmission grid.
10. Power market and system operating unit is the unit steering and controlling the process of generation, transmission and distribution of power in the national power system; managing and coordinating the transaction of power sale and purchase and ancillary services in the electricity market;
11. Fault factor is the ratio between the value of voltage of phase without break-down after an earth fault short circuit with the voltage value of previous phase prior to earth fault short circuit (applying to cases of earth fault single phase short circuit (01) or two –phase short-circuit ).
12. Distribution power system is the power system including the distribution power grid and power plants connected to the distribution power grid;
13. Metering system is the system including the metering devices and integrated circuits for metering and determining the amount of power transmitted through a metering position.
14. SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) system is the data collection system to serve the monitoring, control and operation of the power system.
15. Power users are organizations or individuals purchasing power from the distribution power grid for use, not for re-sale to other organizations or individuals;
16. Electricity users of distribution power grid is organizations or individuals having electrical devices and power grid connected to the distribution power grid for using the power distribution services, including:
a) Electricity users;
b) Organizations or individuals possessing the generating units connected to the distribution power grid;
c) Power distributing and retailing units;
17. Power electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station are the electricity users having separate substation and power grid connected to the distribution grid at medium-voltage level and 110kV
18. Large electricity users of distribution power grid are the ones using the distribution power grid and possessing generating units with scale of installed capacity and the power electricity users with scale of power consumption provided for by the Electricity Regulatory Department;
19. Distribution power grid is the power grid including transmission lines and substations with voltage level from 35 kV or less, the transmission lines and substations with 110kV voltage having power distribution function.
20. Transmission power grid is the grid including transmission lines and substations with voltage level from 220 kV or more, the transmission lines and substations with voltage of 110kV having transmission function to receive power from the power plants into the national electricity system.
21. Typical day is the day which is selected and has mode of typical power consumption of power substation. The typical day includes the typical day of working day and weekends for years, months and weeks.
22. Stoppage or reduction in power supply as planned is the stoppage of power supply for the electricity users to do the repair, maintenance, overhaul, construction and installation of power works; regulation and restriction of load due to shortage of power under the load restrictions plan notified by the power market and system operating unit;
23. Level of short-term voltage flicker (Pst) is the value measured over a period of ten (10) minutes by standard metering device according to IEC868;
Pst95% is the value threshold of Pst so that in approximately 95% of the measurement period (at least a week) and 95% of number of measured positions Pst shall not exceed this value.
24. Level of long-term voltage flicker (Plt) is calculated from 12 consecutive Pst measurement result (during a period of approximate two (02) hours) by the following formula:
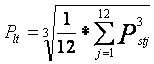
Pst95% is the value threshold of Plt so that in approximately 95% of the measurement period (at least a week) and 95% of number of measured positions Plt shall not exceed this value.
25. Blackout is the loss of connection between power plants and electric power substation resulted in power failure of a part or a whole of regional power system or national power system;
26. Operation boundary is the boundary determining the responsibility for operation of power grid or electrical equipment between the power distribution unit and electricity users of distribution power grid or other power distribution units;
27. Load shedding is the cut-off of load out of power grid when there is break-down in the power system or short-term local overload in order to ensure the safe operation of power system. This is done through the automatic load shedding system or dispatch order;
28. Harmonics is the voltage wave and sinusoidal current having frequency as multiple of the fundamental frequency.
29. Separation of connection is the separation of power grid or electrical devices of electricity users of distribution power grid from the distribution power grid at the Point of connection.
30. Metering equipment is the equipment including the meters, current transformers, voltage transformers and auxiliary equipment for power metering;
31. Connection Agreement is the written agreement between the power distribution unit and electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station for connection the electricity users’ electrical devices to the distribution power grid;
32. IEC standard is the standard of electrical technique issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission
33. Metering position is the physical position on the first circuit, in which the power sold and purchased is metered and determined;
Chapter II
OPERATION STANDARDS OF DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
SECTION 1. TECHNICAL STANDARDS
Article 4. Frequency
Rated frequency in the national power system is 50Hz. In normal conditions, the power system frequency may oscillate within ± 0.2 Hz compared with the rated frequency. In case of unstable power system, power system frequency may oscillate within ± 0.5 Hz compared with the rated frequency.
Article 5. Voltage
1. Nominal voltage
Levels of nominal voltage in the distribution power system include 110kV, 35kV, 22kV, 15kV, 10kV, 6kV and 0,4kV.
2. In the mode of normal operation, the voltage operated at the Point of connection may oscillate compared with the nominal voltage as follows:
a) At the point of connection with the electricity users is ±5%;
b) At the point of connection with the power plant is +10% and -5%.
3. In the mode of single break-down or during the restoration of stable operation after break-down, the rate of voltage oscillation at the Point of connection with the electricity users directly affected by the break-down may be from +5% and –10% compared with the nominal voltage;
4. In the mode of serious break-down of power transmission systems or break-down recovery, the voltage oscillation may be ±10% compared to the nominal voltage
5. Where the electricity users of distribution power grid require the higher quality of voltage than specified, the electricity users of distribution power grid may agree upon the voltage oscillation value at other Point of connections with the values specified in Clause 2 of this Article;
Article 6. Phase balance
In the mode of normal operation, negative sequence component of phase voltage shall not exceed 3% of nominal voltage for the voltage level of 110 kV or 5% of nominal voltage for the medium or low voltage level;
Article 7. harmonics
1. Total harmonic distortion (THD) is the ratio of the effective value of voltage of harmonics with the effective value of the fundamental voltage, expressed in units of percent (%), by the following formula:
![]()
In which:
|
THD: |
Total harmonic distortion of voltage; |
|
Vi: |
Voltage composition in the harmonics of level i; |
|
V1: |
Voltage composition in the fundamental frequency (50Hz). |
2. Total harmonic distortion of voltage at all Point of connection must not exceed the value specified in Table 1 as follows:
Table 1: Harmonic distortion of voltage
|
Voltage level |
Total harmonic distortion |
Individual distortion |
|
110kV |
3,0% |
1,5% |
|
Medium and low voltage |
6,5% |
3,0% |
3. Allowing the abnormal voltage peak on the distribution power grid during short time to exceed the total harmonic distortion specified in Clause 2 of this Article but not cause damage to the electrical devices of the electricity users of distribution power grid;
Article 8. Voltage flicker
1. In the conditions of normal operation, the rate of voltage flicker at all Point of connection must not exceed the limit specified in Table 2 below:
Table 2: Rate of voltage flicker
|
Voltage level |
Permitted rate of voltage flicker |
|
110kV |
Pst95% = 0.80 Plt95% = 0.60 |
|
Medium voltage |
Pst95% = 1,00 Plt95% = 0.80 |
|
Low voltage |
Pst95% = 1,00 Plt95% = 0.80 |
2. At the Point of connection of medium, the short-term rate of flinker (Pst) must not exceed 0.9 and the long-term rate of flinker (Plt) must not exceed 0.7 based on IEC1000-3-7 standard;
Article 9. Short circuit and time of eliminating break-downs
1. Permitted ultimate short circuit current and the time of eliminating break-downs are specified in Table 3 as follows:
Table 3: Permitted ultimate short circuit current and the time of eliminating break-downs
|
Voltage |
Ultimate short circuit current (kA) |
Time of elimination of break-downs (ms) |
Endurance time of equipment (s) |
|
Medium voltage |
25 |
500 |
3 |
|
110kV |
31,5 |
150 |
3 |
2. In special cases, the power distribution unit is responsible for proposal to have permission for application of rate of ultimate short circuit current for a certain areas in the distribution power system higher than the rate specified in Table 3;
3. The power distribution unit is responsible for prepare documents including the evaluation of effect of applying the value of ultimate short circuit higher than the specified rate in Table 3 to the electricity users of distribution power grid directly affected, and submit them to the Electricity Regulatory Department for consideration and approval;
4. The power distribution unit shall notify the value of permitted ultimate short circuit at the Point of connection for the large electricity users using the distribution power grid for coordination during installation of equipment;
Article 10. Earthing mode
The neutral earthing mode in the distribution power system is specified in Table 4 as follows:
Table 4: Earthing mode
|
Voltage level |
Neutral point |
|
110kV |
Direct earthing |
|
35 kV |
insulated neutral or earthed through impedance |
|
15, 22 kV |
Direct earthing (3-phase 3-wire) or multiple earthing (3-phase 4-wire) |
|
6, 10 kV |
Insulated neutral |
|
Below 1000V |
Direct earthing (neutral earthing, multiple earthing, combined neutral earthing) |
Article 11. Fault factor
The fault factor of the distribution power grid must not exceed 1.4 for the power grid with direct neutral earthing and 1.7 for the power grid with insulated neutral or power grid with earthing neutral through impedance;
SECTION 2. RELIABILITY STANDARDS
Article 12. Indicators of reliability of distribution power grid
1. Indexes of reliability of distribution power grid include:
a) System Average Interruption Duration Index - SAID
b) System Average Interruption Frequency Index - SAIFI
c) Momentary Average Interruption Frequency Index - MAIFI
2. Indexes of reliability of distribution power grid is calculated as follows:
a) SAIDI is calculated by the total outage time of electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in a quarter divided by total number of electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in that quarter by the following formula:

In which:
Ti: i th outage longer than 5 minutes in quarter j;
Ki: The number of electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit affected by the i th outage in quarter j;
n: A number of times of outage longer than 5 minutes in quarter j;
K: Total electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in quarter j;
b) SAIFI is calculated by the total times of outage electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in quarter divided by the total electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in that quarter, by the following formula:

In which:
n: A number of outage longer than 5 minutes in quarter j;
K: Total electricity users in quarter j of power distribution unit
c) MAIFI is calculated by a number of transient outages of electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in quarter divided by the total electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in that quarter, by the following formula:

In which:
m: a number of transient outages in quarter j;
K: Total electricity users and power distributing and retailing units purchasing power from the power distribution unit in quarter j;
Article 13. Cases of stoppage of power supply without consideration upon calculation of reliability indexes
1. Electricity users of distribution electricity grid propose the power outage;
2. Devices of electricity users of distribution power grid do not meet the technical standards and safety standards for restoration of power supply;
3. Due to equipment malfunction of electricity users of distribution electricity grid;
4. Due to power outage from transmission grid;
5. Load shedding by the dispatch order of power market and system operating unit;
6. Power outage occurs when there is possibility of causing serious unsafety for people and devices during the operation of power system;
7. Due to electricity users’ violation of regulation of law on power activities and power use specified in Article 6 of Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN dated December 23, 2005 of the Ministry of Industry stipulating the conditions, order and procedures for stoppage or reduction in power supply (hereafter referred to as Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN).
8. Due to unforeseen events and beyond the control of the power distribution unit under the provisions of Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN.
Article 14. Order to approve the annual standards of reliability for distribution power grid
1. Before September 15 annually, Vietnam Electricity Group shall summarize the calculation of reliability for the subsequent year of power distribution units for submission to the Electricity Regulatory Department for consideration and approval;
2. Before October 15 annually, the Electricity Regulatory Department shall approve the criteria for the reliability of the distribution power grid of each power distribution unit as a basis for calculation of power distribution price to the power distribution units;
Article 15. Reporting regulation
1. Before the 15th date of first month of each quarter, the power distribution unit shall report in writing to the Electricity Regulatory Department on implementation of power supply reliability indexes of distribution power grid in the previous quarter
2. The Electricity Regulatory Department stipulates the form of report on reliability of power distribution units;
SECTION 3. POWER LOSS STANDARD
Article 16. Power loss of distribution power grid
The power loss of distribution power grid includes:
1. Technical power loss: caused by power loss due to loss of technical capacity on transmission line and electrical devices on distribution power grid;
2. Non-technical power loss: is power loss due to theft of power, due to the error of power metering device or error of power metering system management;
Article 17. Order to approve indicators of power loss of distribution power grid
1. Before September 15th annually, the Vietnam Electricity Group shall summarize the calculation of power loss of distribution power grid for subsequent year of power distribution units for submission to the Electricity Regulatory Department for consideration and approval;
2. Before October 15th annually, the Electricity Regulatory Department shall approve the indicators of power loss of distribution power grid for power distribution units as a basis for calculation of power distribution price for power distribution units;
SECTION 4. SERVICES QUALITY STANDARDS
Article 18. Types of services quality standard
Types of services quality standard include:
1. Time to consider and sign connection agreement and perform new connection or the time to adjust the connection for electricity users;
2. Quality of response to complaints in writing
Contents of written response to electricity users’ complaint include:
a) Clearly responding that the complaints are accepted or not;
b) Clearly explaining that the settlement of the complaint is accepted;
c) Where the complaints are not accepted, the power distribution unit must clearly specifies the reasons and gives instruction to the electricity users in each specific case;
d) Fully providing other necessary information to help the electricity users evaluate the settlement;
dd) Written response in the time specified at Point b, Clause 2, Article 19 of this Circular;
3. Quality of response to the electricity users’ complaints through telephone is evaluated by the following criteria:
a) The percentage of electricity users’ calls is responded satisfactorily;
b) The time to respond to the calls in the time specified at Point c, Clause 2, Article 19 of this Circular;
Article 19. Services quality standard for distribution power grid
1. The power distribution unit must organize, maintain and upgrade the information system to record all electricity users’ complaints in writing or through telephone;
2. The services quality standard is defined as follows:
a) The time to consider and sign connection agreement after receipt of connection dossier which is complete and valid as prescribed in Article 47 and 48 of this Circular;
b) Quality of written response:
- There are over 85% of documents explaining the stoppage of power supply to the electricity users within twenty four (24) hours from the time of stoppage of power supply;
- There are over 95% of documents responding to complaints in writing ( fax or official dispatches) within five (05) working days;
c) Quality of response to complaints through telephone: there are over 85% of electricity users’ calls are responded within thirty (30) seconds;
Article 20. Report on services quality standard
Before March 31st annually, the power distribution unit shall report to the Electricity Regulatory Department on the result of performance of services quality standard including the following contents:
1. Result of performance of services quality indicators of previous year under the provisions in Article 19 of this Circular;
2. Explanation of cause in case of failing to meet the services quality standards;
3. Plan for improvement of services quality standard;
Chapter III
FORECASTING OF POWER LOAD DEMAND OF DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
Article 21. General provisions
1. Forecasting of power load demand of distribution power system means the forecast of entire load provided with power from the distribution electricity system, except for loads with separate power supply source. The Forecasting of power load demand of distribution electricity system is the grounds to formulate annual plans on investment in development of distribution power grid, plans and methods of operating the distribution power system.
2. Forecasting of power load demand of distribution power system include the forecasting of power load demand for the subsequent year, month and week.
3. Responsibility for making forecast of load power demand of distribution power system:
a) Power distribution units shall make forecast of load power demand of distribution power system under their management and power load at all points of connection with transmission power grid;
b) Power distributing and retailing units and electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating unit are responsible for providing the power distribution units with data of their power load demand including the general Forecasting of power load demand of entire unit and power load demand at each point of connection;
Article 22. Forecasting of annual power load demand
1. Information and data which are used for forecast of annual power load demand include:
a) Data of Forecasting of power load demand in the master plan for power development of provinces, central-affiliated cities and districts already approved;
b) Elements of power price, population growth, orientation of economic development in geographical areas of the power distribution units and other relevant socio-economic elements;
c) Changes of power load demand during the last five (05) years;
d) Forecasting of power demand growth of the existing power loads in subsequent years;
dd) Power demand of new loads, projects, industrial zones – clusters which have had plan on construction investment and progress of operation;
e) Programs on energy savings, management of load demand and solutions to reduce the power loss;
g) Output and electricity production purchased and sold at each point of connection with the grid of other power distribution units;
h) Output and electricity production imported and exported (if any);
i) Social elements or events affecting the load demand.
2. Result of forecasting of annual power load demand
a) For the first year
- Data of power forecast, monthly maximum output of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with the transmission power grid;
- Diagram of monthly typical day of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with the transmission power grid.
b) For four (04) subsequent years;
- Data of power forecast, annual maximum output of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with the transmission power grid;
- Diagram of annual typical day of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with transmission power grid.
3. Responsibility for information provision in service of forecasting of power load demand
a) Electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must provide the following information:
- Diagram of power load of typical day of present conditions;
- Estimated maximum output and electricity production registered for monthly use in subsequent year; estimated output and electricity production registered for annual use in four (04) subsequent years;
- Additional parameters of power grid, circuit breaker and diagram of protection lay-out for devices which are directly connected or affect the distribution power grid.
b) Electricity users of distribution power grid possessing a generating unit must provide the following information:
- Forecasting of monthly production and output possibly generated into the distribution power grid;
- Technical parameter of new generating units and progress of putting them into operation in five (05) subsequent years.
c) The power distributing and retailing units must provide the following information:
- Total customers under statistics of five components;
- Forecast of output and power demand of five customer components in five (05) subsequent years;
- Load diagram of monthly typical day at point of connection for the subsequent year;
- Additional parameters of power grid, circuit breaker and diagram of protection lay-out for devices which are directly connected or affect the distribution power grid.
d) Other power distribution units which have connection to the power grid of power distribution units must provide information on maximum output and estimated production of delivery at point of connection in each month of subsequent year; maximum output and estimated production at point of connection in each year of the period of four (04) subsequent years.
4. Process of implementation:
a) Before June 01st annually, the subjects specified in Clause 3 of this Article must provide information to the power distribution units in order to make Forecasting of power load demand for next year and four (04) subsequent years;
b) Before July 01st annually, the power distribution units must finish the forecast result of annual power load demand as prescribed in Clause 2 this Article in order to provide to the power market and system operating unit.
Article 23. Forecast of monthly power load demand
1. Information and data which are used for forecast of monthly power load demand:
a) Result of forecasting of annual power load demand;
b) Statistical data of consumed power, day and night peak output in corresponding month of previous year;
c) Other necessary information.
2. Result of forecasting of monthly power load demand:
a) Weekly maximum output and consumed power of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with the transmission power grid;
b) Maximum output and the power weekly delivered at the points of electricity sale with foreign countries through power grid of power distribution unit;
c) Maximum output and the power weekly delivered of large electricity users of distribution power grid;
d) Diagram of weekly typical day of the whole power distribution unit.
3. The large electricity users of distribution power grid must provide the power distribution unit with the forecast of consumed electricity and maximum output in subsequent month at points of connection in the following cases:
a) Difference of output of consumed power of more than 2MW in comparison with data of corresponding month in the forecasting of annual power load demand;
b) Generating outputs of electricity users as power plants with difference of more than 1MW in comparison with the estimated generating outputs of corresponding month in the forecast of annual power load demand.
4. Process of implementation
a) Before the 15th date monthly, the large electricity users of distribution power grid must provide the power distribution units with information as prescribed in Clause 3 of this Article to serve Forecasting of power load demand in subsequent month;
b) Before the 20th date monthly, the power distribution units must finish the Forecasting of power load demand for the subsequent month and notify the the power market and system operating unit.
Article 24. Forecasting of weekly load power demand
1. Result of forecasting of weekly power load demand includes the following parameters:
a) The maximum output and daily consumed power of the whole power distribution unit and at each point of connection with the transmission power grid;
b) The maximum output and power delivered daily at the points of at the points of electricity sale with foreign countries through the power grid of power distribution unit;
c) Diagram of daily load in week of whole power distribution unit.
2. Before 11:00 PM of Thursdays weekly, the power distribution units must finish and provide the Forecasting of power load demand in two (02) subsequent weeks to the power market and system operating unit in order to set operating mode for two (02) weeks.
Article 25. Load research
1. The power distribution units shall do load research in service of forecasting of power load demand and calculation of power retail price.
2. The Electricity Regulatory Authority shall formulate Circular on content, process and procedures for load research and submit it to the Minister of Industry and Trade for promulgation.
Chapter IV
MAKING PLAN FOR INVESTMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF DISTRIBUTION POWER GRID
Article 26. General principles
1. Annually, the power distribution units shall make plan for investment and development of distribution power grid for the subsequent year taking into account of 04 (four) subsequent years within their scope of management;
2. Annual plan for investment and development of distribution power grid shall be made based on the following grounds:
a) Result of annual power load demand forecast;
b) Being in line with the provincial electricity development plan approved and connection agreements signed;
Article 27. Requirement on annual plan for investment and development of distribution power grid
1. Ensuring the power supply for the load demand of current electricity users and new ones and ensuring the connection of new power sources to the distribution power grid;
2. Meeting the operational standards of distribution power system specified in Chapter II of this Circular;
3. Proposing list and progress to put the projects of distribution power system into operation in need of investment in subsequent year and total volume of investment of works items for four (04) subsequent years;
4. Proposing list and projects of transmission power grid in need of investment and upgrade in order to meet the requirements on progress of investment and development of distribution power grid;
Article 28. Content of plan for investment and development of distribution power grid
The plan for investment and development of distribution power grid includes the following contents:
1. Evaluating the present condition of distribution power system;
2. Forecasting the power load demand of subsequent year of each point of connection with the transmission power grid and forecasting the power load demand under the load compositions of the whole power distribution unit for four (04) subsequent years.
3. Evaluating the implementation of investment of projects of distribution power system approved;
4. List of new points of connection with large electricity users of distribution power grid together with the estimated points of connection agreed;
5. The calculation, analysis, selection of optimal grid connection diagram include:
a) Calculation of operation mode of distribution power grid;
b) Calculation of voltage loss;
c) Calculation of short-circuit to the medium-voltage busbar of 110kV stations;
d) Calculation of power loss on distribution grid;
dd) Calculation of reactive power compensation
e) Plan for reactive power compensation on distribution power grid;
6. List of works of transmission line and power distribution substation newly built or improved for the subsequent year and the total volume of investment in new construction and improvement of distribution power grid under voltage levels and work items for four subsequent (04) years as prescribed in Annex 1 to this Circular.
7. Summarizing new investment capital and improvement of distribution power grid under voltage levels;
Article 29. Order to prepare, appraise and approve the plan for distribution power grid
1. Documents of annual plan for investment and development of distribution power grid submitted for appraisal and approval include:
a) Written proposal for approval;
b) The annual plan for investment and development of distribution power grid under the contents complies with the contents specified in Article 28 of this Circular;
2. Annually, the power distribution units must submit documents of plan for investment and development of distribution power grid to the Vietnam Electricity Group under their management for summary and formulation of plan for investment in nationwide distribution power grid for subsequent year;
3. Before August 31st annually, the Vietnam Electricity Group shall submit the plan for investment in nationwide distribution power grid and of each power distribution unit to the Electricity Regulatory Department for subsequent year;
4. Before September 30th annually, the Electricity Regulatory Department shall appraise and adopt the plan for investment in nationwide distribution power grid and of each power distribution unit as a basis for calculation and setting of electricity price;
Chapter V
CONNECTION TO THE DISTRIBUTION POWER GRID
SECTION 1. GENERAL PRINCIPLES
Article 30. Point of connection
1. Point of connection is:
a) Point connecting equipment, power grid and power plant of electricity users of distribution power grid to the distribution power to the distribution power grid of power distribution unit;
b) Point of connection of power devices and grid between two power distribution units;
c) Point of connection of power devices and grid of electricity users to the distribution power grid of power distributing and retailing units;
2. Point of connection must be described in detail with drawings, diagrams and relevant explanation in the connection agreement or power sale and purchase contract;
Article 31. Asset delimitation boundary and operational management
1. The asset delimitation boundary between the power distribution units or power distributing and retailing units with the electricity users of distribution power grid;
2. The assets of each party at the asset delimitation boundary must be listed in detail together with the relevant drawings and diagrams in the connection agreement or power sale and purchase contract;
3. If the assets belong to any party, that party shall take responsibility for investment, construction, management and operation under the standards and regulations of law, unless otherwise agreed;
Article 32. Compliance with power development planning
1. Plan for connection of new electrical devices, power grid and power plant to the distribution power grid must comply with the power development planning already approved by competent state authority.
2. The power distribution unit shall notify the electricity users of the distribution power grid in case where the connection plan as suggested by customers is not consistent with the power development planning approved.
3. In case where the plan on connection to the 110kV voltage level or connection to the new power plant is not consistent with the approved power development planning, the investor having plan on connection shall prepare documents to report to the provincial People’s Committee for submission to the Electricity Regulatory Authority for appraisal and submission to the Minister of Industry and Trade to approve and adjust the provincial power development planning.
4. In case where plan on connection to the medium voltage level is not consistent with the approved power development planning, the investor having plan on connection shall prepare documents to request the adjustment or supplementation and submit them to the Service of Industry and Trade for appraisal and submission to the provincial People’s Committees for approving the adjustment of the district-level power development planning.
Article 33. Responsibility for implementation coordination
1. The power distribution units shall coordinate in implementing the connection plan when the electricity users have valid documents for connection. The connection and adjustment of connection must ensure the satisfaction of operational standards at the point of connection specified in section 2 of this Chapter.
2. If the devices at point of connection of electricity users of distribution power grid fail to satisfy the technical standards and operational standards of distribution power grid, the power distribution units shall notify and coordinate with the electricity users to provide remedial measures. The electricity users of distribution power grid must cover all costs for remedial measures.
SECTION 2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS AT POINT OF CONNECTION
Article 34. Requirements on phase balance
In normal working mode, the electricity users of distribution power grid must ensure that their devices do not cause the negative sequence component of phase voltage at point of connection in excess of 3% of nominal voltage for the 110 KV voltage level or in excess of 5% of nominal voltage for voltage level of less than 110kV.
Article 35. Requirements on harmonics
1. The permitted maximum value (under the absolute value of electric current or % of load electric current at point of connection) of total electric current deformation due to components of high-level harmonics depending on voltage level defined as follows;
a) For point of connection to low voltage level with output of 10kW:
- The electricity users are connected to in 1-phase low voltage level: the electric current value of high-level harmonics does not exceed 5A;
- The electricity users are connected to 3-phase low voltage side the electric current value of high-level harmonics does not exceed 5A;
b) For connection to medium voltage level or connection with output of between 10kW and 50kW: the electric current value of high-level harmonics at high level does not exceed 20% of load current.
c) For connection to high voltage or connections with output of 50kV or more: the electric current value of high-level harmonics does not exceed 12% of load current.
2. Total deformation of harmonics measured by the power distribution units at point of connection of electricity users of distribution power grid metered under standard IEC1000-4-7, lasting at least 24 hours with cycle of 10 minutes/time. No later than six (06) months after detecting the electricity users’ devices fail to reach the value specified in Clause 1 of this Article, the electricity users must take remedial measures in order to reach total deformation of harmonics within the permissible limits.
Article 36. Requirements on voltage flicker
The permissible maximum voltage flicker at point of connection with distribution power grid must comply with the Article 8 of this Circular.
Article 37. Grounding requirement
1. The electricity users of distribution power grid must use mode of neutral grounding in their power grid as prescribed in Article 10 of this Circular, unless otherwise agreed.<>
2. Where the electricity users are provided with power from many parties, they shall install appropriate protective devices in order to prevent and limit electric current to run through the neutral point into the ground.
Article 38. Requirements on output factor
The electricity users utilize for production, business and services with the maximum utilization output of 80 KW or transformers with capacity of 100kVA or more shall maintain the output factor (cos) at point of connection not less than 0.85, unless otherwise agreed.
Article 39. Requirements on low-frequency relay system
In case of necessity, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station connected to the voltage level of 110 KV shall equip and install low-frequency relay for automatic load shedding of load by the calculation of power distribution units. The requirements on low-frequency relay at low frequency must be clearly stated in agreement in the connection agreement.
Article 40. Requirements on information system
1. The electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the power plant connected into the distribution power grid with output of more than or equal to 10MW and 110kV substations shall be installed with the information system under their management and connect this system with information system of power distribution units in service of communications and transmission of data in operation of electricity system. The electricity users’ devices of distribution power grid must be compatible with the existing information system of the power distribution units.
2. The electricity users not subject to the cases specified in Clause 1 of this Article are entitled to make an agreement on installation of information system and it must be clearly stated in the connection agreement;
3. The power distribution units shall invest and manage the information system within their power grid management in service of operating the distribution power system.
4. Power distribution units shall provide necessary requirements on information data, data transmission and information interface for the electricity users of distribution power grid and coordinate with the electricity users in testing, inspection and connecting the electricity users’ information system and data to the existing information and date system under their management.
Article 41. Requirements on SCADA/DMS system
1. The power plant connected to the distribution power grid with output of more than or equal to 10MW and 110kV substations must be equipped with the distributed control system (DCS) or remote terminal unit (RTU) with two (02) independent gates and connected directly to the SCADA/DMS system of power distribution units.
2. For power plants with output of less than 10MW connected directly to 110kV power grid, the requirements on SCADA/DMS system may be agreed between parties depending on each specific case and must be clearly stated in the connection agreement.
3. The electricity users of distribution power grid shall be responsible for purchase, installation and connection of data transmission line of SCADA/DMS system from power grid within management to the SCADA/DMS system of power distribution units.
4. The electricity users’ SCADA/DMS system must have compatible technical characteristics and ensure the connection to the SCADA/DMS system of the power distribution units.
5. The connection of electricity users’ SCADA/DMS system to the existing SCADA/DMS system of power distribution units must be coordinated in implementation by the two parties. The power distribution units shall provide transmission line to point of connection and integrate the parameters of electricity users’ SCADA/DMS system with their SCADA/DMS system.
6. Where the power distribution units’ SCADA/DMS system has technological changes and approved by competent authority after signing the connection agreement which lead to changes or upgrade of electricity users’ SCADA/DMS system, the power distribution units and electricity users shall coordinate in implementing necessary adjustment of electricity users’ devices to be compatible with changes of SCADA/DMS system. The electricity users shall purchase and upgrade the SCADA/DMS system in order to ensure the connection with SCADA/DMS system of the power distribution units.
7. Requirements on list of data and technical standards of equipment under DCS/RTU system are specified in the Regulation on technical requirements and management of operation of SCADA/DMS system.
8. The Electricity Regulatory Authority shall organize, formulate and promulgate Regulation on technical requirements and management of operation of SCADA/DMS system.
Article 42. Requirements on protection system
1. The protection relay system of electric stations and 110kV voltage lines must comply with regulations on technical requirements for the protective and automatic relay system in power plants and substations promulgated by Electricity Regulatory Authority.
2. The power distribution units and electricity power of distribution power grid with separate station must agree upon requirements on protection system in the connection agreement.
3. The dispatch level which has the right to control the distribution power grid shall issue slip of relay adjustment within the distribution power grid and approve adjusted numbers related to the distribution power grid for protective devices of relay electricity users of the distribution power grid.
4. The electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must coordinate with the power distribution units to design, install, test and operate the protection system on their power grids to satisfy standards and technical requirements on duration of impact, sensitivity and selectivity against break-downs to minimize influence on the distribution power grid.
5. The electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station are prohibited from intentionally installing devices to limit short-circuit electric current at busbar connected to the distribution power grid, unless otherwise agreed with the power distribution units.
6. The power distribution units must provide the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station with the parameters of protection relay system on the distribution power grid in connection agreement.
Article 43. Requirements for generating unit connected to the distribution power grid
The generating unit connected to the distribution power grid must satisfy the following requirements:
1. The circuit breaker of generating unit at point of connection must be able to switch off the permitted maximum short-circuit electric current and isolate the generating unit from the distribution power grid in all operation mode.
2. Being able to generate the rated active output continuously in frequency range of between 49Hz and 51Hz. In the frequency range of between 47Hz and 49Hz, the output reduction level must not exceed the value calculated at the required rate of frequency reduction level of electrical system and must be in line with characteristic of relation between active output and frequency of generating unit. In case where the frequency is lower than 47Hz or higher than 51Hz, the electricity users of distribution power grid with generating unit are entitled to the connection or disconnection to the generating units from the electric distribution grid.
3. In conditions of normal operation, the generating unit connected to the distribution power grid must be able to generate the reactive power under the power characteristic of generating unit and keep the voltage deviation in the range as specified in Article 5 of this Circular.
4. The power plant connected to the distribution power grid being able to provide the reactive power must satisfy the following requirements:
a) Being able to continuously adjust the reactive power generated on the distribution power grid to adjust voltage on the distribution power grid;
b) Having magnetic ignition system to ensure the maintenance of stability of output voltage in operation range of generating unit connected to the distribution power grid.
5. The generating units connected to the distribution power grid must be able to withstand the loss of voltage symmetry in electrical system specified in Article 6 of this Circular and withstand the component of zero sequence current and negative sequence current not less than the elimination time of phase-to-phase and phase-to-ground short-circuit nearby the standby protection generator related to point of connection.
6. In case where point of connection is equipped with automatically switching devices, the protection relay system of power plant must ensure the coordination with automatically switching devices of power distribution units and must be designed to ensure the disconnect the generating unit from the distribution power grid right after the circuit breaker or devices switches off automatically or segment knife of distribution power grid opens for the first time and maintain insulation of generating unit from the distribution power grid until the distribution power grid is restored completely.<>
7. In addition to technical requirements specified in this Article, the generating units connected to the distribution power grid must satisfy the provisions in Articles 34, 35, 36, 40 and 41 of this Circular.<>
Article 44. Technical requirements at point of connection between the electricity users and the power distributing and retailing units
The electricity users and the power distributing and retailing units shall:
1. Ensure that equipment of the distribution power grid satisfies the operational standards as prescribed in Section 1 Chapter II of this Circular.
2. Ensure that technical requirements at point of connection satisfy the provisions in Articles 34, 35, 36, 37 and 38 of this Circular.
Section 3. THE PROCESS AND PROCEDURES FOR CONNECTION AGREEMENT
Article 45. Documents for connection
1. In case of connection to the low-voltage level, when having need for new connection to the distribution power grid or changing the existing connection, the electricity users of distribution power grid must send the power distribution unit documents specified in Annex 2A, 2B and comply with Article 48 of this Circular.
2. In case of connection to the medium-voltage and 110kV level, when having need of new connection into the distribution power grid or change the existing connection, the electricity users of distribution power grid must send the power distribution unit the following documents:
a) Documents to request the connection under the Forms specified in Annex from 2C to 2DD of this Circular;
b) Principle diagram of main electrical devices behind point of connection;
c) Technical documents of the equipment intended for connection or expected changes in the existing points of connection, estimated time to complete the project, technical and economic data of new connection projects or change of current connection.
Article 46. Process of agreement on connection to the medium-voltage and 110kV level
1. When receiving documents for connection, the power distribution unit shall verify them and notify in writing of the completeness and validity of documents.
2. After receiving complete and valid documents for connection, the power distribution unit shall implement the following steps:
a) Considering the requirements related to estimated electrical devices expected at the Point of connection;
b) Assessing the effect of connection of electrical devices, power grid and power plant of electricity users who request the connection with the distribution power grid about load-bearing capacity of existing transmission lines and substations; effect on short-circuit current and power quality of distribution power grid after connection and the coordination with protective systems;
c) Making and agreeing upon the one-wire diagram with technical parameters, equipment and the plan diagram of points of connection of power grid of electricity users to the distribution power grid to use as the official diagram used in connection Agreement;
d) Drafting the connection Agreement under the contents specified in Annex 3 of this Circular and it to the electricity users requesting the connection;
3. The electricity users requesting the connection shall provide necessary information for the power distribution units in service of consideration and agreement on implementation of connection plan and signing of connection agreement with power distribution units.
4. In case of failing to reach agreement on connection plan, the power distribution unit shall notify the electricity users in writing and report to Electricity Regulatory Authority of the reasons of disagreement on connection plan.
Article 47. Time limit for consideration and signing of connection agreement
The time limit for negotiation and signing of connection Agreement is specified in Table 5 as follows:
Table 5. Time limit for consideration and signing of connection agreement
|
Steps of preparing and reaching connection agreement |
Time |
Responsibility for implementation |
|
|
Medium-voltage power grid |
110kV power grid |
||
|
Sending documents for connection |
|
|
Electricity users requesting the connection |
|
Considering documents for connection |
10 working days |
20 working days |
Power distribution unit |
|
Preparing draft connection Agreement |
10 working days |
10 working days |
Power distribution unit |
|
Conducting negotiation and signing of connection Agreement |
15 working days |
20 working days |
Power distribution unit and Electricity users requesting the connection |
Article 48. Process of power supply to electricity users connected to the low voltage level
1. In case of power supply for domestic purposes, within seven (07) working days after receiving full and valid documents from the electricity users, the power distribution unit or power distributing and retailing units shall sign and send the electricity users the power supply contracts.
2. In case of power supply other than domestic purposes, within ten (10) working days after receiving full and valid documents from the electricity users, the power distribution unit or power distributing and retailing units shall check, survey and make plan for power supply to the electricity users who request the power supply;
3. In case of failing to provide power for the electricity users, the power distribution units or the power distributing and retailing units electric shall notify the electricity users clearly stating the reasons with the certification of competent state authority.
4. The Electricity Regulatory Authority shall organize, formulate and promulgate the Regulations on order of power supply to electricity users connected into the low voltage level.
SECTION 4. PERFORMING CONNECTION
Article 49. Right to access devices at point of connection
1. The power distribution units have the right to access devices at points of connection during the building, installation, replacement, disassembly, inspection, testing, maintenance and operation of these devices.
2. The electricity users have the right to access the devices under their management at points of connection during the building, installation, replacement, disassembly, inspection, testing, maintenance and operation of these devices.
Article 50. Providing documents of conditions for power switching of point of connection
1. Before the estimated day of power switching of point of connection, the electricity users have to send the power distribution units two (02) sets of dossier for general inspection the conditions for power switching of point of connection ( in Vietnamese or English for technical documents with certification of electricity users requesting the connection and copy of certified legal documents), including:
a) The technical design documents approved, modified and supplemented (if any) compared with the initial design, including general explanation, main power connection diagram, plan for electrical device layout, principle diagram of protection and control system and other relevant diagrams and technical parameters of main electrical devices;
b) Manufacturers’ materials guiding the operation and management of devices;
c) The partial or full acceptance records of connection devices of power plants, transmission lines and substations to the distribution power grid must comply with Vietnam’s technical standards or international standards which Vietnam has recognized and meet the technical requirements of connection devices specified from Article 34 to 44 of this Circular;
d) Expected running trial and operation schedule;
2. Unless otherwise agreed, the electricity users requesting the connection shall fully provide documents specified in Clause 1 of this Article within the permitted time limit as follows:
a) No later than two (02) months before the estimated day to put the power plant into the first trial operation;
b) No later than one (01) month before the estimated day to put the transmission line and substation into the first trial operation;
3. No later than twenty (20) working days after fully receiving documents, the power distribution units shall deliver the following documents to the electricity users requesting the connection:
a) Device numbering diagram;
b) Requirements for setting of electricity users’ protection relay from point of connection on electricity users’ side; slip of relay setting and relevant setting numbers for devices of protection relay of electricity users requesting the connection are issued by the dispatching level having the right to control the distribution power grid;
c) Requirements on testing and adjustment of devices;
d) Requirements on modes of receipt of dispatching order;
dd) Requirements on setting the communications system for dispatch;
e) Requirements on collection and data transmission of SCADA/DMS system (if any);
g) Mode of automatic control (if any);
h) Start-up mode (for power plant);
i) List of procedures relating to the operation of national power system, the distribution power system and procedures for operational coordination;
k) List of related staff members and engineers operating the power system together with the telephone and fax numbers;
4. No later than ten (10) working days before the estimated day of power switching of point of connection, the electricity users requesting the connection shall provide the power distribution units with the following contents:
a) Schedule of trial running (for power plants) and switching for operation of electrical devices;
b) Agreement to determine responsibilities of each party upon management and operation of connection devices;
c) Internal rules for safe operation of connection devices;
d) List of operation staff of electricity users including full name, professional title, responsibility together with telephone and fax number;
Article 51. Inspection the conditions for switching of point of connection
1. The electricity users requesting the connection shall agree with the power distribution units upon the day for actual inspection at point of connection;
2. Where the power distribution units announce the ineligibility for power switching of the point of connection or devices related to the point of connection of electricity users requesting the connection, these electricity users must adjust, supplement or replace these devices and make re-agreement with the power distribution units upon the time for subsequent inspection;
3. The power distribution units and electricity users requesting the connection shall simultaneously sign the record of eligibility for switching of point of connection and agree upon the time for switching of point of connection;
Article 52. Switching of point of connection
1. Before switching of point of connection, the electricity users requesting the connection must complete and provide the power distribution units with documents to certify that the works have adequate legal and technical procedures as follows:
a) The devices for switching of power have been tested and qualified for operation;
b) The power metering system has been perfected and the parameters of power meters have been recorded;
c) The power sale contracts have been signed;
d) Primary electrical devices have been numbered in line with the primary diagram issued by the dispatching level having the right to control.
dd) The protection and auto relay have been set in line with the requirements of dispatching level having the right to control.
e) Operating staff have been trained as qualified operators and have certificate of operation issued by the power market and system operating units including full name, professional title and responsibilities;
g) Dispatching information means (information duty, dialing telephone and fax) must be in good operation;
h) Finishing the connection with SCADA/DMS system;
2. The power distribution units shall prepare and register mode of power switching of point of connection with the dispatching level having the right to control the distribution power grid;
3. The power distribution units and electricity users of distribution power grid shall perform the power switching of point of connection by the mode approved by the dispatching level having the right to control;
Article 53. Order of testing to put the devices into operation behind point of connection
1. During the time of testing to put the devices into operation behind point of connection of electricity users requesting the connection, these electricity users must appoint their staff to be on duty and inform the list of on-duty staff with telephone and fax number to the power distribution units for operational coordination in case of necessity;
2. During the time of trial running for acceptance, the electricity users requesting the connection shall coordinate with the power distribution units to ensure that the operational parameters meet the technical requirements at the point of connection within the permitted limit specified in Section 2 of this Chapter;
3. Upon the end of trial running for acceptance, the electricity users requesting the connection shall confirm the actual operational parameters at point of connection of electrical devices, transmission lines, substations and generating units. Where the operational parameters at point of connection do not meet the technical requirements specified in Section 2 of this Chapter due to the cause of power grid or electricity users’ electrical devices, the power distribution units shall have the right to disconnect the power plant or electricity users’ power grid from the distribution power system and require the electricity users to take remedial measures;
4. The power grid and power plant and electrical devices behind the point of the electricity users requesting the connection are only allowed to be officially put into operation after acceptance from partial and full trial running and satisfaction of technical requirements at the point of connection specified in Section 2 of this Chapter. During the trial running for acceptance and official operation, the electricity users must comply with the Procedures for dispatch of national power system and other related procedures;
Article 54. Inspection and supervision of operation of connection devices
1. The electricity users of distribution power grid shall operate the devices to ensure the operational standards and technical requirements at point of connection within the limit specified in this Circular. Where the operational parameters of electricity users’ electrical devices do not meet the operational standards and technical requirements at point of connection, the power distribution units shall have the right to require the electricity users to re-inspect and test the devices under their management in order to determine causes and take remedial measures;
2. Where the two parties cannot reach an agreement upon the result of inspection and causes of violation, they have to agree upon the scope of inspection so that the electricity users hire a third party to independently perform the inspection and testing again. Where the third party’s result of inspection finds that the violation is caused by the electricity users’ devices but they do not accept the remedial measures, the power distribution units have the right to disconnect the electricity users’ devices from the distribution power grid;
3. The electricity users of distribution power grid shall bear the costs of additional inspection and testing in case where the inspection result finds that the electricity users’ devices have breached the operational standards and technical requirements at point of connection. The power distribution units shall bear the costs of additional inspection and testing in case where the inspection result finds that the electricity users’ devices have not breached the operational standards and technical requirements at point of connection.
4. Before the inspection of connection devices in order to determine the violation of operational standards of point connection, the power distribution units shall notify in advance the electricity users of distribution power grid of the time of inspection and list of inspectors. Where the inspection can cause the electricity users’ power failure, the power distribution units must inform the electricity users of distribution power grid at least fifteen (15) days in advance. The electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station shall coordinate and create necessary conditions to perform the inspection;
5. During the inspection, the power distribution units are allowed to install electrical metering and testing devices at connection devices but must not affect the safe operation of power plant, power grid and electricity users’ devices of power distribution grid.
6. During the operation, if any risk found at point of connection cannot ensure the safe operation for the power system due to the electricity users’ devices, the power distribution units must immediately notify the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and require the time for remedy to eliminate the risk of unsafe operation for power system. In case after the time of required remedy but the technical causes have not settled down, the power distribution units have the right to disconnect the point of connection and notify the electricity users who shall perform the re-testing in order to put the devices behind the point of connection under the provisions of Article 53 of this Circular;
Article 55. Replacement of devices at point of connection
1. Where the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station intend to replace, upgrade the connection devices or install new electrical devices possibly affecting the performance and the working mode of the distribution power grid, they must inform and agree with the power distribution units of these changes and contents of change must be supplemented in the connection Agreement;
2. In case of failing to accept the electricity users’ proposal, the power distribution units must inform the electricity users in writing of other necessary additional requirements for new devices expected to change;
3. All devices replaced at point of connection must be examined, tested and accepted under the provisions from Article 49 to Article 53 of this Circular;
Article 56. Performing the connection to low-voltage grid for electricity users of distribution power grid;
1. In case of power supply for domestic purpose, within seven (07) working days after fully receiving valid documents from the electricity users, the power distributing and retailing units must finish the installation and acceptance of power supply and metering system for the electricity users;
2. In case of power supply other than domestic purposes, within five (05) working days after the day of actual inspection of point of connection under the provisions of Article 48 of this Circular, the power distributing and retailing units must finish the installation and acceptance of power supply and metering system for the electricity users;
SECTION 5. CONNECTION SEPARATION AND RESTORATION
Article 57. General regulations
1. Cases of connection separation include:
a) Voluntary connection separation is the connection separated at the proposal of electricity users of distribution power grid, including permanent and temporary connection separation;
b) Compulsory connection separation is done in case where the electricity users of distribution power grid violate the connection Agreement or power sale contract or at the proposal of competent authority when the electricity users of distribution power grid violate the regulations of law;
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid must bear all costs of connection separation and restoration;
Article 58. Voluntary connection separation
1. Permanent connection separation
a) Cases of permanent connection separation when the electricity users of distribution power grid disconnect from the distribution power grid and the responsibilities of parties concerned must be regulated in the connection Agreement and power sale contract;
b) When having need of permanent connection separation from the distribution power system, the electricity users of distribution power grid must inform the power distribution units in writing at least one (01) month before the expected day of permanent connection separation. In case where the electricity users of distribution power grid possess the generating units connected to the distribution power grid, they must inform in writing the power distribution units and related dispatching levels at least three (03) months before the expected day of permanent connection separation;
2. Temporary connection separation
The electricity users of distribution power grid shall agree with the power distribution units upon the time for temporary connection separation from the distribution power system;
Article 59. Compulsory connection separation
The power distribution units have the right to separate the connection of electricity users of distribution power grid from the distribution power system in the following cases:
1. Upon the request for connection separation of the competent state authority;
2. The cases of compulsory connection separation are specified in the power sale contract or the connection Agreement;
Article 60. Connection restoration
The power distribution units shall restore the connection for the electricity users of distribution power grid in the following cases:
1. Upon the request for connection restoration of the competent authority or when the causes leading to connection separation have been eliminated and the consequences have been remedied and the electricity users have paid the related costs;
2. Upon the proposal for connection restoration from the electricity users of distribution power grid and all related costs have been paid by the electricity users in case of temporary connection separation;
Chapter VI
OPERATION OF DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
SECTION 1. RESPONSIBILITY FOR OPERATION
Article 61. Responsibility of power distribution units
1. Managing and operating the electrical devices and power grid under their management;
2. Making annual, monthly, weekly and daily plan for operation, maintenance and repair of electrical devices and power grids under the provisions of Section 2 and 3 of this Chapter;
3. Operating and maintaining the quality voltage of distribution power grid and ensuring the power supply to the electricity users who meet the operational standards specified in Chapter II of this Circular;
4. Purchasing, installing, managing, operating and ensuring the SCADA/DMS system and protection relay system shall work stably, reliably and continuously under their management. Preparing methods and calculating the protection relay system for the protection system of electricity users of distribution power grid at point of connection with the distribution power grid to ensure the selectivity, sensitivity and the capacity of break-down elimination;
5. Complying with the dispatch order of the power market and system operating units except for cases where the implementation is at risk of threatening human life or the electrical devices or dispatch order violates the regulations issued;
6. Operating the distribution power system and complying with the provisions in the Regulation on transmission power system and Procedures for dispatch of national power system;
7. Coordinating with other power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station during the operation of devices at point of connection with their power grid;
8. Complying with regulations on electrical safety, safety protection of power grid corridor and electrical works as stipulated by law.
Article 62. Responsibility of electricity users of distribution power grid
1. The electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station shall:
a) Operate the electrical devices and power grid under their management to ensure the accordance with the standards specified in Section 2, Chapter V of this Circular;
b) Complying with the steering right, dispatch order and operation of power distribution units under the Procedures for dispatch of national power system;
c) Correctly and promptly providing information for the power distribution units to prepare the plan for operation, maintenance and repair of distribution power system;
d) Coordinating with the power distribution units to maintain the quality of power and economically operate the distribution power system under the agreement with the power distribution units;
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the power plant connected to the distribution power grid shall:
a) Comply with the provisions in Clause 1 of this Article;
b) Ensure the operation of power plant under commitment in the connection Agreement and power sale contract;
c) Correctly and promptly providing the plan and date of operation of power plant for the power distribution units;
3. The electricity users of distribution power grid connected to the low-voltage level shall operate their electrical devices and power grids to ensure the accordance with the standards specified in Section 2, Chapter V of this Circular;
SECTION 2. PLAN FOR MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR OF DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
Article 63. General regulations on maintenance and repair of distribution
1. The power distribution units shall prepare the annual, monthly and weekly plan for maintenance and repair including the plan for maintenance and repair of distribution power grid and power plants with the installed output of 30MW or less connected to the distribution power grid to prepare plan for operation of distribution power system;
2. The plan for maintenance and repair of distribution power system once prepared needs consideration of plan for maintenance and repair of power grid and power plant of the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station. The power distributing and retailing units must meet the following requirements:
a) Ensuring the safe, stable and reliable power supply;
b) Optimizing the coordination of maintenance and repair of power source and power grid;
3. In case of failing to implement the plan for maintenance and repair of expected distribution power system, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units must notify again and coordinate with the power distribution units for adjustment;
Article 64. Annual plan for maintenance and repair
1. Before July 01st annually, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units shall provide the power distribution units with information on the plan for maintenance and repair of the two (02) subsequent years, including:
a) List of transmission line and electrical devices related to point of connection to the power grid of power distribution units for expected maintenance and repair;
b) Reasons for maintenance and repair;
c) Scope of power supply stoppage due to maintenance and repair;
d) Amount of power and design output of load are suspended from power supply stoppage;
dd) Amount of power and design output cannot be generated to the distribution power grid of power plant;
2. Before August 01st annually, the power distribution units must finish the draft plan for maintenance and repair of the subsequent two (02) years on the basis of consideration of following elements:
a) Result of forecasting power load demand;
b) Plan for maintenance and repair of the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station, the power distributing and retailing units and requirements for change of maintenance and repair schedule (if any);
c) Requirements for maintenance and repair of transmission power grid;
d) Coordination with plan for maintenance and repair of electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units in line with the conditions for actual operation in order to optimize the technical economic operation of distribution power system;
dd) Other requirements related to the maintenance and repair;
3. In case of failing to agree upon the plan for maintenance and repair of the power distribution units, before August 15th annually, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units have the right to send the written proposal to the power distribution units to adjust the annual plan for maintenance and repair. The power distribution units shall consider and adjust the annual plan for maintenance and repair in line with the electricity users’ request. In case of failing to adjust the plan for maintenance and repair at the electricity users’ request, the power distribution units must inform the electricity users in writing stating the reasons;
4. Before October 1st annually, the power distribution units must finish and announce the plan for maintenance and repair for the two (02) subsequent years on their websites including the following contents:
a) List of electrical devices and transmission lines in need of maintenance and repair;
b) Reasons for maintenance and repair of electrical devices and transmission lines;
c) Main contents of work;
d) Expected time for maintenance and repair;
dd) Other requirements related to the maintenance and repair;
Article 65. Monthly plan for maintenance and repair
1. Where the plan for maintenance and repair of the following month has changes compared with the annual plan for maintenance and repair announced, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units must provide the power distribution units with information specified in Clause 1, Article 64 of this Circular before the 15th date monthly;
2. Before the 20th date monthly, the power distribution units must finish the draft plan for maintenance and repair of the following month on the basis of considering the following elements:
a) Annual plan for maintenance and repair announced;
b) Result of power load demand forecasting of subsequent month;
c) Proposal for adjustment of plan for maintenance and repair of the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units;
d) Requirements for maintenance and repair on transmission grid;
3. Before the 25th date monthly, the power distribution units must finish and announce the plan for maintenance and repair for the next month on their website, including the following information:
a) Name of electrical devices and transmission lines in need of maintenance and repair;
b) Reasons for maintenance and repair of electrical devices and transmission lines;
c) Main contents of work;
d) Expected time for starting and ending of maintenance and repair;
dd) Other requirements related to the maintenance and repair;
e) Estimated output and power cannot be supplied due to maintenance and repair;
Article 66. Weekly plan for maintenance and repair
1. Every week, the power distribution units shall prepare the plan for maintenance and repair for the third week from the week preparing the plan for the two (02) subsequent weeks based on the following grounds:
a) Monthly operation plan approved;
b) Result of load forecasting of two (02) subsequent weeks;
c) Plan for maintenance and repair of power source and power grid updated;
d) Request for adjustment of plan for maintenance and repair of the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station and the power distributing and retailing units;
2. In case of change compared with the monthly plan for maintenance and repair, the large electricity users of distribution power grid and the power distributing and retailing units must provide the power distribution units with information specified in Clause 1, Article 64 of this Circular before 16:30 PM on Tuesday of two (02) weeks earlier;
3. In case of need for maintenance and repair of power grid under their management, before 16:30 PM on Tuesday of every week, the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station connected at medium-voltage level shall register the plan for maintenance and repair with the power distribution units to coordinate the plan for maintenance and repair of the subsequent week, including the following information:
a) List of electrical devices in need of separation for maintenance and repair;
b) Reasons for separation of electrical devices;
c) Expected time for starting and ending of maintenance and repair;
4. Before 16:30 PM on Thursday of every week, based on the monthly plan for maintenance and repair and information provided by the electricity users of distribution power grid, the power distribution units must finish and announce the plan for maintenance and repair for the two (02) subsequent weeks on their websites, including the following contents:
a) Name of electrical devices and transmission lines in need of maintenance and repair;
b) Reasons for maintenance and repair of electrical devices and transmission lines;
c) Main contents of work;
d) Expected time for starting and ending of maintenance and repair;
dd) Other requirements related to the maintenance and repair;
e) Estimated output and power cannot be supplied due to maintenance and repair;
5. Before 16:30 PM on Friday of every week, based on the weekly plan for maintenance and repair announced by the power distribution units, the power distributing and retailing units shall prepare the plan for maintenance and repair of low-voltage grid under their management and inform the electricity users affected under the provisions of Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN.
SECTION 3. OPERATION PLAN
Article 67. Annual operation plan
1. The power distribution units shall prepare the operation plan of distribution power system for the subsequent year including the following contents:
a) Power load demand forecasting of subsequent year;
b) Plan for maintenance and repair of subsequent year;
c) Forecasting of power generated in the subsequent year of the power plants with the installed output of 30 MW or less connected to the distribution power grid;
2. Before December 01st annually, the power distribution units shall finish the operation plan of subsequent year and announce it on their websites while announcing the operation plan of subsequent year of 110 kV power grid, the generating units connected to the distribution power grid and points of connection with the transmission power grid to the power market and system operating units, the power transmission units and other relevant power distribution units to coordination their implementation;
Article 68. Monthly operation plan
1. The power distribution units shall prepare the operation plan for the distribution power system of subsequent month based on the annual operation plan announced for the distribution power system, including the following contents:
a) Power load demand forecasting of the subsequent month;
b) Plan for maintenance and repair of the subsequent month;
c) Forecasting of power generated of the subsequent month of each power plant with the installed output of 30 MW or less connected to the distribution power grid;
2. Before the 25th date of every month, the power distribution units shall finish the operation plan of subsequent month and announce it on their websites while announcing the operation plan of subsequent month of 110 kV and medium-voltage power grid, the generating units connected to the distribution power grid and points of connection with the transmission power grid to the power market and system operating units, the power transmission units and other relevant power distribution units to coordination their implementation;
Article 69. Weekly operation plan
1. The power distribution units shall prepare the operation plan for the distribution power system of two (02) subsequent weeks based on the monthly operation plan announced, including the following contents:
a) Forecasting of power load dement of two (02) subsequent weeks;
b) Plan for maintenance and repair of two (02) subsequent weeks;
c) Forecasting of time and scope of power supply stoppage of two (02) subsequent weeks;
d) Forecasting of power generated of two (02) subsequent weeks of each power plant with the installed output of 30 MW or less connected to the distribution power grid;
2. Before 15:00 PM on Thursday of every week, the power distribution units shall finish the operation plan of two (02) subsequent weeks and announce it on their websites while announcing the operation plan of two (02) subsequent weeks of 110 kV and medium-voltage power grid, the generating units connected to the distribution power grid and points of connection with the transmission power grid to the power market and system operating units, the power transmission units and other relevant power distribution units to coordination their implementation;
3. Before 15:00 PM on Friday of every week, based on the weekly operation plan, the power distribution units and the power distributing and retailing units shall finish the operation plan of low-voltage power grid and inform the electricity users affected under their management;
Article 70. Mode of daily operation
1. Every day, based on the weekly operation plan announced, the power distribution units shall prepare the operation mode of subsequent day, including the following contents:
a) List of power source and power grid in need of maintenance and repair;
b) Forecasting of time and scope of power supply stoppage of subsequent day;
c) Forecasting of power generated hourly of subsequent day of each power plant with the installed output of 30 MW or less connected to the distribution power grid;
2. Before 15:00 PM of every day, the power distribution units shall finish and announce the mode of operation of subsequent day on their websites;
Article 71. Operation of distribution power system
1. The power distribution units shall operate the distribution power system by the mode daily operation announced and comply with the Procedures for dispatch of national power system and relevant regulations;
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must comply with the dispatch order of dispatch level which has the right to control the distribution power grid, coordinate and provide information for the power distribution units in service of dispatch of distribution power system.
SECTION 4. OPERATION IN EMERGENCY SITUATION
Article 72. Emergency situation
1. Emergency situation on the distribution power system is the situation when the power outage of the whole or part of transmission power system or distribution power system occurs and affects the normal mode of operation or causing widespread power outage in the distribution power system;
2. The emergency situations include:
a) Break-down or blackout of the whole or part of transmission power system affects the normal mode of operation of the distribution power system;
b) Break-down occurring on the transmission power system leads to one part of distribution system operating in the state of invert separation;
c) Break-down on the transmission lines or substation of 110kV voltage power supply distribution causing widespread power outage in the distribution power system;
Article 73. Operation of distribution power system in case of break-down or blackout of the whole or part of transmission power system
1. Where the break-down occurring on the transmission power system affects the normal mode of operation or power outage on the distribution power grid, the power distribution units shall:
a) Immediately contact the power market and system operating units and the power transmission units to know the information about the expected time for power supply stoppage and scope of effect on the load of distribution power system from this break-down;
b) Take measures to control the load output and other measures of operation to minimize the scope of effect due to break-down on the load of distribution power system;
2. In case of blackout of the whole or part of transmission power system affecting the normal mode of operation or power outage on the distribution power grid, the power distribution units shall:
a) Comply with the Procedures for black start and restore the national power system and Regulations on transmission power system;
b) Separate the distribution power grid under the units’ management into separate loading area under the Procedures for dispatch of national power system;
c) Restore the load by the order of priority and comply with the mode approved by the power market and system operating units within the scope of distribution power grid managed by the power distribution units;
d) Maintain the direct contact with the power market and system operating units until the power system is completely restored;
3. The power distribution units and the large electricity users of distribution power grid must keep contact information and send technical experts and announce the list of full name, positions and power of these experts to the related parties to coordinate the operation during the handling and restoration of emergency situation;
Article 74. Operation of distribution power system in case of invert separation
1. Where one part of distribution power system is inverted, the power distribution units must consider and decide upon the operation of power plants connected with this part of distribution power grid. The power distribution units must steer the dispatch of power plants to operate in the mode of invert and ensure the readiness for synchronizing with the power system upon the order from the power market and system operating units;
2. Where the power plant is designed with the mode of operation of independent invert separation and has the agreement with the power distribution units, the power plant connected to the distribution power grid may be operated with invert using the auxiliary and supplying power to the load or other electricity users’ electrical devices with the following conditions:
a) The power plant is fully designed with the protection relay system and has modes of control for the generating units in both mode of invert and mode of operation connected with the distribution power system;
b) Ensuring the possibility of determining and handling the break-downs during the operation of invert separation to protect the generating units and power grids of the electricity users of other distribution power grids in the distribution power grid inverted;
c) Ensuring the standards of neutral earthing of the distribution power grid inverted;
3. Where the part of distribution power grid inverted is unable to synchronize with the part of power system restored, the power distribution units must separate the power plant connected with the part of distribution power grid inverted to restore the power supply for the area inverted from the power system restored and then restore the operation of power plants inverted;
Article 75. Operation of distribution power system upon the occurrence of serious break-down on the distribution power grid
In case of occurrence of break-down on the transmission lines or substation of 110kV voltage power supply distribution causing widespread power outage in the distribution power system, the power distribution units shall:
1. Expeditiously isolate and handle the break-down and comply with the Procedures for handling of break-down of national power system;
2. Inform the break-down to the power market and system operating units, the power transmission units and the large electricity users of distribution power grid that are affected from the break-down;
3. Change the wiring mode to ensure the maximum power supply capacity to the load of distribution power system during the break-down;
Article 76. Restoration of distribution power system
1. When the distribution power system is disintegrated and operated in the mode of invert or when there is major break-down occurring on the distribution power grid, the power distribution units shall coordinate with the power market and system operating units, the power transmission units and the large electricity users of distribution power grid and the related units to put the distribution power system back to the normal mode of operation as soon as possible;
2. The power distribution units shall separate the loading areas with the scale consistently with capacity of power plants having black start and report to the power market and system operating units and ensure the quick restoration of distribution power system;
3. The power plants connected to the distribution power grid in the mode of invert and synchronizing operation must comply with the dispatch order of the power distribution units;
4. Where the distribution power grid does not have the power plants able to automatically start for invert operation and the distribution power grid is only restored from the transmission power system, then the power distribution units must restore the distribution power system by the order of the power market and system operating units. The power distribution units must restore the load by the priority order and plan approved;
5. The power distribution units shall inform the large electricity users of distribution power grid for coordination during the handling of break-down and restoration of distribution power system;
SECTION 5. CONTROL OF LOAD AND VOLTAGE
Article 77. Control of load
The control of load includes measures of stoppage or reduction in power supply, load shedding or control of reduced active output of power load under the voluntary registration of electricity users participating in programs of power demand management to avoid the blackout or overload on the power grid;
Article 78. Stoppage and reduction in power supply
1. The power distribution units shall implement the stoppage and reduction in power supply as planned and comply with the announced weekly operation plan specified in Article 69 of this Circular;
2. The power distribution units are entitled to stop the power supply not as planned in the following cases:
a) At the proposal of the power market and system operating units
b) Occurrence of break-down or threatening break-down causing loss of serious safety to people, electrical devices and power system;
c) Upon the unforeseen circumstances on the distribution power grid;
3. In case of stoppage and reduction in power supply, the power distribution units or the power distributing and retailing units must perform the procedures for notifying to the electricity users affected under the provisions in the Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN.
Article 79. Preparing plan for load shedding
1. The power distribution units shall prepare the plan for load shedding under their management based on the following:
a) Requirements for safe operation of power system;
b) Plan for stoppage of power supply due to threat of power supply security of the power market and system operating units;
c) Priority order of loads;
d) Measures to minimize the effect to the electricity users of distribution power grid having the same priority order of power supply;
2. Plan for load shedding must include levels of output, implementation order and time of load shedding;
3. Before 15:00 PM on Thursday of every week, the power distribution units shall finish and announce the plan for load shedding for the two (02) subsequent weeks;
Article 80. Measures of load shedding
1. Automatic load shedding is the shedding due to the impact of frequency relay for selective break of load at medium-voltage level in order to keep the frequency within the permitted limit and avoid the widespread power outage;
2. Load shedding by the order is the shedding upon the requirement of the power market and system operating units or the power distribution units in case of shortage of power source or break-down on power system to ensure the power supply security;
Article 81. Implementation of load shedding
1. The power distribution units must implement the load shedding under the plan for load shedding prepared and announced;
2. In case of load shedding by the order of the power market and system operating units or for the protection of distribution power grid, the power distributing and retailing units must notify the electricity users under the provisions in the Decision No. 39/2005/QD-BCN.
3. After the automatic load shedding or load shedding by the order of the power market and system operating units, the power distribution units shall:
a) Report to the power market and system operating units on the output, time, load area shed and load shedding levels under the set impact value of frequency relay;
b) Restore the load shed upon the order of the power market and system operating units;
4. Where the load under the management of electricity users suffers from automatic load shedding or by the order from the power distribution units, the electricity users shall:
a) Report to the power distribution units on the output, time, load area shed and load shedding levels under the set impact value of frequency relay;
b) Restore the load shed upon the order of the power distribution units;
Article 82. Implementation of control of voltage
1. The power distribution units shall calculate the voltage at the nodes on distribution power grid under their management by modes of operation and coordinate with the electricity users of distribution power grid to ensure the maintenance of quality of voltage through measures to control the reactive output and adjust the voltage division step of transformer;
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid shall coordinate the operation with the power distribution units to maintain the voltage on the distribution power system as agreed;
Article 83. Remote supervision and control
1. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid must agree upon the mode of supervision and control;
2. The power distribution units shall install the telemetry stations and necessary integrated devices to supervise the electricity users’ power grid upon the two parties’ agreement. In that case, the power distribution units must install the necessary remote control stations, including the control of circuit breaker and have the right to control the system of circuit breaker within the electricity users’ power grid;
3. The large electricity users of distribution power grid shall coordinate with the power distribution units in installation and operation of remote supervision and control systems;
SECTION 6. INFORMATION EXCHANGE IN OPERATION AND REPORTING REGULATIONS
Article 84. Forms of information exchange
1. The power distribution units, the large electricity users of distribution power grid and other the power distribution units must agree upon the form of information exchange to ensure the operation communication is continuously and smoothly for 24 hours
2. The power distribution units and the large electricity users of distribution power grid must appoint their officers in charge of operation communication and exchange of list of officers in charge of communication and operators;
Article 85. Information exchange in operation
1. The power distribution units shall notify the large electricity users of distribution power grid if they find that the mode of operation of distribution power grid may affect the mode of operation power grid or the electricity users’ generating units, including the following information:
a) The mode of operation of distribution power grid and effects possibly occur to the power grid or the electricity users’ generating units;
b) The cause of effect to the power grid or the electricity users’ generating units;
2. The large electricity users of distribution power grid shall immediately inform the power distribution units when they find that the mode of operation of power grid or their generating units may affect the distribution power grid, including the following information:
a) The cause of changing the mode of operation of electricity users’ power grid;
b) The effects which possibly occur to the power grid of the power distribution units;
Article 86. Announcement of abnormal situations
1. Abnormal situation is the one where the distribution power system has break-down or threatening break-down or the operation parameters are outside the permitted range;
2. When there are abnormal situations on the distribution power grid, the power distribution units shall:
a) Immediately notify the large electricity users of distribution power grid of the possible effects to the electricity users’ power grid;
b) Supplementing and clarifying the information provided for the large electricity users of distribution power grid possessing power plants upon requirement;
3. The large electricity users of distribution power grid shall immediately inform the power distribution units upon the abnormal situations on the electricity users’ power grid affecting the distribution power system;
Article 87. Notification of serious break-down
1. Serious break-down is the one causing the separation of transmission lines or substation of 110kV voltage power supply distribution from the operation resulted in widespread power outage in the distribution power system;
2. The power distribution units or the large electricity users of distribution power grid shall notify the break-down on their power grids right after the serious break-down;
3. Notification of serious break-down includes the main contents as follows:
a) Day and time of occurrence of break-down;
b) Duration of existence of break-down;
c) Location of break-down and affected areas;
d) Devices broken down;
dd) Brief description of break-down;
e) Cause of break-down (if any);
g) Expected time for remedy of break-down;
h) Measures of load shedding implemented (if any);
4. The power distribution units or the large electricity users of distribution power grid shall supplement and clarify the contents in the announcement of serious break-down upon requirement;
5. The power distribution units shall report on serious break-down in writing to the Service of Industry and Trade where the break-down has occurred with the contents specified in Clause 3 of this Article;
Article 88. Report on result of operation of distribution power system
1. The power distribution units shall make the monthly and yearly report on the implementation and result of operation of distribution power grid to assess the compliance with the standards of operation specified in Chapter II of this Circular; assess the result of operation of distribution power system, the overload, break-down of devices and causes and propose the measures to ensure the safe, reliable and effective operation of power grid;
2. Before January 31st of every year, the power distribution units must prepare the report on the result of operation of distribution power system of previous year; prepare the report on the result of operation of distribution power system of previous month before the 5th date of every month for submission to the Electricity Regulatory Authority and the power market and system operating units;
3. In the extraordinary cases, the power distribution units shall make a report on the result of operation of distribution power system upon the requirement of the Electricity Regulatory Authority;
SECTION 7. OPERATION COORDINATION
Article 89. Responsibility for operation coordination
1. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must agree upon the responsibility and scope of operation control for the devices on the relevant distribution power grid between the two parties and appoint persons responsible for safe operation coordination of power grid and devices;
2. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must coordinate, formulate and maintain the implementation of necessary safe measures upon implementation or testing under their management;
3. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must formulate the procedures for operation coordination to ensure the safety for people and devices in operation and testing, including the following contents:
a) Principles and procedures for operation coordination;
b) Responsibility and power in the control, operation and testing of distribution power system;
4. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station shall agree upon the operation coordination, storage, management and exchange of relevant documents;
Article 90. Operation coordination
1. When performing work on power grid, the power distribution units units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must comply with regulations on safe operation coordination and other related regulations on dispatch and safe operation;
2. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station must coordinate to install the signs, warning devices and safety instruction and provide means in service of work consistently at the work positions to ensure safety for work.
3. The inspection, supervision and control of connecting devices at the operation boundary must be done by the persons appointed by the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid with separate station;
SECTION 8. TESTING ON DISTRIBUTION POWER SYSTEM
Article 91. General requirements on testing on distribution power system
1. The testing on distribution power system includes the testing on the power grid of the power and power grid distribution units, the power plants or electrical devices of the electricity users of distribution power grid;
2. The testing is only conducted within the working capacity of electrical devices or generating units and during the time of announced testing with the presence of representatives of parties concerned and must comply with the existing procedures and regulations;
3. The power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid must ensure not to cause danger to people and devices on the distribution power system during the testing;
4. The testing of electrical devices at the point of connection with the transmission power grid must comply with the Regulations on transmission power system;
5. The costs of testing shall be born by the party proposing the testing if the result of testing proves that the power grid or generating units have met the standards of operation specified in this Circular or parameters stated in the connection Agreement. Where the result of testing proves that the power grid or generating units have not met the standards of operation specified in this Circular or are not in line with the parameters stated in the connection Agreement, then the party possessing the power grid or the generating units which do not statisfy the standards of operation shall pay the costs of testing.
Article 92. Cases of conducting the testing of devices on distribution power grid
1. Periodic testing of devices on distribution power grid;
2. Irregulat testing of devices on distribution power grid in cases:
a) To ensure the safety and reliability of distribution power grid;
b) When there are complaints of the electricity users of distribution power grid related to the violation of quality of power on distribution power grid specified in Chapter II of this Circular or in the connection Agreement;
c) Upon the requirement of the power distribution units when they find that the devices of the electricity users of distribution power grid negatively affect the distribution power grid;
Article 93. Cases of conducting the testing of generating units
1. The power distribution units have the right to conduct the testing of each generating unit connected to the distribution power grid no more than two (02) times a year, except for the following cases:
a) The result of testing has determined one or a lot of operational characteristics of generating units are not in accordance with the characteristics stated in the connection Agreement;
b) When the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing power plant do not agree upon the parameters and operational characteristics of generating units in the result of testing;
c) At the proposal of the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the power plant;
d) Testing on fuel conversion.
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the power plant have the right to require the testing in the following cases:
a) To re-inspect the operational characteristics of generating units which have been set after each break-down related to the generating units;
b) To inspect the generating units after installation, major repair, replacement, improvement or re-assembly.
Article 94. Responsibility in testing of devices on distribution power grid
1. The power distribution units are responsible for:
a) Conducting the periodic testing of devices on the distribution power grid under their operational management;
b) Conducting the irregular testing on the distribution power grid in cases of necessity to ensure the distribution power grid is operated safely and stably;
c) Conducting the testing on the electricity users’ power grid at the request of the electricity users of distribution power grid;
d) Coordinating with other power transmission units and the power distribution units to conduct the testing of devices at related points of connection;
dd) Giving prior written notice to the electricity users of distribution power grid and other related units of the testing schedule;
2. The electricity users of distribution power grid are responsible for:
a) Conducting the testing of power grid and generating units under their management;
b) Coordinating with the power distribution units in the testing of electrical devices at the points of connection with the distribution power grid;
c) Giving prior written notice to the power distribution units of the testing schedule;
d) Organizing the periodic testing and maintenance of electrical devices connected to the distribution power grid and must annually send the records of testing to the power distribution units for monitoring.
Article 95. Order and procedures for testing at the proposal of power distribution units
1. When in need of testing, the power distribution units shall give a written notice to the large electricity users of distribution power grid that suffer from the stoppage and reduction in power supply due to the testing and the large electricity users of distribution power grid that have the electrical devices at least fifteen (15) days in advance prior to the expected day of testing. The notice includes the following contents:
a) Purpose of testing;
b) Position of testing;
c) Expected time of testing;
d) Expected items and order of testing;
dd) Plan for stoppage and reduction in power supply due to the testing requirements (if any);
2. Where the testing is done under the management of the large electricity users of distribution power grid, if failing to agree with the testing notice from the power distribution units, within seven (07) working days after receiving the notice, the electricity users must reply and propose the settlement plan to agree with the power distribution units upon the adjustment of testing plan;
Article 96. Order and procedures for testing at the proposal of the large electricity users of distribution power grid
1. When in need of testing, the power distribution units shall send a written proposal for the testing to the power distribution units, including the following contents:
a) Purpose of testing;
b) Reason for testing;
c) Positions and items of testing;
d) Expected time of testing;
2. In case of testing the gererating units, the electricity users must supplement the following information:
a) Profile of generating units;
b) Characteristics of generating units;
c) Expected mode of operation of generating units during the time of testing;
3. Within seven (07) days after receiving the proposal for testing, the power distribution units shall review and request the electricity users to supplement necessary information;
4. Within fourteen (14) days after receiving the valid written proposal for testing, the power distribution units shall inform in writing the electricity users requesting the testing and related units of the testing plan;
5. The power distribution units shall inform in writing the electricity users requesting the testing of result of testing after the completion of testing;
Article 97. Responsibility for implementation after testing
1. The power distribution units must adjust and upgrade the devices on the distribution power grid in case where the result of testing finds that the devices on the distribution power grid under the management of the power distribution units do not ensure the technical standards specified in Section 2, Chapter II of this Circular;
2. The large electricity users of distribution power grid must adjust and upgrade the devices within the time limit agreed with the power distribution units grid in case where the result of testing finds that the devices on the distribution power grid under the management of the power distribution units do not ensure the technical standards specified in Section 2, Chapter II of this Circular or the requirements in the connection Agreement;
Chapter VII
POWER METERING
SECTION 1. GENERAL REGULATIONS ON POWER METERING
Article 98. Principle to identify the main metering position
1. The main metering position identified to be coincident with or adjacent to the point of connection;
2. In case of ineligibility for arrange the power meering system under the provisions in Clause 1 of this Article or the main metering position does not ensure the precise power metering delivered, the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid or other the power distribution units shall agree upon the alternative power metering position while identifying the mode of power conversion from the alternative metering position to the point of connection;
Article 99. Identification of metering position for high and medium-voltage level
1. Where the electricity users of distribution power grid are the power distributing and retailing units and the electricity users:
a) For the points of connection at 110kV voltage level, at each point of connection, it is required to identify the main metering position and one (01) alternative metering position;
b) For points of connection of voltage level from 1000V to 35 kV, the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid may agree upon the alternative metering position in case of necessity;
c) Point of connection of the power distribution units’ substations:
- The main metering position is identified at the outgoing feeders of transmission lines of the power distribution units’ substations, unless otherwise agreed;
- The alternative metering position is identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
d) Point of connection of substations of the electricity users of distribution power grid:
- The main metering position is identified at the master circuit breaker or high-voltage terminal of transformer directly connected to the distribution power grid unless otherwise agreed;
- The alternative metering position is identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
dd) Where the point of connection is different from the provisions at Point c and d of this Clause, the main metering position and alternative metering position are identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
2. Where the electricity users of distribution power grid are the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units:
a) For power plants connected at the voltage levels of 110kV, at each point of connection, it is required to identify the main metering position and two (02) alternative metering positions;
b) For power plants connected at the voltage levels from 1000V to 35kV, at each point of connection, it is required to identify the main metering position and one (01) alternative metering position;
c) The point of connection of substation of the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units:
- The main metering position is identified at the master circuit breaker or high-voltage terminal of the booster transformer directly connected to the distribution power grid unless otherwise agreed;
- The alternative metering position is identified at the outgoing feeders of transmission lines of the power plant’s substation, unless otherwise agreed;
- The second metering position: in case where the point of connection at the voltage level of 110kV is identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units;
d) The point of connection does not belong to the substation of the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units;
- Where the substation of the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units connected to the distribution power grid has a transmission line related to the point of connection without power moving through the busbar of electricity users’ substation, then the main metering position is coincident with or adjacent to the point of connection;
- Where the substation of the electricity users of distribution power grid has the generating unit with two (02) transmission lines or more and the power moving through the busbar of electricity users’ substations, then the main metering position is selected under the provisions at Point a, Clause 1 of this Article;
- The alternative metering positions are identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units;
dd) Where the point of connection is different from the provisions at Point c and d of this Clause, the main metering position and alternative metering positions are identified under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units;
3. Point of connection between two power distribution units:
The main metering position and alternative metering positions are identified under the agreement of the power distribution units;
4. The point of connection between the power distributing and retailing units and electricity users:
The main metering position and alternative metering positions (if any) are determined under the agreement of both parties;
Article 100. Identification of meter position for the electricity users of distribution power grid of low-voltage connection
The metering position for the electricity users of distribution power grid of low-voltage connection is identified at the point of connection of the electricity users of distribution power grid, unless otherwise agreed;
Article 101. Power metering system
1. The power metering system must be arranged at the main metering position to accurately and completely identify the quantities of power metering and delivery through points of connection and eliminate the elements affecting the metering results from the loop structure of power system;
2. The alternative metering system is installed at the alternative metering position to perform the following functions:
a) Replacing the metering system at the main metering position as a basis for calculating the quantities of power sale and purchase in case where the metering system at the main metering position is operated imprecisely or has break-down;
b) Supporting the supervision and inspect the metering result of the metering system at the main metering position in case where the metering system at the main metering position normally works;
c) Coordinating with the metering system at the main metering position and other alternative metering systems to calculate the power production delivered in a certain special cases;
SECTION 2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR POWER METERING SYSTEM
Article 102. Configuration of the power metering system
1. The full configuration of the power metering system consists of:
a) Current transformer;
b) Voltage transformer;
c) Power meter;
d) Electrical circuit and secondary cable;
dd) Devices collecting the metering data and data transmission line;
e) Safety devices, sealing and lead seal position;
g) Auxiliary devices, switching devices of connection, insulation devices of metering circuit for testing, logic devices for VT voltage switching, voltage and current testing devices;
2. The specific configuration of a metering system is determined by the voltage level and particularity of metering position;
Article 103. Metering system of 110kV voltage level
1. Requirements for power meter:
a) As the 3 phase 4 wire type;
b) Type of electronic integrated and programmable functions;
c) Having multiple rates;
d) Metering of active and reactive power by two separate receiving and transmitting ways by four-quadrant;
dd) Having maximum capacity metering functions and recording the total load diagram;
e) Having appropriate protocols for collecting, reading data on the spot and from a distance;
g) Provided with source from metering secondary voltage system and compulsorily ensuring the operation upon the loss of any one or two phase voltage;
h) Having levels of password;
i) Having sealing and lead seal positions to ensure no access to the wiring terminals and change of set parameters without break of seal lead;
k) Having storage functions of metered information and load diagram at least 60 days with the cycle of recording the metered value not exceeding 30 minutes;
l) For the metering system at the main metering position, the meter of active power must reach the precision level of 0.2 by the IEC 62053-22 standard and the precision level of 2.0 by IEC 62053-23 standard if metering the reactive power or other equivalent standards;
m) For the alternative metering system at the main metering position, the meter of active power must reach the precision level of 0.5 by the IEC 62053-22 standard and the precision level of 2.0 by IEC 62053-23 standard if metering the reactive power or other equivalent standards;
2. Requirements for current transformer used for power metering:
a) Having the secondary metering coil used for power meter;
b) Value of nominal secondary current is 1A or 5A;
c) Having the sealing and lead seal position on the lid of wiring box of metering secondary coil for power meter to ensure no impact on the connected circuit without break of seal;
d) Current transformer for main metering must reach the exact level 0.2 by the IEC 60044-1 standard or other equivalent standards;
dd) Current transformer for alternative metering must reach the exact level 0.2 by the IEC 60044-1 standard or other equivalent standards;
3. Requirements for voltage transformers used for power metering:
a) Having the metering secondary coil separately used for power meter;
b) The voltage value of nominal secondary system is 100V or 110V;
c) Having seal position on the lid of wiring box of metering secondary coil for power meter to ensure no impact on the connected circuit;
d) The voltage transformer for main metering must reach the precision level of 0.2 by the IEC 60044-2 standard for inductive voltage transformer and the 60044-5 standard for the capacitive voltage transformer or other equivalent standards;
dd) Transformer for alternative metering must reach the precision level of 0.5 by IEC 60044-2 for inductive voltage transformer and the 60044-5 standard for the capacitive voltage transformer or other equivalent standards;
Article 104. Metering system of voltage level from 1000V to 35 kV
1. Requirements for power meter:
a) Meeting the requirements specified at Points a, b, c, d, dd, g, h, i, k, Clause 1, Article 103 of this Circular;
b) For the main metering system, the meter of active power must reach the precision level of 0.5 by the IEC 62053-22 standard and the precision level of 2.0 by the IEC 62053-23 if metering the reactive power or other equivalent standards;
c) The precision level of alternative metering system (if any) is determined under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
2. Requirements for current transformer used for power metering:
a) Having the metering secondary coils separately used for metering devices and power meter;
b) Value of nominal secondary current is 1A or 5A;
c) Having the sealing and lead seal position on the lid of wiring box of metering secondary coil for the metering devices and power meter to ensure no impact on the connected circuit without break of seal;
d) The current transformer for main metering must reach the precision level of 0.5 by IEC 60044-1 standard or other equivalent standards;
e) The precision level of current transformer for alternative metering (if any) is determined under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
3. Requirements for voltage transformer used for power metering
a) Having the metering secondary coils separately used for metering devices and power meter;
b) The voltage value of nominal secondary system is 100V or 110V;
c) Having seal position on the lid of wiring box of metering secondary coil for the metering devices and power meter to ensure no impact on the connected circuit;
d) The voltage transformer for main metering must reach the precision level of 0.5 by the IEC 60044-2 standard for inductive voltage transformer and the 60044-5 standard for the capacitive voltage transformer or other equivalent standards;
e) The precision level of voltage transformer for alternative metering (if any) is determined under the agreement between the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid;
Article 105. Low voltage metering system
1. Requirements for power meter:
a) As 3 phase 4 wire or 3 phase 3 wire type for 3 phase meter and 1 phase 2 wire type for 1 phase meter;
b) Having sealing and lead seal positions to ensure no access to the wiring terminals and change of parameters set in the meter without break of seal;
c) For 3-phase meter and meter of active power that must reach the precision level of 1.0 by IEC 62053-21 standard for electronic meter, the IEC 62053-11 standard for inductive meter or other equivalent standards. For 1 phase meter and meter of active power that must reach the precision level of 2.0 by IEC 62053-21 standard for electronic meter and the IEC 62053-11 standard for inductive meter or other equivalent standards;
2. Requirements for current transformer if used for low-voltage metering:
a) Having the metering secondary coil separately used for metering devices and power meter;
b) Value of nominal secondary current is 1A or 5A;
c) Having the sealing and lead seal position on the lid of wiring box of metering secondary coil for power meter to ensure no impact on the connected circuit without break of seal;
d) Reaching the precision level of 0.5 by the IEC 60044-1 standard or other equivalent standards;
Article 106. Technical requirement of metering circuit
1. The secondary cable of metering circuit must be wired by the shortest way and the number of point of connection through the clamp line is the least and there must be conditions for seal and lead seal of metering circuit at points of connection;
2. For the metering system of 110 kV, the secondary coil of CT, VT and secondary cable connected to the power meter of the main metering system are not used for other purposes and must be independent from the alternative metering system. The secondary cable of the main metering system must be wired separately and connected directly from the wiring box of CT and VT to the meter cabinet without passing the clamp line in the intermediate cabinet;
3. Where the meter is supplied with voltage from one VT busbar through the voltage switch, the wiring connector of voltage switch must ensure the conditions for seal and lead seal and the power meter must be programmed to record the time and duration of voltage switch;
4. The load of secondary circuit of CT and VT including the power meter must not exceed the rated load of CT and VT.
5. Where the current circuit of the alternative metering system is used in conjunction with the other metering devices, it must ensure no effect to the precision degree of the metering system and be eligible for seal and lead seal of the entire current circuit, metering devices and power meter;
6. The testing junction box must be installed for the inspection of metering devices and eligible for seal and lead seal;
Article 107. Technical requirement for seal and lead seal and security
1. The whole system of power metering includes the wiring box of CT and VT, power meter, clamp line, connector, current circuit, voltage circuit, auxiliary devices, switching logic circuit, meter cabinet and information network must be sealed and sealed with lead to prevent illegal intervention.
2. For the electric power meter, the software of meter must have protection password with different access permission levels;
3. Where the power distribution units have installed and used the automatic metering data collection system, they have to ensure the following requirements:
a) The power metering data after being read and transmitted to the server placed at the metering position must be encrypted to prevent unauthorized changes;
b) Management software systems reading, transmitting and integrating the power metering data must be secured with multiple levels of password to ensure the security, accuracy and reliability of the measured data.
SECTION 3. INVESTMENT, INSTALLATION AND MANAGEMENT OF OPERATION OF POWER METERING SYSTEM
Article 108. Responsibility for investment and installation of power metering system
1. For the points of connection between the power distribution units and power distributing and retailing units and electricity users;
a) The power distribution units shall:
- Purchase and install the main metering system, alternative metering systems and metering data collection system at the metering positions and devices in service of data collection if necessary;
- Ensure the metering position is consistent with the metering position agreement between the related units;
- Ensure the data metering and collection system placed on the spot meets the technical requirements and is consistent with the design of metering system agreed and the relevant legal regulations on metering;
- Assume the prime responsibility for the following tasks:
+ Initially testing and inspecting the metering devices, programming and installing the working parameters of meter of the metering systems;
+ Taking measures to seal or seal with lead the metering devices including the meters, CT, VT, metering circuit, clamp line and intermediate box to ensure the security of metering system;
+ Preparing the plan for acceptance of metering system and making an agreement with the related units;
b) The electricity users and the power distributing and retailing units shall coordinate with the power distribution units to install and inspect the entire metering system in case where the metering position is within the the electricity users’ power grid;
2. For the point of connection between the power distribution units and power plants:
a) The electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units shall purchase and install the metering system under the contents specified at Point a, Clause 1 of this Article;
b) The power distribution units shall coordinate with the electricity users of distribution power grid possessing the generating units during the installation and inspection of the entire metering system;
3. For points of connection between two power distribution units
The responsibility for investment in metering system at the point of connection is done under the agreement between the power distribution units;
4. For points of connection between the power distributing and retailing units and the electricity users;
a) The power distributing and retailing units are responsible for installing the power metering system under the contents specified at Point a, Clause 1 of this Article;
b) The electricity users shall coordinate with the power distributing and retailing units to install and inspect the entire metering system in case where the metering position is within the electricity users’ power grid;
Article 109. Responsibility for management and operation of metering system
1. The units investing and possessing the metering system shall assume the prime responsibility in the management, operation and implementation of periodical testing, inspection and maintenance of metering system;
2. The power distribution units must agree with the electricity users of distribution power grid and other power distribution units to connect to their power grid for coordination of management, operation, maintenance and replacement of metering systems in order to ensure the metering systems work with precision, stability, reliability and security.
3. During the management and operation, the power distribution units and the electricity users of distribution power grid are responsible for regularly monitoring and inspecting the operational status of meter system. In case of abnormal findings or break-down in the metering system, they must immediately notify the parties concerned for coordination of settlement;
Article 110. Responsibility for formulating the procedures for management and operation of metering system
The Electricity Regulatory Department shall organize, formulate and promulgate the Procedures for delivery and operation of power metering system;
Chapter VIII
EXEMPT IMPLEMENTATION
Article 111. Cases of considered exempt implementation
The units subject to the application of this Circular are entitled to submit dossier to be considered for exempt implementation in the following cases:
1. Having had contracts signed before the effective date of this Circular but these contracts have contents different from the provisions of this Circular;
2. The application of this Circular have increased the cost excessively and unreasonably for these units;
3. The units have proved that the exemption is consistent with the principles of this Circular.
Article 112. Authority and grounds for decision on exempt implementation
1. The Electricity Regulatory Department shall consider and approve the cases of exempt implementation under the provisions in Article 111 of this Circular;
2. The grounds for considering the exempt implementation include:
a) The right of parties in the power sale contracts and the connection Agreement that have been signed before the effective date of this Circular;
b) The costs incurred for the relevant units to meet the provisions of this Circular;
c) Opinion of the power market and system operating units on the effect of exempt implementation and the assurance of standards of operation specified in Chapter II of this Circular;
d) Scope and time limit for requesting the exempt implementation;
Other grounds related to the enjoyment of exemption (if any);
Article 113. Dossier for exempt implementation
Dossier for exempt implementation consists of:
1. Written request for exemption must be accompanied with the contents specified in Clause 2, Article 112 of this Circular;
2. Valid copy of electricity operation Permit of power units;
3. Detailed explanation of effect to the operation of power system and commitments if exempted from implementation;
Article 114. Procedures for evaluating dossier for exempt implementation
1. Within seven (07) days after receiving dossier for exempt implementation, the Electricity Regulatory Department shall inform in writing the units submitting dossier of its validity. Where the dossier is not valid, the Electricity Regulatory Department shall inform the contents in need of supplementation;
2. Within thirty (30) working days after fully receiving valid dossier, the Electricity Regulatory Department must finish the evaluation of dossier for exempt implementation and issue the written permission for exempt implementation. In case of disapproval for the exempt implementation, Electricity Regulatory Department shall issue a written notice to the requesting units stating the reasons for disapproval;
3. Where the request for exempt implementation has a lot of complex circumstances relating to other units, the extended evaluation period is allowed but not exceeding fifteen (15) working days;
4. The units submitting dossier must pay the costs of evaluation for exempt implementation as prescribed;
Article 115. Responsibility for information provision
The power distribution units, the power market and system operating units and the related units shall provide information and give out their written opinion on the request for exemption and comply with the requirements of the Electricity Regulatory Department;
Article 116. Withdrawing the request for exempt implementation
In case of withdrawing the request for exempt implementation, the units submitting dossier for exempt implementation must give a written notice to the Electricity Regulatory Department;
Article 117. Annulment of Decision to permit the exempt implementation
The Electricity Regulatory Department has the right to annul the Decision to permit the exempt implementation in the following cases:
1. Detecting deception in request for exempt implementation;
2. The units having the exempt implementation have failed to implement or improperly implement the conditions and committed obligations and the time for implementation as prescribed in the Decision to permit the exempt implementation
3. The conditions allowing the exempt implementation no longer exist;
Chapter IX
SETTLEMENT OF DISPUTE AND HANDLING OF VIOLATION
Article 118. Settlement of dispute
Where the disputes occur between the units in relation to the implementation of this Circular, these units have the right to refer the case to the Electricity Regulatory Department for settlement under the provisions of the order and procedures for settlement of dispute in electricity activities issued by the Ministry of Industry and Trade
Article 119. Handling of violation
1. When detecting the acts of violation of provisions in this Circular, the individuals and organizations have the right to report them to the Electricity Regulatory Department;
2. Making a report on acts of violation must state the following information:
a) Individuals and organizations committing the violation of provisions of this Circular;
b) Acts of violation;
c) Time of violation;
d) Individuals and organizations are affected due to acts of violation;
dd) Other relevant information (if any);
3. The Electricity Regulatory Department has the right to require the parties concerned to provide information on acts of violation during the inspection and handling of violation;
Chapter X
IMPLEMENTATION ORGANIZATION
Article 120. Time limit for satisfying the standards of Regulations on distribution power system
1. Within one (01) year after the effective date of this Circular, the electricity users of distribution power grid are responsible for investing and upgrading their devices to satisfy the standards specified in this Circular;
2. Within two (02) years after the effective date of this Circular, for the areas where the current distribution power grids have not satisfied the standards specified in this Circular, the power distribution units shall invest and upgrade the power grid to satisfy the standards specified in this Circular;
Article 121. Implementation organization
1. The Electricity Regulatory Department shall publicize, guide and inspect the implementation of this Circular;
2. Any problem arising during the implementation should be promptly reported to the Electricity Regulatory Department for considering and proposing the Ministry of Industry and Trade to amend and supplement this Circular;
Article 122. Effect
1. This Circular takes effect on September 15, 2010;
2. Annulling Decision No. 37/2006/QD-BCN dated October 16, 2006 of the Minister of Industry issuing the Decision on connection to the national power system;
|
|
FOR THE MINISTER |
APPENDIX 2C
GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT REGISTRATION OF CONNECTION FOR USERS OF DISTRIBUTION
GRID CONNECTED TO
MEDIUM VOLTAGE GRIDS OR HIGHER)
(Promulgated
together with Circular No. 32/2010/TT-BCT dated July 30, 2010 on electricity
distribution system)
Information about registration of connection for new connections or changes of old connections, including:
1. Name of customer:
2. Position:
3. Workplace:
4. Headquarters registed in:
5. Address:
6. Tel:
7. Fax:
8. Email
GENERAL INFORMATION
1. Project description:
a) Name of project;
b) Business lines/forms of production;
c) Estimated production/production capacity;
d) Intended commencement date;
dd) Intended inauguration date;
e) Current connection points (if any);
g) Connection point applied for;
h) Voltage level and number of lines applied for;
i) Intended date of electrification at the connection point.
2. Map, diagram, and plan
a) A geographical map on a scale of 1:50000 that marks the position of the ecustomer, the part of distribution grid of the distributing unit, and position of the connection point;
b) A site plan on a scale of 1:2000 or 1:5000 that specifies positions of generating units, transformers, buildings, and connection points;
c) A plan for construction of works in the surrounding areas of electrical substations, generating units, construction works, and connection points on a scale of 1:200 or 1:500.
3. Legal documents
Documents about legal status (valid copy of certificate of investment, certificate of enterprise registration, license for electricity operation).
APPENDIX 2D
INFORMATION ABOUT ELECTRICITY DEMAND OF CUSTOMER
(CONNECTED TO MEDIUM
VOLTAGE GRIDS OR HIGHER)
(Promulgated
together with Circular No. 32/2010/TT-BCT dated July 30, 2010 on electricity
distribution system)
Information about major customers of the distribution grid that do not own power plants or generating units:
1. Electrical energy and rated power
|
Active power |
(MW) |
|
Reactive power |
(MVAr) |
|
Daily/monthly/annual electricity consumption |
(kWh) |
2. Forecast about electricity demand at the connection point
a) First year’s electricity consumption
- The customer that requests changes of connection must provide information about the electricity consumption of existing loads at the connection point, load profiles of each day in the latest year, including the following figures:
+ Active power and reactive power received from the distribution grid;
+ Self-generated active power and reactive power (if any).
- The customer that applies for a new connection point must provide information about demand of loads at the connection point, including maximum power, electrical energy, and load profiles of typical days of each month of the commencement year, including the following figures:
+ Active power and reactive power received from the distribution grid;
+ Self-generated active power and reactive power (if any).
b) Forecast about electricity demand in the next 5 years
- The customer that requests changes of connection must provide information about estimated load at the connection point, including maximum power, electrical energy, and load profiles of typical days of each month in the next 5 years. Demand for active power and reactive power received from the distribution grid, self-generated active power and reactive power must be specified.
- The customer that applies for a new connection point must provide forecast about estimated electricity demand, including maximum power, electrical energy, and load profiles of typical days of each month of the next 5 years from the official commencement date. Demand for active power and reactive power received from the distribution grid, self-generated active power and reactive power must be specified.
c) Forecast about electricity demand (if any) includes figures related to electricity consumption such as production, rate of electricity consumption per product, mode of electricity consumption (shift, working days, and days off), total installed power of electrical equipment, maximum power, power coefficient, etc.
3. Specifications of equipment and electrical grid of load at the connection point
a) Electricity diagram
- Diagram of equipment distribution;
- Diagram of electricity connections which specifies:
+ Location of busbar ;
+ Lines (overhead lines, underground cables, transformers,etc.);
+ Phase distribution;
+ Earthing;
+ Switchgears;
+ Operating voltage;
+ Protection method;
+ Location of connection point;
+ Distribution of reactive power compensation devices
This diagram is limited to the electrical substations connected to the the connecton points and other electrical equipment of the customers to be connected that may affect the distribution system; intended expansion and changes (if any) in the future must be specified.
b) Electrical equipment
- Switchgears (circuit breaker, isolator, etc.) of circuits related to the connection point:
+ Rated operating voltage;
+ Rated current (A);
+ Rated 3-phase short-circuit current (kA);
+ Rated 1-phase short-circuit current (kA);
+ Rated 3-phase no-load current (kA);
+ Rated 1-phase no-load current (kA);
+ Rated 3-phase short-circuit peak load current (kA);
+ Rated 1-phase short-circuit peak load current (kA);
+ Basic insulation level (kV).
- Transformer:
+ Rated voltage and coil arrangement;
+ Rated power MVA of each coil;
+ Voltage division coil (underloaded or no-loaded), voltage division area (quantity of outputs and length of voltage steps)
+ Voltage division cycle;
+ Earthing (direct earthing, no earthing, and earthing via the reactor);
+ Saturation curve;
+ Positive sequence reactance and resistance of the transformer at the nominal, minimum, and vaximum voltage step out of percentage of rated power of the transformer. Provided the transformer has 3 coils that are connected to the outside, the resistance and reactance between each couple of coils must be calculated with the third coil as an opened circuit;
+ Zero sequence reactance and resistance of the transformer at the nominal, minimum, and maximum voltage steps (Ω);
+ Basic insulation level (kV).
- Reactive power compensation devices (capacitors, inductors):
+ Type of device (fixed or changeable), electricity capacitance and/or ratio of inductance or operating zone MVAr;
+ Resistance, reactance, charged/discharged current;
+ For controllable capacitors/inductors, it is required to provide detailed specifications such as voltage, load, operating duration, and other installations.
- Voltage transformer/current transformer
+ Variable ratio;
+ Certificate of conformity with regulations on electricity measurement.
- Protection and control system:
+ Protection system configuration;
+ Proposed installed value;
+ Time for resolving issues of the primary and backup protection systems;
+ Automatic closing cycle (if any);
+ Control management and data transmission
- Overhead lines and cables related to the connection point.
+ Resistance/reactance/capacitance;
+ Rated current and maximum current
c) Figures related to short-circuit
- 3-phase short-circuit current (instantaneously occur at the point of breakdown and after the transient breakdown) from the customer’s electricity system to the distribution grid at the connection point.
- Value of zero sequence reactance and resistance of the customer’s electricity system at the connection point.
- Value of voltage before breakdown that matches the highest breakdown current;
- Value of negative sequence reactance and resistance of the customer’s electricity system at the connection point.
- Value of zero sequence reactance and resistance of Pi-equivalent circuit of the customer’s electricity system.
d) Required backup level
Every customer that uses electricity directly from the distribution grid and wishes to receive electricity from 2 sources or more must specify:
- The backup sources;
- Requested backup power (MW and MVAr).
4. Load characteristics
Every customer that uses electricity directly from the distribution grid must provide the following information:
- Details about load components of the customer that uses electricity directly from the distribution grid, especially information about the loads that can cause fluctuation over 5% total power of the electricity received by the customer directly from the distribution grid at the connecton point and the possibility of causing voltage drop of such loads.
- Details about load characteristic of load at each connection point:
|
Parameter |
Unit |
|
Power coefficient in reactive power mode |
|
|
Sensitivity to voltage |
MW/kV, MVAr/kV |
|
Sensitivity to frequency |
MW/Hz, MVAr/Hz |
|
Maximum and average phase imbalance possibility |
% |
|
Maximum harmonic wave possibility |
|
|
Short-term and long-term voltage drop possibility |
|
|
Load fluctuation, including both increase and decrease |
kW/s and kVAr/s |
|
Shortest interval of load fluctuation |
second |
|
Highest change in electricity demand |
kW and kVAr |
5. Other requirements related to load




