Nội dung toàn văn Decision 4156/QD-BYT 2021 guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID19 at home
|
MINISTRY OF HEALTH |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No. 4156/QD-BYT |
Hanoi, August 8, 2021 |
DECISION
ISSUANCE OF GUIDELINES ON TAKING CARE OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
MINISTER OF HEALTH
Pursuant to Law on prevention and control of infectious diseases dated 2007;
Pursuant to the Law on Medical Examination and Treatment in 2009;
Pursuant to Decree No. 75/2017/ND-CP dated June 20, 2017 of the Government on functions, tasks, powers, and organizational structure of the Ministry of Health;
At request of Director of Vietnam Administration of Medical Services and Ministry of Health,
HEREBY DECIDES:
Article 1. The “Guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID-19 at home” are attached hereto, including:
1. Guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID-19 at home.
2. Guidelines on diet for persons infected with COVID-19 at home.
Article 2. The “Guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID-19 at home” are applied in facilities assigned to oversee persons infected with COVID-19 at home to provide instructions for persons infected with COVID-19 and caretakers thereof.
Article 3. Health Departments of provinces and central-affiliated cities and medical authorities are assigned to implement Guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID-19 at home in medical facilities assigned to oversee persons infected with COVID-19 at home. The Guidelines on taking care of persons infected with COVID-19 at home shall be applied on effective date of Decision No. 4038/QD-BYT dated August 21, 2021 of Minister of Health on “Provisional guidelines on overseeing persons infected with COVID-19 at home”.
Article 4. This Decision comes into effect from the day of signing.
Article 5. Chief of Ministry Office, Chief of Ministry Inspectorate, Directors of Departments affiliated to Ministry Inspectorate; Chairpersons of Steering Committees for COVID-19 epidemic management of provinces and cities; directors of hospitals and institutes affiliated to Ministry Inspectorate; directors of Departments of Health of provinces and central-affiliated cities and provinces; heads of medical sector are responsible for implementation of this Decision. /.
|
|
PP. MINISTER |
LIST OF EDITORS
GUIDELINES
ON TAKING CARE OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
(Attached to Decision No. 4156/QD-BYT dated August 28, 2021)
|
Compilation director |
|
|
Assoc. Prof. PhD Nguyen Truong Son |
Deputy Minister of Health |
|
Chief editor |
|
|
Assoc. Prof. PhD Luong Ngoc Khue |
Director of Vietnam Administration of Medical Services - Ministry of Health |
|
Participants in compilation and appraisal |
|
|
PhD. Vuong Anh Duong |
Vice Director of Vietnam Administration of Medical Services - Ministry of Health |
|
MD. Ha Thi Kim Phuong |
Director of Department of Nursing - Nutrition - Infection control, Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health |
|
MD. Nguyen Thi Thanh Lich |
Vice Director of Department of Intensive Care and Assessment, Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health |
|
MD. Lu Mong Thuy Linh |
Chief nurse of Department of Health of Ho Chi Minh City |
|
PhD. Tran Thuy Khanh Linh |
Vice of Department of Nursing – Medical Technique, University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City |
|
MD. Tran Van Oanh |
Head of Nursing Department, Vietnam German Friendship Hospital |
|
MD. Bui Thi Thuy |
Head of Nursing Department, National Children’s Hospital |
|
Specialist level I Nurse. Phan Canh Chuong |
Head of Nursing Department, Hue Central Hospital |
|
MD. Nguyen Thi Oanh |
Head of Nursing Department, Cho Ray Hospital |
|
MD. Nguyen Thi Hong Minh |
Head of Nursing Department, University Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City |
|
MD. Nguyen Thi Bich Nga |
Head of Nursing Department, National Lung Hospital |
|
MD. Bui Thi Hong Ngoc |
Head of Nursing Department, Hospital for Tropical for Diseases of Ho Chi Minh City |
|
Editor secretaries |
|
|
PhD. Tran Ninh |
Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health |
|
MD. Doan Quynh Anh |
Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health |
|
MD. Nguyen Hong Nhung |
Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health |
GUIDELINES
TAKING CARE OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
TABLE OF CONTENTS
REGARDING COVID-19 EPIDEMIC
GOALS IN TAKING CARE OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
ELIGIBILITY OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 FOR QUARANTINE AND SUPERVISION AT HOME
1. LEVEL OF INFECTION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19
2. PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 CAPABLE OF TAKING CARE OF THEMSELVES
NECESSARY ACTIVITIES
SELF-MONITORING OF INFECTED PERSONS’ HEALTH AT HOME
HEALTH MONITORING:
USE OF THERMOMETER
RESPONSES FOR CERTAIN SYMPTOMS
MENTAL STRESS AND RESPONSES THERETO
PHYSICAL TRAINING AND EXERCISES
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PERSONS WITH DISABILITIES INFECTED WITH COVID-19
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE ELDERLY INFECTED WITH COVID-19
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PERSONS WITH MENTAL ILLNESSES INFECTED WITH COVID-19
TAKING CARE OF CHILDREN INFECTED WITH COVID-19
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PERSONS WITH UNDERLYING MEDICAL CONDITIONS AND PREGNANT WOMEN INFECTED WITH COVID-19
PREVENTION OF COVID-19 INFFECTION IN FAMILY
GENERAL RECOMMENDATIONS
SPECIFIC ACTIONS
UNDERLYING MEDICAL CONDITIONS TO BE MONITORED AND TREATED AT HOSPITALS UPON INFECTED WITH COVID-19
HEALTH MONITOR CHECKLIST FOR INFECTED PERSONS AT HOME
PHYSICAL EXERCISES
|
REGARDING COVID-19 EPIDEMIC |
|
• COVID-19 is an acute pneumonia caused by a variant of Corona virus (called SARS-CoV-2) After 2 years since its first appearance, the epidemic has infected nearly 215 million people and killed nearly 4.5 million people worldwide and keeps on increasing. • COVID-19 can spread from human to human or from animals to humans via: |
|
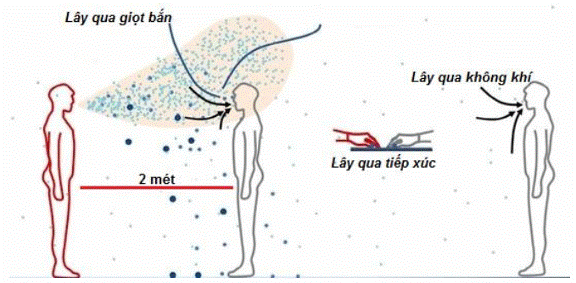
- Physical contact:
+ Direct physical contact with infected persons such as: handshake, hugging, kissing.
+ Indirect physical contact: touching surfaces containing viruses and touching one’s mouth, eyes, or nose.
- Droplets: when staying close (under 2 meters) to infected persons who speak, cough, or sneeze which create droplets containing virus and sticking to eyes, nose, or mouth, or inhaling these droplets.
- Air: In closed space with poor ventilation or when performing medical care which creates aerosol droplets containing virus spreading through the air and potentially causing infection if inhaled.
|
|
|
|
• Persons infected with COVID-19 may experience complications, life-threatening situations, and decease. The danger lies in cases where no symptom is exhibited or only mild symptoms are exhibited and cases where infected persons are naturally relieved of the infection.
• Persons infected with COVID-19 who exhibit no symptom or mild symptoms, have no underlying medical conditions, and satisfy all health and quarantine requirements may be placed under supervision and quarantine at home.
|
GOALS IN TAKING CARE OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME |
• Closely monitor and promptly detect symptoms of worsening medical condition in order to request medical assistance or transfer infected persons to hospitals in a timely manner.
• Improve physique, nutrition, and mental condition of infected persons to improve resistance against the infection.
• Ensure safe care and prevent infection to members in the family and community.
|
ELIGIBILITY OF PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 FOR QUARANTINE AND SUPERVISION AT HOME |
Persons infected with COVID-19 shall be placed under quarantine and supervision at home by the authority when they satisfy all following eligibility:
|
|

• Display no symptoms or mild symptoms (no dyspnea: SpO2 ≥ 96%, breathing rate ≤ 20 times/minutes).
• Age: More than 12 months of age and under 50 years of age.
• Accompanying medical conditions and physical conditions: no underlying medical conditions (List of underlying medical condition can be seen in Page 20).
• Not currently pregnant.
|

• Capable of taking care of themselves such as eating, cleaning clothes, performing personal hygiene, etc.
• Capable of measuring body temperature.
• Capable of contacting medical personnel to be supervised and monitored. In case of emergency, use available communication devices such as phones, computer, etc.
• Capable of using medicine as per prescription of doctors and/or physicians.
• If persons infected with COVID-19 are incapable of taking care of themselves, health family members who know how to take care of infected individuals and are capable of preventing infection must assist infected persons in satisfying eligibility under this section. However, number of caretakers must be limited.
|

|
|
As soon as receiving notice on quarantining infected persons at home, family members must prepare the followings: |
• Keep phone numbers of epidemic management hotline, individuals assigned to monitor health of infected persons, and other necessary phone numbers.
• Identify and agree with the whole family on spaces reserved specifically for infected persons.
• Assign the most appropriate individual to take care of infected persons (if any).
• Prepare necessary items:
- Disposable medical face masks (sufficient for family use in 2-3 weeks);
- Clean medical gloves (at least sufficient for caretakers in 2-3 weeks);
- Thermometer: mercury thermometer or electronic thermometer, blood pressure meters;
- Containers for infectious waste with cover and lined with yellow nylon bags on the inside;
- Personal belongings of infected persons: toothbrush, towel, handkerchief, washing buckets, cutlery, soap, washing machine (if any), personal clothe drying equipment;
- Medicine currently taken by infected individuals with underlying medical conditions such as: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, gout, etc. in sufficient amount for use in at least 30 days;
- Medicine and prescriptions of doctors and/or physicians for infected persons (if any).
NOTE:
• When a member of your household is infected with COVID-19, you and other members of the household are potentially infected and thus must perform quarantine at home to avoid spreading infection in the community.
• Do not worry about stocking up food and other supplies. The local government, relatives, forces, and organizations shall assist the family during period of quarantine at home.
|
SELF-MONITORING OF INFECTED PERSONS’ HEALTH AT HOME |
|
|
• Fill in Health monitor checklist twice per day in the morning and in the evening. Health monitor checklist can be seen in page 21.
• Signs to be monitored on a daily basis:
- Breathing rate, pulse, temperature, oxygen saturation level in blood - SpO2 (if possible) and blood pressure (if possible).
- Symptoms: Fatigue, coughing, coughing with sputum, shivering, conjunctivitis, loss of sense of taste or smell, diarrhea; Coughing blood, panting or having difficulty breathing, prolonged chest pain, not alert;
- Other symptoms namely: Sore throat, headache, vertigo, anorexia, nauseating and vomiting, muscle pain, etc.
• Symptoms that must be reported to medical personnel:
If patients displaying ANY of the following symptoms, immediately report to medical personnel in charge for solutions and timely hospitalization:
1) Dyspnea, shortness of breath or irregular breathing in children: grunting, nose flaring, wheezing, retractions.
2) Rising breathing rate:
- Adult: breathing rate ≥ 21 times/minute
- Children from 1 years of age to under 5 years of age: breathing rate ≥ 40 times/minute,
- Children from 5 years of age to under 12 years of age: breathing rate ≥ 30 times/minute
(Note when counting breathing rate of children: count all breaths taken in 1 minute when the children lie still without crying).
3) SpO2 ≤ 95% (if measurable). Upon detecting any irregularity, measure the second time after 30 seconds to 1 minute, when doing so, maintain measuring positions. Remove nail polish (if possible) before measuring.
4) Rapid pulse > 120 beats/minute or under 50 beats/minute.
5) Hypotension: maximum blood pressure < 90 mmHg, minimum blood pressure < 60 mmHg (if measurable).
6) Regular chest tightness and increasing when taking deep breaths.
7) Change of consciousness: Confusion, drowsy, tired, children crying, lethargy, convulsions.
8) Discolored lips, discolored extremities, discolored skin, pale lips, cold extremities.
9) Unable to drink. Children breastfeeding poorly, eating poorly, vomiting.
10) Children exhibiting: High fever, redness in the eyes, lips, tongue, swollen extremities with erythema, petechial, etc.
11) Any conditions that you feel nervous about.
|
|
• Prepare 2 thermometers: One for infected individuals and the other for the remaining individuals.
• Always measure body temperature of infected persons at least twice per day in the morning and in the evening and in case of irregularities, and record in health monitor checklist.
Activities to be done:
• Follow attached instructions when using electronic thermometer.
• Wash hands and sanitize thermometer with alcohol-soaked cotton before and after each use.
• Contact medical personnel in charge in any family member is having fever (above 38 oC) or hypothermia (under 36 oC).
Thermometer use instructions:
1. Wash hands carefully with soap and water in at least 20 seconds and wipe dry.
2. Sanitize thermometer with cotton soaked in 70o alcohol before and after each use.
3. For mercury thermometer, shake the thermometer down a few times to drop mercury level down below 36.5 oC before measuring.
4. Follow attached instructions to reach temperature. For mercury thermometer, when having difficulty reading temperature, tilt the thermometer to read the temperature.
5. Wash hands and sanitize thermometer. Store thermometer in safe locations.
|
|
In case of simple symptoms, proceed as follows:
1. In case of fever:
• For adults: > 38.5 oC or having headache, body ache: Take a tablet of antipyretic such as paracetamol 0.5 g each time and another every 4-6 hours with no more than 4 tablets per day, take oresol in case of poor hydration.
• For children: > 38.5 oC, take antipyretic such as paracetamol with 10-15 mg/kg/time, may take another within 4-6 hours with no more than 4 times per day.
• If an individual’s fever does not relieve after taking antipyretic twice, immediately inform medical personnel in charge.
2. In case of coughing: take cough medicine as per prescription of doctors and/or physicians.
3. May use vitamin as per prescription of doctors and/or physicians.
|
|

• When a family member is infected with COVID-19, other members may feel nervous, anxious.
• A person infected with COVID-19 may face nervous situations such as:
- Fear and worry for their health and other member’s health.
- Change to sleeping habit, have difficulty breathing, or difficulty concentrating.
- Eat poorly, not regularly.
- Severe chronic illnesses such as stomach illnesses, cardiac illnesses, etc.
- Mental illnesses that can worsen.
- Consume alcoholic drinks, smoke cigarettes, or use other medicine more frequently.
Responses to mental stress
• Avoid reading, watching, or listening to news on COVID-19 on social media such as: Zalo, Facebook, Youtube, Tiktok, etc.
• Take care of physical and mental health:
- Take deep breaths or practice meditation.
- Eat healthy and balance nutrition.
- Exercise regularly and do not stay up late.
- Refrain from using alcoholic drinks, cigarette, and food and drink containing stimulants.
• Spend time resting and relaxing. Do hobbies such as: reading books, drawing, watching movies, listening to music, working on models, cooking (if possible), etc.
• Contact medical personnel in charge if mental stress affects daily activities in multiple days consecutively.
• Communicate with other people. Talk about worries.
• Connect with community organizations, religious organizations, or social forums.
• Admit that being worried is fine and asking for help is nothing to be ashamed of.
|
|
Persons infected with COVID-19 must perform breathing exercises and daily physical exercises with positive mental health in addition to taking care and appropriate nutrition. Practice and exercises during this period help:
• Expand chest and improve airflow in the lungs and practice breathing better.
• Expel sputum for cases of increased sputum production.
• Increase effectiveness of motor capacity and respiratory muscles.
• Prevent loss of physical health and improve mental health.
Some breathing and motor exercises include:
• Breathing exercises.
• Exercise on bed
• Muscle stretching exercises
• Endurance exercises
Detail instruction for exercises are in page 22 through page 25.
• In case of exhibiting any irregularity: fatigue, dyspnea or increased chest pain during exercise, cease exercises and monitor body conditions. If these symptoms increase even when resting, immediate inform medical personnel for timely supervision.
|
|

• For persons with disabilities and infected with COVID-19, in addition to taking care in similar manner to other people, provide special care for people having difficulty in performing daily activities, etc.
• Be confident and believe in yourself, we will overcome the epidemic when armed with knowledge on COVID-19 epidemic management and medical quarantine, treatment at home.
• Some persons with severe disabilities require caretakers.
• Persons with disabilities face risks of a more severe COVID-19 infection and thus caretakers thereof must prepare scenarios where contacting medical personnel is required; closely monitor signs of infected persons and transfer to emergency medical aid in local COVID-19 treatment facilities when seeing emergency signs.
• Combine with rehabilitation, mental, and physical exercises to make up for restriction on outside activities, and anxiety, depression, disappointment.
• Regularly sanitize aids of persons with disabilities before and after use.
• Provide information on COVID-19 epidemic management and medical quarantine suitable for persons with disabilities issued by Ministry of Health on YouTube and website http://kcb.vn
|
|

• The elderly face a risk of COVID-19 infection more severe than any other age groups. The older a person gets, the more severe of COVID-19 infection he/she potentially gets.
• The elderly and caretakers thereof must be aware and monitor to prevent any complication and hospitalize when the elderly exhibit any emergency sign.
• Follow healthy and scientific lifestyle.
• Have a nutritious, balance, healthy diet (1,700 – 1,900 Kcal/day) with lots of vegetables. Guarantee 3 – 4 meals per day, when not having sufficient meals, take 1 – 2 cups of supplementary milk per day.
• Strictly comply with diet and medicine available as per recommendations of doctors and/or physicians.
• Increase exercises in quarantine rooms or on bed on a case-by-case basis with rehabilitation exercises, massages, and support to improve health.
Detail instruction for exercises are in page 22 through page 25.
|
|

If persons with mental illness infected with COVID-19 are taken care of at home, in addition to care recommendations above, persons with mental illnesses and caretakers thereof must:
• Prepare every items necessary for quarantine, especially medicine for mental illnesses for 1 - 3 months.
• Do not deliberately cease or drop medicine. If re-examination appointment is delayed due to epidemic, perform remote consultation with medical personnel as per appointment.
• Perform simply physical and rehabilitation exercises on a daily basis.
• Maintain hobbies and daily activities as much as possible or create new hobbies in new environment such as: exercises, proper hygiene, etc.
• Increase connection with relatives (via phones, e-mail, social communication devices, or video calls).
• For patients addicted to opioids and receiving replacement treatment with methadone or buprenorphine, inform treatment facilities for appropriate medicine provision plans.
• Caretakers and family members must monitor and detect any emergency such as: seizure, suicidal thoughts or behavior, refusing to eat or drink, drug withdrawal or poisoning. Contact medical personnel to receive instruction on assisting and performing emergency medical procedures.
|
|
• Parents must remain calm when their children are infected with COVID-19 and believe in their caring capacity.
• Pay attention to whether the children change behavior, especially:
- Crying or being grumpy (in children).
- Overly worrying or depressing.
- Possessing unhealthy eating or sleeping habit.
- Being grumpy and "acting inappropriately" (in teenagers).
- Having poor learning results or avoiding online classes.
- Having difficulty paying attention and concentrating.
- Ceasing to participate in activities that the children used to enjoy.
- Having headache or body ache for unknown reason.
- Drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes, or using other drugs (in children).
Activities to support and care for children infected with COVID-19:
• Talking and calming the children down about COVID-19.
• Answer questions and share factual information on COVID-19 epidemic to prevent the children from misunderstanding and becoming panic.
• Restrict making family contact and talking about COVID-19 news and evens to prevent confusion and panic.
• Maintain regular hobbies and scientific routine. Prepare timetable for studying, resting, and recreational activities.
• Instruct children to perform daily routine to reduce infection such as: washing hands regularly; using tissues or elbow to cover the mouth when coughing or sneezing then removing the tissues in waste containers.
• Allow children to participate in appropriate recreational activities in quarantine rooms such as online games or playing with parents, etc.
|
|

All persons infected with COVID-19 and having underlying medical conditions, pregnant, overweight, persons above 50 years of age, and children under 12 months of age must receive treatment at hospitals.
While waiting for transfer to hospitals:
• Must receive care and undergo infection prevention in a manner similar to other infected persons.
• Closely monitor to detect all irregularities.
• Contact medical personnel in charge to monitor family’s health or contact local authority, or reach the hotline upon exhibiting or seeing any irregularity.
• Carry available medicine to hospitals to use and inform admitting doctors about underlying their medical conditions and medicine.
• Family must motivate and console infected persons.
|
PREVENTION OF COVID-19 INFFECTION IN FAMILY |
|
|
In order to prevent infection for family members and community members, members of a family must comply with the followings:
• Isolate infected persons from other people
• Clean hands on a regular basis
• Wear face masks and gloves appropriately
• Clean cutlery to prevent infection
• Clean all surfaces thoroughly
• Process fabric items and other items appropriately
• Manage wastes and expelled fluid appropriately
|
SPECIFIC ACTIONS |
1. Isolate infected persons from other people
• Assign infected persons with separate bedrooms and bathrooms, or mark separate spaces for infected persons
|
• Maintain distance of at least 2 meters from infected persons • Infected persons MUST NOT - Eat with other people. - Move out of quarantined areas - Make close contact with other people and domestic animals |
|
• Do not share cutlery, glasses, dishes, towels, or bed sheets with other people in the family.
2. Ensure well-ventilated houses
• Keep windows open and doorways (if possible) to keep the air being refreshed.
• Do not share central air-conditioning unit with other rooms.
• Do not allow airflow to go from rooms of infected individuals to common spaces.
• Use fans and air purifiers.
3. Wash hands on a regular basis
|
• Washing hands is the best method for reducing COVID-19 infection • Wash hands with soap under running water for at least 30 second or hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol in at least 15 seconds Time of washing hands: • Before and after cooking • Before and after eating |
|
• After coughing, sneezing, blowing nose.
• After touching items and surfaces.
• After using the restroom.
• After collecting wastes.
Steps of washing hands with soap:
1. Wet hands under running tap (warm or cold water), turn off the tap.
2. Rub soap onto both hands and scrub both hands. Rub soap onto the back of the palm, in between fingers, and under the nails.
3. Scrub both hands for at least 30 seconds.
4. Rinse both hands under running tap carefully.
5. Wipe dry with clean towel or let dry naturally.

Wash hands with hand sanitizer containing alcohol:
1. Extract a small amount of hand sanitizer onto the palm.
2. Rubbing both hands and scrubbing all fingers, palms, back of the palms, and gaps between fingers until the sanitizer dries: about 30 seconds.
3. Let dry naturally, hands must be completely dry before touching other items.
Note when washing hands with hand sanitizer:
• Leave hand sanitizer containing alcohol outside of reach of children. Instruct children on how to use hand sanitizer.
• Do not touch eyes, mouth, or nose after using hand sanitizer to prevent allergic reactions.
• Do not use hand sanitizer before cooking with open flame or dealing with fire since the alcohol component is combustible.
• Do not store hand sanitizer in areas with high temperature.
|
4. Wear face masks appropriately Who needs to wear face masks? • Infected persons • Persons taking care of infected persons • All family members |
|
Who ARE NOT required to wear face masks?
• Children under 2 years of age
• Persons having difficulty breathing, persons incapable of removing face masks without assistance.
When to wear face masks?
• Caretakers: Caretakers must wear face masks when staying in the same room or space with infected persons and other people.
• Infected persons: Infected persons must wear face masks as frequent as possible, even when quarantined to reduce risk of infecting other people.
• Family members: Other family members must wear face masks when sharing the same room or space with other people.
Methods of selecting face masks
• Disposable medical face masks are highly recommended.
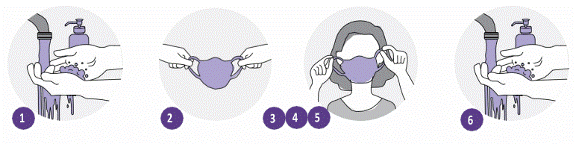
Methods of wearing face masks:
1. Wash hands with soap or sanitizer thoroughly in 30 seconds
2. Pick up face masks by gripping one side with one hand
3. Raise facemasks to the face The front of the face masks (in darker color) points outward, the side lined with metal nose clip must be positioned upwards.
4. Hold the face masks fixed on the face with one hand and use the other hand to wrap the strap over one ear and do the opposite for the other side.
5. Adjust face masks:
- Use 2 index fingers to adjust the metal nose clip to closely wrap the nose bridge and face.
- Pinch the lower edges of the face masks with both index fingers and both thumbs and pull downwards slightly and inwards to allow the face masks to closely hug the face under the chin.
Remove face masks:
1. Clean hands
2. Hold the face mask straps with both hands from behind the ears, remove them from the ears, while still gripping on the straps, take the masks off the face, and place in waste containers.
Note: Only touch the straps when removing the face masks. Do not touch the front of the face masks.
3. Clean hands again.
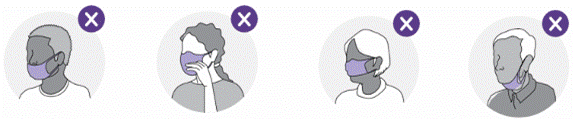
Do not wear face masks as shown below:
• Nose is exposed
• Chin is exposed
• Face mask is fully lowered below the chin
• Touch the outside of the face masks while wearing.
|
5. Perform respiratory hygiene • Always wear face masks. • Do not spit in common spaces. • Cover mouth and nose with tissues with coughing and sneezing. • Remove used tissues in closed garbage bins. • Wash hands with water and soap after coughing and sneezing. |
|
|
6. Clean cutlery to prevent infection • When preparing separate cutlery for persons infected with COVID-19, single-use cutlery is recommended. • Leftover food and single-use cutlery must be placed in garbage containers in rooms of persons infected with COVID-19. • Wash dishes with hot water and soap. |
|
• Persons infected with COVID-19 must wash their dishes in their rooms. If caretakers are required, caretakers shall wear gloves when gathering food and washing dishes.
• Dishes and cutlery of infected persons must be placed in separate locations after washing. Placing in rooms of infected persons in highly recommended.
7. Process fabric items safely
|
• Allowing infected persons to wash their clothes is highly recommended. • If caretakers are required to wash, wear clothes when processing fabric items of infected persons. • Clean or sterilize wash baskets and clothes baskets. • Wash with washing machines or manually with the warmest water possible. • Dry or hang until completely dry. |
|
• Remove gloves and wash hands after processing fabric items of infected persons.
• Clothing items of infected persons must be washed separately from those of other people.
• Do not shake dirty clothing items to limit risks of dispersing the virus.
|
8. Clean all surfaces thoroughly • Allowing infected persons to clean their areas is highly recommended. • Clean floor, wall, and surfaces then wipe with sanitizing liquid. Wipe again with clean water. • If caretakers are required, caretakers must wear gloves before cleaning. |
|
• Use separate cleaning equipment for areas of infected persons.
• May wrap electronic appliances with nylon sheet and clean the outside surface.
• Remove gloves and wash hands after cleaning.
• Clean surfaces at least once per day.
Methods of mixing sanitizing liquid:
• Chloramine B 25% powder: 5 teaspoons + 1 liter of water, or
• 5% Javel water: mix 10 times the Javel water amount instructed on the label in the same water amount or
• 1:10 mix of bleach and water: 5 tablespoons or 1/3 cups + 250 ml of water
NOTE:
• Mixed solution is only effective for use in 24 hours.
• DO NOT mix chemicals or cleaning solutions with each other.
• DO NOT leave under direct sunlight.
• DO NOT leave cleaning products or sanitizing products directly on the skin.
• DO NOT use cleaning products or sanitizing products for food.
|
9. Collect and process waste appropriately • Place garbage containers with cover and foot pedal for opening, lined with nylon bag on the inside in rooms of infected persons. • Collect and process waste on daily basis or when the containers are full. • Wear gloves when processing waste and remove gloves after processing. • Wash hands immediately after processing wastes. |
|
|
10. Use gloves • Caretakers must use gloves when sanitizing surfaces and indoor items, and when taking care of infected persons. • Wearing gloves is not an alternative to other preventive measures such as: distancing, washing hands, and wearing face masks. • Do not reuse gloves. Each pair of gloves are for single use only. |
|
• Do not touch any surface while wearing gloves.
Methods of removing gloves
1. While both hands are wearing gloves, grip the outer part of the gloves near the wrist without touching the bare skin.
2. Pulling the gloves inside out to remove them.
3. Hold removed gloves with the other gloved hand.
4. Line the hand without glove under the glove of the gloved hand.
5. Remove the other glove and turn the glove inside out when removing so that both gloves are turned inside out and one contains the other.
6. Dispose gloves in a safely manner – do not reuse.
7. Wash hands with soap and water
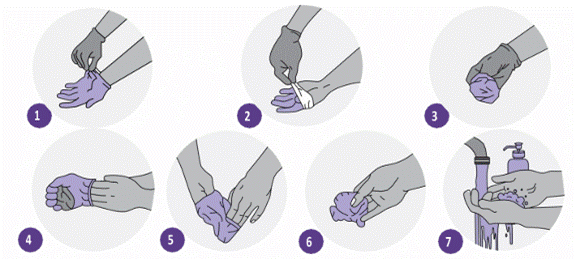
11. For families with domestic animals
|
• infected persons must not make physical contact with domestic animals due to evidence of COVID-19 virus infection in animals. • People living in the same house with persons not infected with COVID-19 must not make close physical contact with domestic animals. • Do not allow domestic animals to make contact with humans and other animals outside of the family. |
|
12. Prevent infection when purchasing food, groceries, and other essentials
|
• Order online with delivery services that deliver to door, gate, or assigned persons. • Upon receiving commodities, do not make physical contact, if physical contact is required, request delivery persons to leave commodities outside of the house and maintain a distance of at least 2 meters with the delivery persons. • Wash hands after receiving and opening commodities. • Open the commodities safely at home. DO NOT spray disinfectant for surface and clothing disinfection on food even just the exterior. |
|
|
UNDERLYING MEDICAL CONDITIONS TO BE MONITORED AND TREATED AT HOSPITALS UPON INFECTED WITH COVID-19 |
|
Persons with the following underlying medical conditions upon being infected with COVID-19 must be monitored and treated at hospitals:
1. Diabetes mellitus.
2. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and other pulmonary diseases.
3. Cancer.
4. Chronic kidney illnesses
5. Organ transplant or stem cell transplant.
6. Overweight.
7. Cardiovascular diseases (heart failure, coronary artery disease, or heart muscle disease).
8. Cerebrovascular conditions.
9. Down syndrome.
10. HIV/AIDS.
11. Neurological conditions (including dementia).
12. Sickle cell trait, thalassemia, other chronic blood disorders.
13. Bronchial asthma.
14. Hypertension.
15. Immunodeficiency.
16. Liver diseases.
17. Substance use disorder.
18. Under treatment with corticoid or other immunosuppressant drugs.
19. Systemic illnesses.
20. Other conditions in children: Primary or secondary pulmonary hypertension, congenital cardiac diseases, congenital metabolic disorders, congenital or acquired endocrine disorders.
|
|
INFORM MEDICAL PERSONNEL IF YOU OR PERSONS YOU KNOW ARE INFECTED WITH COVID-19 WHILE HAVING UNDERLYING MEDICAL CONDITIONS OR PREGNANT. |
|
HEALTH MONITOR CHECKLIST FOR INFECTED PERSONS AT HOME |
Full name: ________________ Date of birth: __/__/___ Gender: □ Male. □ Female Phone: ____________
Full name of caretakers: ____________________ Date of birth: __/__/____ Phone: __________________
|
No. |
↓ Entry |
Date of monitor → |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
8 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
S |
C |
|
|
|
Contact medical personnel if: SpO2 ≤95 %, breathing rate ≥ 21 times/minute, pulse <50 or >120 times/minute, or blood pressure < 90/60 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. |
Pulse (times/minute) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
Daily temperature(oC) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
Breathing rate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
SpO2 (%) (if measurable) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
Highest blood pressure (mmHg) (if measurable) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lowest blood pressure (mmHg) (if measurable) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
NO SYMPTOMS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pay attention to your health. If you exhibit any symptom, write (C) or (K) for NO below for each symptom on a daily basis. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
7. |
Fatigue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
Coughing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
Coughing and sputum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10. |
Shivering |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. |
Conjunctivitis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12. |
Loss of sense of taste or sense of smell |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. |
Diarrhea |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Immediately contact medical personnel upon exhibiting any of the following symptoms |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
14. |
Coughing blood |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
Panting or dyspnea |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
Prolonged chest tightness or pain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16. |
Drowsy, not alert |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other symptoms: Sore throat, headache, vertigo, anorexia, nauseating and vomiting, muscle pain, etc. should be added to the “Note” section
Note: ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………………
|
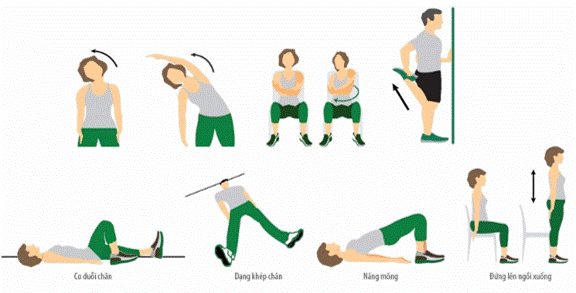
PHYSICAL EXERCISES |
1. Breathing exercises:
- Improve dyspnea condition
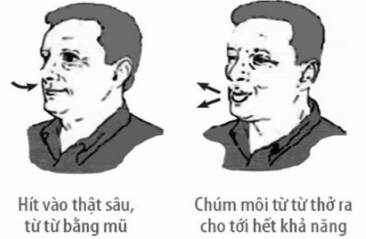
- Some breathing exercises such as: pursed lips breathing, diaphragmatic breathing, belly breathing. If infected persons expel a lot of sputum, practice active breathing cycle technique and coughing techniques.
• Pursed lip breathing
|
|
• Diaphragmatic breathing:
|
|
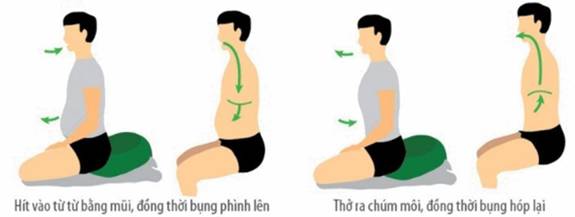
• Belly breathing
- Place one hand on the chest and the other hand on the belly (to feel movement of the chest and the belly)
- Inhaling via the nose (pursed lips) and expand the belly (the hand on the belly rises)
- Exhaling via the mouth slowly with pursed lips (in a manner similar to whistling) and flatten the belly (the hand on the belly declines)
|
- Inhale on the count of 1-2, exhale on the count of 1-2-3-4 (exhaling in twice the time it takes to inhale) |
|
• NOTE:
- When inhaling and exhaling, great effort is not required.
- Combine pursed lip breathing with belling or diaphragmatic breathing with hands in a single breath and practice regularly (at least three times per day, with 5-10 minutes per time)
- These two motions can be performed even when sitting or lying (when lying, place pillow under head and under the knees)
• Effective coughing techniques
- Pursed lip breathing: in 5-10 minutes to move sputum from small bronchus to larger bronchus
- Exhaling through the mouth: 5-10 times with increasing speed to remove sputum from the trachea
- Coughing: take a deep breath, hold your breath, and cough 1-2 times. Cough lightly the first time and intensively to expel all the sputum.
|
• Active breathing cycle technique - Breathe under control: breathe gently for 20-30 seconds - Expand the diaphragm: inhale deeply with the nose, hold your breath for 2-3 seconds, and exhale gently, repeat 3-5 times. - Exhale: take a deep breath, hold your breath for 2-3 seconds, and exhale intensively to expel the air. Repeat 1-2 times. |
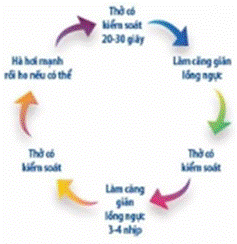
|
2. Resting position.
if SpO2 result is under 94% or the patients feel fatigue or dyspnea, infected persons may adopt a proning position with elevated head. Continue to monitor SpO2 after changing the position.
• Proning position
Keep your head lower than your body and turned to one side for easy breathing
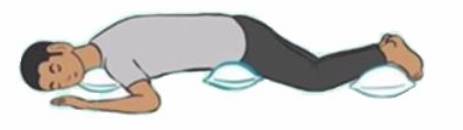
|
Wedge towel/pillow under the neck for comfort |
Wedge towel/pillow under the hip to avoid back pain. Refrain from wedging under the belly which will restrict breathing |
Wedge towel/pillow under the legs for comfort |
Maintain proning position for 1-2 hours every 4 hours for up to 14 hours per day.
|
• Lying with elevated head |
Lying on one side |
|
|

• NOTE:
- In case of exhibiting any irregularity: fatigue, dyspnea or increased chest pain during exercise, cease exercises and monitor body conditions. If these symptoms increase even when resting, immediate inform medical personnel for timely supervision.
3. Physical exercise on bed
Persons infected with COVID-19 from mild to moderate level are recommended to rest on bed and adopt suitable physical exercises.
Exercise to support digestion, improve blood circulation, and help relax.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
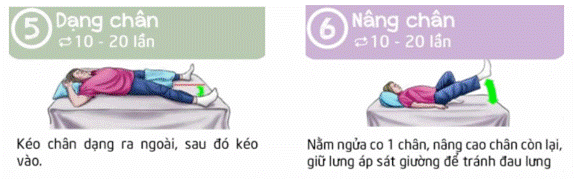
4. Exercises for improving physique and endurance
|
|
|
|
GUIDELINES
DIET FOR
PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
(Attached to Decision No. 4156/QD-BYT dated August 28, 20121 of Minister of Health)
Compilation director
Assoc. Prof. PhD Nguyen Truong Son, Deputy Minister of Health.
Chief editor
Assoc. Prof. PhD Luong Ngoc Khue, Director of Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health.
Participants in compilation and appraisal
1. PhD. Vuong Anh Duong Vice Director of Vietnam Administration of Medical Services - Ministry of Health.
2. PhD. Chu Thi Tuyet, Nutrition Department of Friendship Hospital.
3. PhD. Luu Ngan Tam, Head of Nutrition Department of Cho Ray Hospital.
4. PhD. Luu Thi My Thuc, Director of Clinical Nutrition Department of National Children’s Hospital.
5. Specialist level 2 Doctor Nguyen The Thanh, Vice Director of Nutrition Center of Bach Mai Hospital.
6. PhD. Nguyen Thanh Ha, Head of Nutrition Department, National Lung Hospital
7. PhD. Nguyen Thi Thuy Linh, Vice Director of Nutrition Department, Hanoi Medical University Hospital.
8. MD. Ha Thi Kim Phuong, Director of Department of Nursing - Nutrition - Infection Control, Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health.
9. MD. Ha Thanh Son, Official of Department of Nursing - Nutrition - Infection control, Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health.
10. MD. Nguyen Hong Nhung, Official of Department of Nursing - Nutrition - Infection Control, Vietnam Administration of Medical Services, Ministry of Health.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General information
ROLE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES REGARDING NUTRITION IN TREATING COVID-19 AT HOME
Role of nutrition in treating COVID-19 patients at home
General principles regarding diet for F0
Food selection
DIET FOR PERSONS INFECTED WITH COVID-19 AT HOME
Diet principles for adults
Diet principles for children
Child nurture practice
ANNEX 1. REFERENCE MENU FOR ADULTS
ANNEX 2. REFERENCE MENU FOR CHILDREN
ANNEX 3. ILLUSTRATION FOR FOOD ESTIMATION
I. GENERAL INFORMATION
The COVID-19 epidemic is seriously threatening health of the general public and claiming lives of millions of people worldwide. COVID-19 is a Class-A acute communicable disease caused by a virus called SARS-CoV-2. COVID-19 patients usually develop unexpectedly and complicated. In early stages, the infection progresses slowly and silently without symptoms where multiple cases suddenly worsen, require oxygen breathing, mechanical breathing, or assisted ventilation, lead to multiple organ failure, and death especially in the elderly, persons with chronic diseases, immunodeficiency, co-infection, or opportunistic infection such as bacteria and fungus.
In order to restrict worsening, patients must be monitored on a regular basis and have a proper diet. Cases where COVID-19 patients exhibit no or mild symptoms and may receive treatment at home, compliance with a proper diet is truly necessary as nutrition helps support and improve body “barriers” such as immune cells, antibodies, skin, respiratory mucous membrane, and stomach mucous membrane to improve resistance.
Upon having infection, patients usually suffer a sudden loss in sense of smell or sense of taste which reduce palate and thus must be supplemented with a proper diet to avoid malnutrition.
All COVID-19 patients have increased nutrition demand due to increased energy consumption and may suffer from severe malnutrition if not properly fed. Malnutrition will increase the chance of opportunistic infection, worsen the condition, prolong the period of mechanical ventilation, and increase treatment costs.
Thus, providing sufficient nutrition for COVID-19 patients with mild infection and no symptoms is necessary to improve physique, boost resistance, and limit symptoms.
II. ROLE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES REGARDING NUTRITION IN TREATING COVID-19
1. Role of nutrition in treating COVID-19 patients with mild infection and no symptoms
- Malnutrition negatively affects functions of immune system and reduce effectiveness of immune system. Malnutrition affects severity of the infection, recovery time, complication rate, and mortality rate.
- A good diet with treatment solutions help prevent, assist, remediate infection, prevent COVID-19 epidemic, and save up costs and resources for healthcare system, for the patients, and for patients’ family.
Purpose of diet solutions:
- Provide an adequate and proper diet to balance energy and micronutrients required by each group age, medical conditions, and tolerance.
- Prevent muscle atrophy and malnutrition.
- Maintain growth and development of children.
|
|
|
|
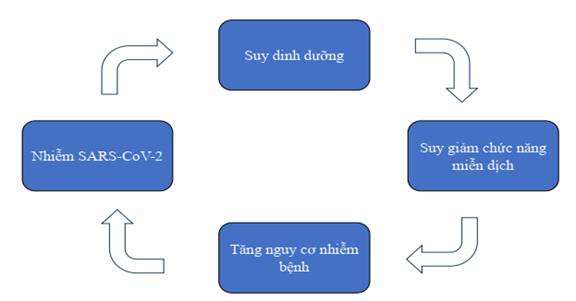
Illustration 1. Correlation between malnutrition, immunodeficiency, and susceptibility to SARS-COV-2 infection
2. General principles regarding diet for COVID-19 patients with mild infection and no symptoms
- Eat normally and balance nutrients with a variety of food (if possible) to maintain adequate physique and conditions.
- Add 1 to 2 additional meals such as milk or dairy products, especially when having reduced palate due to fever, coughing, fatigue, etc.
- Consume protein food (meat, fish, etc. beans and peas) to prevent muscle atrophy and boost resistance.
- Consume more fruit or juice, vegetables, and spices (such as garlic and ginger) to boost resistance.
- Stay sufficiently hydrated (about 2 liters/day) or more in case of fever, diarrhea.
2.1. Adequate and balance nutrition
- Ensure adequate and diverse food such as: starch, dairy, dairy preparations, fat, vegetables, meat, eggs, beans, yellow-dark green vegetables.
- Do not skip meal: Have all 3 main meals and additional meals.
- Do not have too much sweet food (recommended sugar is < 10% of total food).
- Do not refuse to eat certain food if not having allergic reaction or not advised against by doctors.
- People having a thin build and children must have more food rich with energy and protein such as milk and dairy products.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
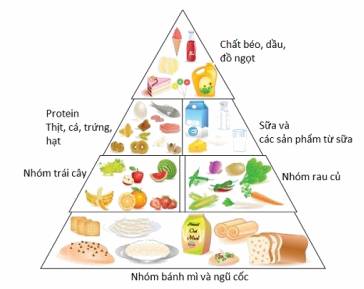
Illustration 2. Food pyramids
2.2. Safety eating
- Avoid food and drink with a lot of sugar, salt, alcohol, and beer.
- Food must be safe and hygienic. Do not use spoiled, rancid, or expired food.
- Maintain hygiene when processing food. Wash hands before and after processing food.
- Use necessary dietary supplements as per instruction of nutritionists.
3. Food selection
3.1. Recommended food
- Rice, wheat, corn, potato, etc.
- Beans: peanuts, sesame, etc.
- Milk and dairy products: powdered milk, fresh milk, yogurt, etc.
- Meat, fish, shrimp, etc.
- Eggs and egg products: chicken eggs, duck eggs, quail eggs, etc.
- Vegetable oil, olive oil, fish oil, etc.
- Vegetables.
- Fresh fruits.
3.2. Food for use in limited amount
- Animal fat, animal entrails.
- Salt-heavy food (canned food, pickles, etc.).
- Sparkling drinks, sweet confectioneries.
- Stimulants such as: alcohol, beer, coffee, cigarette.
3.3. Food rich with vitamin and minerals to boost physical conditions
|
Vitamin and minerals |
Role |
Demand/day |
Food (amount/100g of food) |
|
Vitamin A |
Maintain integrity of mucous membrane of respiratory and digestive tract, and create resistance on mucous membrane. |
Male: 650 mcg Female: 500 mcg |
Liver (6500 mcg), yolk (140 mcg). Vitamin A in form of Beta-Carotene such as: carrot (835 mcg), sweet potato (709 mcg), pumpkin (369 mcg), papaya (55 mcg), mango (38 mcg), broccoli (800 mcg), spinach (681 mcg), etc. (Note that common food in daily meals may provide sufficient amount of vitamin A) |
|
Vitamin C |
Boost resistance, limit development of pneumonia caused by virus, and improve respiratory function |
85 mg |
Fresh vegetables and fruits: Pomelo (95 mg), lemon (77 mg), kiwi (93 mg), guava (62 mg), strawberry (60 mg), papaya (54 mg), orange (40 mg), bell pepper (103-250 mg), etc. |
|
Vitamin D |
Boost immune system, digestive system, circulation system, and neurological system. |
15 mcg |
COVID-19 patients make contact with direct sunlight for 15-30 minutes per day (airy rooms with windows allowing sunlight) Include food rich with vitamin D such as carp, grass carp (24.7 mcg); eel (23.3 mcg); milk (7.8 – 8.3 mcg); egg yolk (2.68 mcg); and food reinforcing vitamin D (milk, cereal), etc. |
|
Vitamin E |
Promote growth of immune organs |
Male: 6.5 mg Female: 6.0 mg |
Products made from soy beans, bean sprout, etc. |
|
Selenium |
Strong antioxidant to boost anti-infection capacity |
Male: 34 mcg Female: 26 mcg |
Brown rice, fish, shrimp, seaweed, etc. |
|
Zinc |
Regulate immune system and regulate flammatory reactions |
Male: 10 mg Female: 8 mg |
Poultry meat, shelled animals and seafood: oyster (31 mg); mussels (13.4 mg); beef (4.05 mg); egg yolk (3.7 mg); powdered milk (3.34-4.08 mg); crabs (3.54 mg); etc. Peas: beans (3.8 – 4.0 mg); sesame seed (7.75 mg); etc. |
|
Omega 3 |
Boost immune system Act as anti-flammatory agent |
2 g |
Salmon, sardine, basa, halibut, herrings, tuna, oyster, fish liver oil, macadamia nut, walnuts, chia seed |
|
Flavonoid |
Act as antioxidant and boost resistance. |
|
Fragrant vegetable namely: basil, perilla frutescens, broccoli, apple, green tea, ginger, garlic, turmeric, green leafy vegetables. |
|
Probiotic |
Boost resistance |
|
Cheese, yogurt, etc. |
3.4. Equivalent substitute
Use equivalent substitute to diversify the meals
3.4.1. Protein: 100 g of lean pork is equivalent to
|
- 100 g of lean beef, skinless lean chicken meat - 120 g of lean fish, shrimp - 200 g of tofu - 150 g of paddy crab |
- 80 g of rib (boneless) - 200 g of snails and mussels - 400 g of mussels - 40 g of acetes |
- 2 duck eggs, 3 chicken eggs or 8 quail eggs - 65 g of pork belly |
3.4.2. Starch: 100 g of rice is equivalent to
- 400 g of fresh tuber (potato, sweet potato, taro)
- 100 g of dry rice noodle, noodle, fresh corn, wheat
- 170 g of bread
- 250 g of fresh rice noodle
- 200 g of fresh corn
3.4.3. Fat: 1 spoon of cooking oil (5 ml) is equivalent to 8 g of peanuts, 8 g of sesame.
3.4.4. Fruit: 200 g of papaya is equivalent to 200 g of pomelo, 200 g of guava, 160 g of kiwi, 400 ml of fresh orange, 200 g of mandarin, 150 g of pineapple, 200 g of mango, 130 g of persimmon; 300 g of wax apple, 200 g of soursop
3.4.5. Salt: 1 g of salt is equivalent to 1 yogurt spoon of salt; 1.5 spoon of soup powder; 5 ml of fish sauce; 7.5 ml of soy sauce.
III. DIET FOR COVID-19 PATIENTS WITH MILD INFECTION AND NO SYMPTOMS
1. Diet principles for adults
- Achieve 30-35 kcal of energy/kg of weight/day, protein accounts for 15-20% of total energy, fat accounts for 20-25% of total energy demand, starch accounts for 50-65% of total energy.
- Provide all vitamin and minerals according to group age. Use more food rich with vitamin A, C, D, and E; food rich with zinc and selenium. 300 g of vegetable per day, 200 g of fruit per day.
- 18-20 g of fiber/day.
- 5g of salt/day.
- Drink sufficient amount of water (40-45 ml/kg of weight/day), drinking warm water and drinking throughout the day are recommended, refrain from waiting until thirsty in order to drink, regular water and juice are recommended. Patients who have fever are recommended to take Orezol to supply water and electrolytes.
2. Diet principles for children
- On a periodic basis, monitor diet of children via weight and food intake.
- A balance diet consists of 4 major components: lipid (animal lipid and plant lipid), vitamin and minerals, energy components (protein, lipid, carbohydrate), and protein (animal protein and plant protein). Children must have at least one balance meal per day.
- On a daily basis, have at least 5 out of 8 food categories (starch, milk and dairy preparations, fat, vegetables, meat, egg, beans, yellow-dark green vegetables).
- Do not have too much sweet food (recommended sugar is < 5% of total food intake).
- Do not have too much salty food.
- Stay sufficiently hydrated, especially with juice, and avoid industrial soft drinks.
- Encourage children of 1-2 years of age to drink at least 600 ml of formula milk/day (for children who do not receive breastfeeding) and children > 2 years of age to drink at least 500 ml of formula milk/day to have sufficient nutrients and balance diet (multi micronutrients are not necessary). In case children fail to eat as per recommendations, use oral supplement with high energy density (1 Kcal/ml) to replace formula milk entirely or partly.
- Avoid using food that can cause vomiting or nausea by using flavors palatable to the children, digestible and highly nutritious food.
3. Child nurture practice
3.1. Monitor nutrition of children on a periodic basis to determine whether the children will suffer from acute severe malnutrition
- Monitor weight of children on a periodic basis with once 3-5 days if possible. If children lose 1-2% of weight/week, immediately inform medical personnel to be advised.
- Assess digestive tract on a daily basis via symptoms such as anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomachache which will greatly reduce amount of food intake and nutrient absorption.
- Monitor amount of food intake/day. If amount of food intake <70% of the regular demand in the group age, consult medical personnel.
3.2. Nutrition demand for children by age
Schedule 1. Hydration demand for children
|
Age |
Water demand, ml/kg |
|
Children from 11-20 kg |
1000 ml + 50 ml/kg for every kilogram after 10 kg |
|
Children from 21 kg |
1500 ml + 20 ml/kg for every kilogram after 20 kg |
|
Teenager |
40 ml/kg of weight |
Schedule 2. Daily vegetable and fruit demand for children
|
Age |
Demand |
|
Fruit |
|
|
12-24 months of age |
60 ml of crushed fruit |
|
2-3 years of age |
130 g |
|
> 4 years of age |
200 g |
|
Fruit juice (no sugar) |
|
|
2-3 years of age |
200 ml/day (1 cup) |
|
4-13 years of age |
355 ml/day (1.5 cup) |
|
14-18 years of age |
Girl: 1.5 cup Boy: 2 cups. |
|
Vegetables |
|
|
2-3 years of age |
130 g |
|
4-8 years of age |
200 g |
|
Girl of 9-13 years of age |
260 g |
|
Boy of 9-13 years of age |
320 g |
|
Girl of 14-18 years of age |
320 g |
|
Boy of 14-18 years of age |
400 g |
3.3. Diet for children in different group ages
Note: Conversion of “amount” and equivalent is for reference purposes only due to difference among food and containers such as bowl, dish, spoon, etc.
Children of 12-24 months of age: continue to breastfeed or use formula milk for the appropriate group age if breastfeeding is not available and feed 3 meals of concentrated porridge with each meal consisting of 250 ml + 60-100 ml of crushed fruit.
Formula of 250 ml of porridge (1.5 rice bowl)
(Energy: 240 Kcal P:L:G= 10.3g:8.7g:30g)
|
Food |
Amount |
Equivalent |
|
Rice |
35 g |
35 g of meat = 1 average chicken egg = 2/3 average duck egg = 4 average quail egg |
|
Vegetable (pumpkin, carrot, etc.) |
30 g |
|
|
Meat (pork, beef, shrimp, fish, etc.) |
35 g |
|
|
Cooking oil |
7 ml (1 small spoon) |
|
|
Fish sauce |
5 ml |
Note: If scale is not available, use regular spoon with scoop section of 4x6 cm in dimension to measure food

|
A spoon of powder: 5 g |
A spoon of vegetable: 10 g |
A spoon of meat: 10 g |
A spoon of cooking oil: 5 g |
ANNEX 1.
REFERENCE MENU FOR ADULTS
ANNEX 1.1. MENU FOR PEOPLE WEIGHING 45 – 50 kg
Energy: 1350 – 1450 kcal
|
Menu 1 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
Food |
Common measurement |
|
Breakfast |
Chicken rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
120 g of rice noodle |
2 small bowls of rice noodle |
|
|
30 g of chicken meat |
8-10 pieces, shredded |
|
|
4 ml of cooking oil |
|
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Milk and dairy preparations |
|
|
Yogurt/fresh milk |
1 box of 100 g/1 box of 180 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, beef stir-fried with onion, tofu sauteed with tomato, cooked vegetable, and seasonal vegetable soup |
|
|
120 g of rice (60 g of polished ordinary rice) |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
60 g of grounded beef and 25 g of onion |
9-11 medium pieces |
|
|
60 g of white tofu, 30 g of tomato |
2/3 of a small tofu bar |
|
|
100 g of cooked vegetable |
1/2 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
30 g of basella alba |
1 small bow of vegetable soup |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Fruit |
|
|
100g of apple |
1/2 of average size apple (7x4cm) |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, grass carp sauteed with tomato, omelet, cooked vegetable, seasonal vegetable soup, fruit |
|
|
120 g of rice (60 g of polished ordinary rice) |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
70 g of fish sauteed with tomato |
1/2 of average size fish piece |
|
|
1 chicken egg for omelet |
1 chicken egg |
|
|
100 g of cooked vegetable for eating with mix of sesame and salt |
1/2 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
30 g of wax gourd |
1 small bow of vegetable soup |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 of 5 ml spoon |
|
|
120 g of wax apple |
2 of average size wax apples |
|
|
Menu 2 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Shrimp porridge |
|
|
40 g of polished rice |
500 ml of porridge bowl |
|
|
10 g of glutinous rice |
||
|
30 g of shrimp |
||
|
5 g of green beans |
||
|
4 ml of cooking oil |
||
|
Morning secondary meal |
Milk and dairy preparations |
|
|
Yogurt/fresh milk |
1 box of 100 g/1 box of 180 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, pork braised with quail eggs, fish cakes sauteed with tomato, cooked vegetable, seasonal vegetable soup |
|
|
80 g of polished rice |
1.5 small bowl of rice |
|
|
60 g of pork and 20 g of quail eggs |
5 medium size of pork and 2 quail eggs |
|
|
30 g of fish cakes and 30 g of tomato |
2 small pieces |
|
|
100 g of cooked broccoli, carrot, and daikon radish |
1/2 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
20 g of mustard greens |
1 small bow of vegetable soup |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Fruit |
|
|
130 g of papaya |
1 piece of small size papaya |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, chicken steamed with lime leaves, lolot pepper rolls, sauteed vegetable, seasonal vegetable soup, and fruit |
|
|
80 g of polished rice |
1.5 small bowl of rice |
|
|
60 g of chicken steamed with lime leaves |
2 of average size fish pieces |
|
|
1 roll of lolot pepper (20 g of pork) |
1 roll |
|
|
100 g of bean sprout sauteed with onion |
1/2 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
20 g of katuk |
1 small bow of vegetable soup |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 of 5 ml spoon |
|
|
120 g of orange/mandarin |
1/2 of large fruit (9.5x7 cm) |
|
|
Menu 3 |
SOFT MENU AND MILK |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Vermicelli sprouting |
|
|
170 g of vermicelli |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
Mix of 50 g of meat, wood ear, and shiitake mushrooms in form of a ball |
5-6 balls |
|
|
Fragrant vegetables and spring onion |
|
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 of 5 ml spoon |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Fruit and yogurt |
|
|
Yogurt |
1 container of 100 g |
|
|
70 g of kiwi |
1 medium size kiwi |
|
|
Lunch |
Beef noodle |
|
|
170 g of noodle |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
50 g of beef |
8-10 slices |
|
|
Fragrant vegetables and spring onion |
|
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 of 5 ml spoon |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Fruit |
|
|
140 g of guava |
2 of average size wax apples |
|
|
Dinner |
Pumpkin and chicken porridge |
|
|
40 g of chicken |
1 bowl of concentrated porridge (500 ml) |
|
|
40 g of polished rice |
||
|
10 g of glutinous rice |
||
|
10 g of pumpkin |
||
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
||
|
Evening secondary meal |
Milk and dairy preparations |
|
|
200 ml of powdered milk (1 kcal/ml) |
1 glass of milk (200 ml) |
|
ANNEX 1.2. MENU FOR PATIENTS WEIGHING 50 – 55 kg
Energy 1500 – 1600 kcal/day
|
Menu 1 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Chicken rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
150 g of rice noodle |
1 full small bowl |
|
|
30 g of chicken meat |
8-10 pieces, shredded |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
110 g of pear |
1/2 of small pear |
|
Lunch |
Rice, chicken sauteed with ginger, meatball and sauce, stir-fried vegetable |
|
|
240 g of rice (120 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowls |
|
|
70 g of chicken meat |
4 pieces (including bone) |
|
|
30 g of pork |
1 full spoon of 15 ml (2 average size meatball) |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
103 g of soursop |
1/2 of average size soursop |
|
Dinner |
Rice, deep fried fish filet, boiled pork, and cooked vegetable |
|
|
240 g of rice (120 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowls |
|
|
50 g of tilapias |
3 average-size pieces |
|
|
40 g of pork |
4-6 small pieces |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1,5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
In case patients have 1 cup of 250 ml milk (standard 1ml/kcal milk), reduce half of a small bowl of rice, 5-6 small pork pieces, and 1 spoon of 5ml of cooking oil |
||
|
Menu 2 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Beef rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
150 g of rice noodle |
1 full small bowl |
|
|
30 g of beef |
5-6 slices |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Fruit and yogurt |
|
|
Yogurt |
1 container of 100 g |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, fried pork with sesame, pig trotters, cooked vegetable, seasonal vegetable soup |
|
|
240 g of rice (120 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowls |
|
|
70 g of pork |
7-8 slices |
|
|
30 g of pig trotters |
2 thin pieces |
|
|
150 g of cooked brassica integrifolia |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Fruit |
|
|
120 g of orange/mandarin |
1/2 of large fruit (9.5x7 cm) |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, shrimp steamed with ginger and lemongrass, pumpkin stir-fried with garlic, seasonal vegetable |
|
|
240 g of rice (120 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowl |
|
|
60 g of sea crawfish |
4-5 medium size crawfish |
|
|
1 egg for omelet |
1 egg |
|
|
150 g of pumpkin, 2-3 gloves of garlic |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Menu 3 |
SOFT MENU WITH MILK |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
500 ml of pork porridge |
|
|
30 g of polished rice |
|
|
|
40 g of pork |
2 full spoons of 10 ml |
|
|
20 g of minced vegetable |
|
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 spoons of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
180 g of pomelo |
3 average size pieces (9x3.5x2 cm) |
|
Lunch |
Chicken noodle |
|
|
200 g of noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
70 g of chicken meat |
20-22 pieces, shredded |
|
|
50 g of bean sprout |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
130 g of guava |
2 of average size wax apples |
|
Dinner |
Beef rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
200 g of rice noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
60 g of beef |
10-12 thinly sliced pieces |
|
|
50 g of vegetable |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Standard milk with 1 kcal/ml |
1 cup of 240 ml |
ANNEX 1.3. MENU FOR PATIENTS WEIGHING 60 – 70 kg
Energy 1800 - 2000 kcal/day
|
Menu 1 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Rice noodle with lean meat |
|
|
150 g of noodle |
2 small bowls |
|
|
40 g of lean meat |
4-6 small pieces |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
100 g of apple |
1/2 of average size apple (7x4 cm) |
|
Lunch |
Rice, braised grass carp, lolot roll, cooked vegetable |
|
|
240 g of rice (120 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowls of rice |
|
|
70 g of grass carp |
1 average size section |
|
|
40 g of meat |
2 full spoons of 10 ml |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
110 g of watermelon |
2 medium size triangle slices |
|
Dinner |
Rice, braised pork belly, cooked beans, and stir-fried vegetables |
|
|
280 g of rice (140 g of polished rice) |
2 small bowls |
|
|
60 g of pork belly |
8-10 small pieces |
|
|
70 g of tofu |
1 bar |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 spoon of 5 ml |
|
|
In case patients have 1 cup of 250 ml milk (standard 1ml/kcal milk), reduce half of a small bowl of rice, 5-6 small pork pieces, and 1 spoon of 5ml of cooking oil |
||
|
Menu 2 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Chicken rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
200 g of rice noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
50 g of chicken meat |
12-15 pieces, shredded |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 of teaspoon |
|
|
Fragrant vegetables and spring onion |
|
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Powdered milk/fresh milk |
|
|
Powdered milk/fresh milk |
1 glass of milk (200 ml) |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, beef stir-fried with bell pepper, omelet, cooked vegetable, seasonal soup |
|
|
120 g of rice (60 g of polished rice) |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
100 g of beef, 70 g of bell pepper, 1 teaspoon (5 ml) of oil |
1 small dish of stir-fry (15-18 pieces) |
|
|
1 egg for omelet |
1 egg |
|
|
200 g of cooked brassica integrifolia |
1 small bowl |
|
|
20 g of amaranthus tricolor |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Yogurt and fruit |
|
|
1 box of yogurt |
1 box |
|
|
200 g of papaya |
1.5 small size piece |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, mackerel sauteed with tomato, stir-fried morning glory, fruit for dessert, seasonal soup |
|
|
120 g of rice (60 g of polished rice) |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
150 g of mackerel, 100 g of tomato, 1 teaspoon (5 ml) of cooking oil |
2 medium size sections of mackerel |
|
|
100 g of morning glory, 2-3 gloves of garlic, 1 teaspoon (5 ml) of cooking oil |
1/2 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
100 g of guava |
2/3 of large guava |
|
|
20 g of cabbage |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Menu 3 |
SOFT MENU WITH MILK |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Porridge with lean meat |
|
|
130 g of polished rice |
|
|
|
40 g of pork |
2 full spoons of 10 ml |
|
|
20 g of minced vegetable |
|
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
200 g of orange |
1 large orange (9.5 x 7 cm) |
|
Lunch |
Chicken rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
210 g of rice noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
80 g of chicken meat |
20-24 pieces, shredded |
|
|
50 g of vegetable |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Standard milk with 1kcal/ml |
260 ml |
|
Dinner |
Pork rice noodle |
|
|
200 g of noodle |
2 small bowls |
|
|
70 g of pork |
10-12 pieces, shredded |
|
|
50 g of vegetable |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoons of 5 ml |
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Standard milk with 1kcal/ml |
260 ml |
ANNEX 1.4. MENU FOR PATIENTS WEIGHING 70 – 75 kg
Energy 2000 - 2200 kcal/day
|
Menu 1 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Rice noodle with lean meat |
|
|
180 g of noodle |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
50 g of lean meat |
6-8 pieces, shredded |
|
|
Bone broth, spring onion |
|
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
130 g of banana |
1 average size banana (17 x 3 cm) |
|
Lunch |
Rice, fried grass carp, lolot roll, and stir-fried vegetable |
|
|
160 g of rice (80 g of polished rice) |
1.5 small bowl of rice |
|
|
70 g of grass carp |
1 average size section |
|
|
60 g of pork |
3 average-size pieces |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
70 g of kiwi |
1 of average size kiwi |
|
Dinner |
Rice, pork belly braised with eggs, beans sauteed with tomato, cooked vegetable |
|
|
160 g of rice (80 g of polished rice) |
1.5 small bowl of rice |
|
|
80 g of pork belly |
12-14 pieces, shredded |
|
|
Chicken egg |
1 egg |
|
|
60 g of tofu |
1 bar |
|
|
150 g of vegetable |
1 small bowl |
|
|
7 ml of cooking oil |
1.5 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
In case patients have 1 cup of 250 ml milk (standard 1ml/kcal milk), reduce half of a small bowl of rice, 5-6 small pork pieces, and 1 spoon of 5ml of cooking oil |
||
|
Menu 2 |
MEAL PLAN |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Vermicelli sprouting |
|
|
200 g of rice noodle |
2 small bowls |
|
|
50 g of chicken meat |
12-15 pieces, shredded |
|
|
5 ml of cooking oil |
1 of teaspoon |
|
|
Fragrant vegetables and spring onion |
|
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Powdered milk/fresh milk |
|
|
200 ml of powdered milk (1 kcal/ml) |
1 glass of milk (200 ml) |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, chicken sauteed with sesame, cooked tofu, stir-fried root vegetable, and seasonal soup |
|
|
160 g of rice (80 g of polished rice) |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
120 g of chicken, 1 small slice of ginger, and 1 teaspoon of coffee (5 ml) |
5 medium pieces |
|
|
90 g of tofu |
1 medium size tofu bar |
|
|
150 g of root vegetable, 50 g of carrot, 5 ml of cooking oil |
1 small bowl |
|
|
20 g of katuk |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Yogurt and fruit |
|
|
1 box of yogurt |
1 box |
|
|
200 g of dragon fruit |
3 average size pieces |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, salmon sauteed with butter and garlic, cooked vegetable, and fruit for dessert |
|
|
160 g of rice (80 g of polished rice) |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
130 g of salmon, 2-3 gloves of garlic, 1 teaspoon of cooking oil (5 ml), 5 g of butter |
1 average size section of fish |
|
|
200 g of white/green broccoli |
1 small bowl of vegetable |
|
|
100 g of guava |
2/3 of large guava |
|
|
20 g of mustard greens |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Menu 3 |
SOFT MENU WITH MILK |
|
|
|
SAMPLE MENU |
COMMON MEASUREMENT |
|
Breakfast |
Porridge with lean meat |
|
|
30 g of polished rice |
|
|
|
40 g of pork |
2 full spoons of 10 ml |
|
|
20 g of minced vegetable |
|
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
180 g of pomelo |
3 average size (9 x 3.5 x 2 cm) |
|
Lunch |
Beef noodle |
|
|
230 g of noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
90 g of beef |
14-15 average-size pieces |
|
|
50 g of vegetable |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Standard milk with 1kcal/ml |
300 ml |
|
Dinner |
Chicken rice noodle (pho) |
|
|
230 g of rice noodle |
2 full small bowls |
|
|
80 g of chicken meat |
20-24 pieces, shredded |
|
|
50 g of vegetable |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
10 ml of cooking oil |
2 teaspoon of 5 ml |
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Standard milk with 1kcal/ml |
300 ml |
ANNEX 2.
REFERENCE MENU FOR CHILDREN
ANNEX 2.1. MENU FOR CHILDREN FROM 2-5 YEARS OF AGE
Energy: 1300 Kcal
Estimated nutrition P:L:G = 55 g:44 g:171 g, fiber: 7g
|
Food intake for children 2-5 years of age in a day |
Demand |
||
|
Food |
Raw amount |
Cooked amount |
|
|
Rice |
130 g |
260 g of rice |
Energy: 1000 – 1300 Kcal Protein: 13 - 20% Lipid: 30-40% |
|
Fruit |
150 g |
|
|
|
Fish |
145 g |
|
|
|
Green vegetable |
150 g |
95 – 100 g |
|
|
Cooking oil |
20 ml |
140 g |
|
|
Formula milk 1Kcal/ml |
300 ml |
|
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Raw amount |
Note |
|
Morning |
Porridge with minced meat (250 ml), fruit |
||
|
Rice |
35 g |
|
|
|
Pumpkin |
30 g |
|
|
|
Minced pork |
35 g |
|
|
|
Cooking oil |
7 ml |
|
|
|
Apple |
40 g |
1/4 average size apple |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
150 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, braised grounded beef, cooked cabbage, katuk soup |
||
|
Rice |
100 g |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
Beef |
50 g |
35 g after cooked (8-10 thin slices) |
|
|
Cabbage |
80 g |
70 g after cooked (0.5 small bowl) |
|
|
Katuk |
10 g |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Dragon fruit |
100 g |
1/4 average size dragon fruit |
|
Dinner |
Rice, steamed eggs, cooked chayote, mustard green soup |
||
|
Rice |
100 g |
1 small bowl of rice |
|
|
Duck egg |
1 egg (70 g) |
|
|
|
Chayote |
80 g |
70 g after cooked (1/2 small bowl) |
|
|
Mustard green |
10 g |
|
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
150 ml |
|
ANNEX 2.2. MENU FOR CHILDREN FROM 6-9 YEARS OF AGE
Energy: 1800 Kcal
Estimated nutrition P:L:G = 76 g:54 g:252 g, fiber: 8.5 g
|
Food intake for children 6-9 years of age in a day |
Demand |
||
|
Food |
Raw amount |
Cooked amount |
|
|
Rice |
200 g |
400 g of rice |
Energy: 1500-1800 Kcal Protein: 13 - 20% Lipid: 25-35% |
|
Fruit |
150 g |
|
|
|
Fish |
190 g |
120-130 g |
|
|
Green vegetable |
170 g |
140 – 150 g |
|
|
Cooking oil |
25 ml |
|
|
|
Formula milk 1Kcal/ml |
400 ml |
|
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Raw amount |
Note |
|
|
Morning |
Carp porridge (250 ml), fruit |
|||
|
Rice |
35 g |
|
||
|
Carp Katuk |
35 g 30 g |
|
||
|
Cooking oil |
7 ml |
|
||
|
Sweet mandarin |
50 g |
1/2 average size soursop |
||
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
200 ml |
|
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, minced pork stir-fried with corn, fried tofu, cooked broccoli, amaranthus tricolor soup |
|||
|
Rice |
160 g |
1.5 small bowl of rice |
||
|
Minced pork |
40 g |
25 g after cooked - 1 full spoon of 4*6 cm |
||
|
Tofu |
65 g (1/2 of a bar) |
A bar of 7*4*2 cm |
||
|
Broccoli |
100 g |
90 g after cooked - small bowl |
||
|
Amaranthus tricolor |
10 g |
|
||
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Watermelon |
150 g |
3 pieces, shredded |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, beef stir-fried with bean sprout, basella alba |
|||
|
Rice |
160 g |
1.6 small bowl of rice |
||
|
Beef |
70 g |
45 g of cooked meat – 9-11 thin slices |
||
|
Bean sprout |
100 g |
|
||
|
Basella alba |
10 g |
90 g after cooked - small bowl |
||
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
200 ml |
|
|
ANNEX 2.3. MENU FOR CHILDREN FROM 11-12 YEARS OF AGE
Energy: 2100 Kcal
Estimated nutrition P:L:G = 89 g:63 g:294 g, fiber: 12.9 g
|
Food intake for children 10-12 years of age in a day |
Demand |
||
|
Food |
Raw amount |
Cooked amount |
|
|
Rice |
260 g |
520 g of rice |
Energy: 2000-2100 Kcal Protein: 13 - 20% Lipid: 20-30% |
|
Fruit |
160 g |
|
|
|
Fish |
230 g |
|
|
|
Green vegetable |
200 g |
150-160 g |
|
|
Cooking oil |
30 ml |
170-180 g |
|
|
Formula milk 1Kcal/ml |
500 ml |
|
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Raw amount |
Note |
|
Morning |
Chicken and bamboo shoot vermicelli, fruit |
||
|
Vermicelli |
150 g |
1/2 of bowl (2 small bowls) |
|
|
Chicken meat |
50 g |
35 g of cooked meat – 3-4 thin slices |
|
|
Fresh bamboo shoot |
50 g |
1/3 of small bowl |
|
|
Pomelo |
100 g |
3 average-size pieces |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, meatball steamed with potato, carrot, fried spring roll, cooked green beans, katuk soup |
||
|
Rice |
180 g |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
Minced pork |
60 g |
40 g after cooked – 1.5 full spoon of 4*6 cm |
|
|
Potato |
15 g |
3 pieces of 2*2*2 cm |
|
|
Carrot |
15 g |
3 pieces of 2*2*2 cm |
|
|
Fried spring roll |
1 piece (40 g) |
|
|
|
Green beans |
120 g |
110 g after cooked - small bowl |
|
|
Katuk |
10 g |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Banana |
1 egg (70 g) |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, grass carp sauteed in tomato, cooked vegetable, basella alba soup |
||
|
Rice |
180 g |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
Grass carp |
100 g |
80 g after cooked – 1/3 section |
|
|
Brassica integrifolia |
120 g |
110 g after cooked - small bowl |
|
|
Basella alba |
10 g |
|
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
ANNEX 2.4. MENU FOR CHILDREN FROM 13-15 YEARS OF AGE
Energy: 2500 Kcal
Estimated nutrition P:L:G = 106 g:75 g:350 g, fiber: 15.3 g
|
Food intake for children 13-15 years of age in a day |
Demand |
||
|
Food |
Raw amount |
Cooked amount |
|
|
Rice |
330 g |
660 g of rice |
Energy: 2300-2500 Kcal Protein: 13 - 20% Lipid: 20-30% |
|
Fruit |
170 g |
|
|
|
Fish |
290 g |
|
|
|
Green vegetable |
250 g |
180-190 g |
|
|
Cooking oil |
30 ml |
220-230 g |
|
|
Formula milk 1Kcal/ml |
500 ml |
|
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Raw amount |
Note |
|
Morning |
Beef noodle (pho) and fruit |
||
|
Noodle |
150 g |
1/2 of bowl (2 small bowls) |
|
|
Beef |
50 g |
35 g of cooked meat – 8-10 thin slices |
|
|
Bean sprout |
50 g |
1/2 of small bowl |
|
|
Guava |
100 g |
1/2 average size guava |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, lolot roll, chicken stir-fried with shiitake, cooked wax gourd, katuk soup |
||
|
Rice |
200 g |
1/5 of small bowl |
|
|
Minced pork |
60 g |
40 g after cooked – 1.5 full spoon of 4*6 cm |
|
|
Chicken meat |
60 g |
40 g after cooked – 2 small pieces |
|
|
Wax gourd |
140 g |
125 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Katuk |
10 g |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Pear |
100 g |
1/2 average size pear |
|
Dinner |
Rice, pork sauteed with shrimp, cooked cabbage, mustard green soup |
||
|
Rice |
200 g |
1.5 small bowl |
|
|
Pork |
50 g |
35 g after cooked – 3-4 pieces of 5*3*0,5 cm |
|
|
Shrimp |
60 g |
40 g after cooked - 2 sea crawfish |
|
|
Cabbage |
140 g |
125 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Mustard green |
10 g |
|
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
ANNEX 2.5. MENU FOR CHILDREN FROM 16-19 YEARS OF AGE
Energy: 2800 Kcal
Estimated nutrition P:L:G = 119 g:84 g:392 g, fiber: 14.4 g
|
Food intake for children 16-19 years of age in a day |
Demand |
||
|
Food |
Raw amount |
Cooked amount |
|
|
Rice |
380 g |
760 g of rice |
Energy: 2400-2500 Kcal Protein: 13 - 20% Lipid: 20-30% |
|
Fruit |
200 g |
|
|
|
Fish |
320 g |
|
|
|
Green vegetable |
300 g |
210-220 g after cooked |
|
|
Cooking oil |
30 ml |
260-270 g after cooked |
|
|
Formula milk 1Kcal/ml |
500 ml |
|
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Amount |
Note |
|
Morning |
Sticky rice with braised pork and eggs, pickles |
||
|
Sticky rice |
120 g |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Pork |
20 g |
15 g after cooked – 1 piece of 5*3*1 cm |
|
|
Chicken egg |
1 egg (40 g) |
|
|
|
Cucumber |
100 g |
1/2 average size cucumber |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, deep fried tilapia, minced chicken stir-fried with carrot, cooked broccoli, katuk soup |
||
|
Rice |
250 g |
2 small bowl |
|
|
Tilapias |
80 g |
52 g after cooked – 2 average size section |
|
|
Chicken meat |
50 g |
35 g after cooked – 2-3 small pieces |
|
|
Broccoli |
150 g |
130 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Katuk |
20 g |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Wax apple |
150 g |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, beef stir-fried with vegetable, lolot roll, cooked root vegetables, green mustard soup |
||
|
Rice |
250 g |
2 small bowl |
|
|
Beef |
70 g |
45 g of cooked meat – 9-11 thin slices |
|
|
Sweet pepper |
20 g |
4 pieces of 3*3cm |
|
|
Baby corn |
20 g |
4-5 average ears |
|
|
Pork |
60 g |
40 g after cooked – 3-4 pieces of 5*3*0.5 cm |
|
|
Root vegetable |
150 g |
135 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Mustard green |
20 g |
|
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
|
Meal |
Food |
Amount |
Note |
|
Morning |
Sticky rice with braised pork and eggs, pickles |
||
|
Sticky rice |
120 g |
1 small bowl |
|
|
Pork |
20 g |
15 g after cooked – 1 piece of 5*3*1 cm |
|
|
Chicken egg |
1 egg (70 g) |
|
|
|
Cucumber |
100 g |
1/2 average size cucumber |
|
|
Morning secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
|
Lunch |
Rice, deep fried tilapia, minced chicken stir-fried with carrot, cooked broccoli, katuk soup |
||
|
Rice |
250 g |
2 small bowl |
|
|
Tilapias |
80 g |
52 g after cooked – 2 average size section |
|
|
Chicken meat |
50 g |
35 g after cooked – 2-3 small pieces |
|
|
Broccoli |
150 g |
135 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Katuk |
20 g |
|
|
|
Afternoon secondary meal |
Wax apple |
150 g |
|
|
Dinner |
Rice, beef stir-fried with vegetable, lolot roll, cooked root vegetables, green mustard soup |
||
|
Rice |
250 g |
2 small bowl |
|
|
Beef |
70 g |
45 g of cooked meat – 9-11 thin slices |
|
|
Sweet pepper |
20 g |
4 pieces of 3*3cm |
|
|
Baby corn |
20 g |
4-5 average ears |
|
|
Pork |
60 g |
40 g after cooked – 3-4 pieces of 5*3*0.5 cm |
|
|
Root vegetable |
150 g |
130 g after cooked (1 small bowl) |
|
|
Mustard green |
20 g |
|
|
|
Evening secondary meal |
Formula milk |
250 ml |
|
ANNEX 3.
ILLUSTRATION FOR FOOD ESTIMATION
Figure 1. Tofu
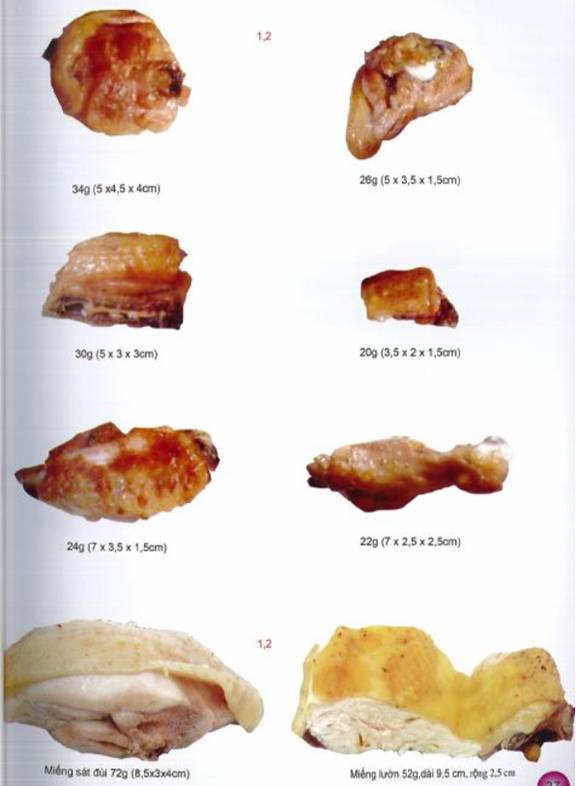

Figure 2. Chicken meat
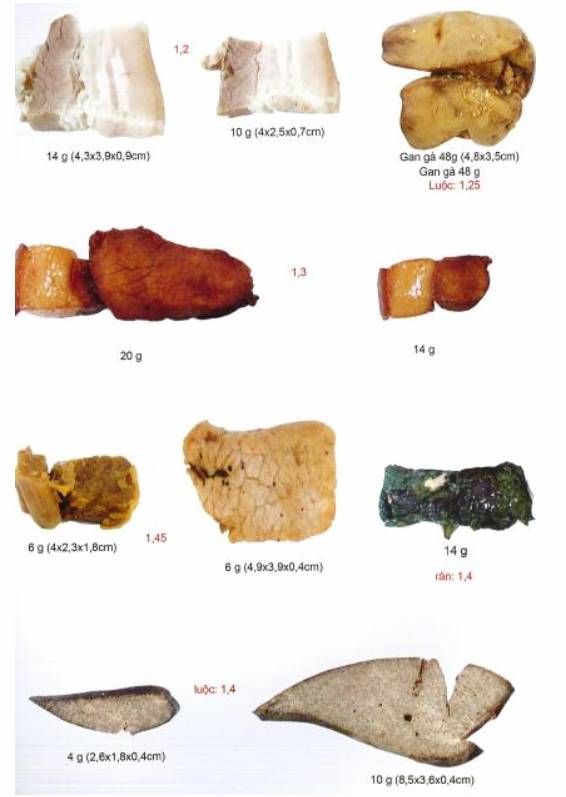

Figure 3. Pork

Figure 4. Pork
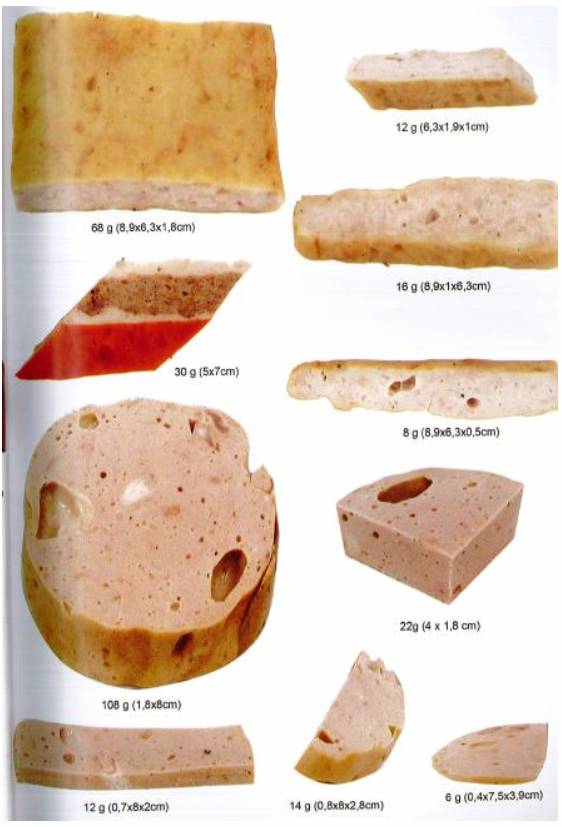

Figure 5. Vietnamese pork bologna
Figure 6. Shrimp and fish