Decision No. 48/2006/QD-BTC accounting regime applicable to small and medium sized enterprises đã được thay thế bởi Circular 133/2016/TT-BTC accounting for small medium enterprises và được áp dụng kể từ ngày 01/01/2017.
Nội dung toàn văn Decision No. 48/2006/QD-BTC accounting regime applicable to small and medium sized enterprises
|
THE MINISTRY OF FINANCE |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM |
|
No: 48/2006/QĐ-BTC |
Hanoi, September 14, 2006 |
DECISION
PROMULGATING ACCOUNTING POLICY FOR SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES
THE MINISTER OF FINANCE
Pursuant to the Law on Accounting No. 03/2003/QH11 on June 17, 2003;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 129/2004/NĐ-CP dated May 31, 2004 detailing and providing guidance on a number of articles of the Law on Accounting in business;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 77/2003/NĐ-CP dated July 1, 2003 defining functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Finance;
Pursuant to the Government’s Decree No. 90/2001/NĐ-CP dated November 23, 2001 on support for development of small- and medium-sized enterprises.
At the request of the Director of the Department of Audit and Accounting Regulation and the Chief of Office of the Ministry of Finance,
HEREBY DECIDES:
Article 1. "Accounting policy for small and medium-sized Enterprises" is promulgated which applies to all small and medium-sized enterprises, all economic sectors in the whole country which are limited liability companies, joint-stock company, partnership, private enterprises and cooperatives. Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises includes 5 parts:
Part 1 General Provisions;
Part 2 System of accounts;
Part 3 Financial reporting system;
Part 4 Regulations on accounting vouchers;
Part 5 Regulations on accounting books
Article 2. Small and medium-sized enterprises base on "Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises" issued under this Decision to conduct research, concretize and apply the accounting policy, specific regulation on contents and application of the list of accounts, vouchers, accounting books, selection of types of accounting books and financial statements in accordance with characteristics of production, business and management requirements of each area of operation, each type of enterprise. If there are any amendments and supplements to level-1 account or level-2 account or amendments to financial statements, a written agreement by the Ministry of Finance is a must.
Article 3. Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises does not apply to state-owned enterprises, state-owned one-member limited liability companies, joint-stock company listed on securities market, agricultural cooperatives and credit cooperatives.
Small and medium-sized enterprises which are subsidiaries shall implement accounting policy as stipulated by their parent company.
Small and medium-sized enterprises in specific areas such as: electricity, oil and gas, insurance, securities ... shall apply specific accounting policy issued or approved to issue by the Ministry of Finance.
Article 4. Limited liability companies, joint-stock company unlisted in securities market , partnership and private enterprises which have large size shall apply accounting policy for enterprises issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 15/2006 / QD-BTC dated March 20, 2006. A small and medium-sized enterprise which applies accounting policy for enterprises issued under Decision No. 15/2006 / QD-BTC dated March 20, 2006 must notify Tax authority which manages such enterprise and must implement the policy stably at least for 2 years. If it changes into accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises, it must notify Tax authority again.
Article 5. This Decision takes effect after 15 days from the date of the Official Gazette.
This Decision replaces the Minister of Finance’s Decision No.1177 TC / QD / CDKT dated December 23, 1996 promulgating "accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises" and the Minister of Finance’s Decision No.144/2001 / QD-BTC dated December 21, 2001 on “supplementation and amendment of accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises issued under Decision No. 1177-TC / QD / CDKT".
Small and medium-sized enterprises shall close their accounting books on December 31, 2006 in order to transfer the old account balance to new account from January 1, 2007 under accounting policy issued under this Decision.
The accounting provisions that are not specified in this Decision shall comply with the Law on Accounting and Decree No. 129/2004 / ND-CP dated May 31, 2004 of the Government on providing instructions on the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Accounting in business.
Article 6. Department of Taxation in central-affiliated cities and provinces shall cooperate with relevant departments to assist People’s Committee in central-affiliated cities and provinces in providing guidance and inspecting the implementation of accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises in administrative division.
The Director of the Department of Audit and Accounting Regulation, the Director of the General Department of Taxation, the Chief of the Ministry Office, the Director of the Department of enterprise finance and the heads of relevant units shall be responsible for guidance, inspection and implementation of this Decision./.
|
|
PP.MINISTER |
Part 1
GENERAL PROVISIONS
1. "Accounting policy for small and medium-sized Enterprises" applies to all small and medium -scale enterprises of all economic sectors economic sectors in the whole country, including: limited liability companies, joint-stock companies, partnerships, private enterprises and cooperatives
Accounting policy of small and medium-sized enterprises does not apply to state-owned enterprises, state-owned one-member limited liability companies, joint-stock companies listed on securities market, agricultural cooperatives and credit cooperatives.
Limited liability companies, joint-stock companies, partnership and private enterprises having large size shall apply accounting policy of enterprises issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 15/2006 / QD-BTC dated March 20, 2006. Medium-sized enterprises may apply accounting Policy for enterprises issued under Decision No. 15/2006 / QD-BTC dated March 20, 2006 but must notify Tax authority which manage such enterprises and must implement the policy stably at least for 2 years. If such medium-sized enterprises changes into accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises, they must change from the beginning of fiscal year and notify Tax authority again.
Small and medium-sized enterprises in specific areas such as: electricity, oil and gas, insurance, securities ... shall apply specific accounting policy issued or approved to issue by the Ministry of Finance.
Small and medium-sized enterprises which are subsidiaries shall implement accounting policy as stipulated by their parent company.
If small and medium-sized enterprises which apply this accounting policy have a demand for amendment or supplementation, they must gain a written approval from the Ministry of Finance.
2. Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises is formulated based on complete application of 7 common accounting standards, incomplete application of 12 accounting standards and non-application of 7 accounting standards because these standards do not arise in small and medium-sized enterprises or they are too complex and unsuitable for small and medium-sized enterprises (attached table).
2.1 Completely applied accounting standards
|
No |
Standard’s code and name |
|
1 |
Standard No. 01- Framework |
|
2 |
Standard No. 05- Investment property |
|
3 |
Standard No.14 - Revenue and other income |
|
4 |
Standard No.16- Borrowing costs |
|
5 |
Standard No.18- provisions, contingent assets and contingent liabilities |
|
6 |
Standard No.23- Events arising after the end of the accounting year |
|
7 |
Standard No.26 – Related parties disclosures |
2.2 Incompletely applied accounting standards
|
No |
Standard’s code and name |
Unapplied content |
|
1 |
Standard No.02- Inventories |
Allocation of fixed overheads under normal capacity of machinery. |
|
2 |
Standard No.03- Tangible fixed assets |
Depreciation period and method |
|
3 |
Standard No.04- Intangible fixed assets |
|
|
4 |
Standard No.06 –Leases |
Selling and subleasing operating leased assets |
|
5 |
Standard No.07 – Accounting for investment in associate companies |
Equity capital method. |
|
6 |
Standard No.08 – Financial reporting of interest in joint ventures |
- Equity method; - When a venturer contributes assets to a joint venture, if the joint-venture capital contributor has transferred ownership of assets, the venturer should recognise only that portion of the gain or loss which is attributable to the interests of the other venturers. - When a venturer sells assets to a joint venture : Where a venturer has transferred ownership and the assets are retained by the joint venture without selling to an independent third party, the venturer should recognise only that portion of the gain or loss which is attributable to the interests of the other venturers.; Where the joint venture resells the assets to an independent third party, the venturer is entitled to recognise that portion of the actual gain or loss which arises from the sale of asset to Joint Venture. |
|
7 |
Standard No.10- Effect of fluctuations in foreign exchange rates |
Exchange rate differences arising upon conversion of financial statements of foreign-based establishments. |
|
8 |
Standard No.15- Construction contracts |
Recording revenues, expenses of construction contract in case contractor is paid according to the schedule. |
|
9 |
Standard No.17- Corporate income tax |
Deferred income tax. |
|
10 |
Standard No.21 – Presentation of financial statements |
Reducing the requirements for presentation in the report. |
|
11 |
Standard No.24- Cash flow statement |
encouraging to apply, not required |
|
12 |
Standard No.29 – changes of accounting policies, accounting estimates and errors |
Applying retroactive to changes of accounting policy |
2.3 Unapplied accounting standards
|
No |
Standard’s code and name |
|
1 |
Standard No. 11 – Business combination |
|
2 |
Standard No. 11- Insurance contract |
|
3 |
Standard No. 22 –Additional presentation in financial statement of banks and similar financial institutions. |
|
4 |
Standard No. 25-Consolidated Financial statements and accounting for investments in subsidiaries |
|
5 |
Standard No. 27 - Interim financial statements. |
|
6 |
Standard No. 28 –Segment reporting |
|
7 |
Standard No. 30- Earning per share |
3. Numerals, language, and unit used in accounting
- Language used in accounting is Vietnamese. The numbers used in accounting are Arabic numerals: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9; there must be a dot (.) after the thousand digit, million digit, billion digit, trillion digit, ...; while there must be a comma (,) after the unit digit.
- The currency unit is Vietnam dong (the national symbol is "d" and the international symbol is "VND"). Transactions must be recorded in the original currency and in dong, at the applicable exchange rate, or recorded in the original currency and converted into dong at the applicable exchange rate announced by the State Bank of Vietnam at the time of such transaction in case such transactions is conducted in a foreign currency, unless otherwise prescribed by law; Where a particular form of foreign currency does not have an exchange rate with the dong, it must be converted via a convertible form of foreign currency.
- Item unit and working time unit applies to small and medium-sized enterprises is official units of measurement of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam; if enterprises use any other units of measurement, such units of measurement must be converted into the official measurement units of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
4. Accounting period
Accounting period applies to small and medium-sized enterprises is accounting year. An annual accounting year includes twelve months, from January 1 to 31 March of a calendar year. An accounting unit that has its own characteristics of organizations and operation is entitled to choose an annual accounting year that includes full twelve months according to calendar year, starting from the beginning of the first day of a month at the beginning of any one quarter until the end of the last day of the last month of the previous quarter in the following year and then notify the Tax authority.
Small and medium-sized enterprises must prepare and submit financial statements to the State agencies under accounting year.
5. Inventory of assets
Asset inventory is weighing, measuring, counting the number; recognizing and assessing the quality and value of assets, capital at the time of inventory to inspect and compare them with the figures in accounting books.
Small and medium-sized enterprises must inventory assets in the following cases:
- At the end of accounting year, before the financial statements;
- Total division, partial division, consolidation, acquisition, dissolution, termination of their operation, bankruptcy, transfer, package contracting or leasing their enterprises;
- Ownership transformation;
- Occurrence of fires, floods and other unusual damage;
- Revaluation of assets under a decision of competent State agencies;
- Other cases prescribed by law.
After an inventory of assets, enterprises must prepare general reports on inventory results. Where there are differences between the actual inventory data with the data recorded in accounting books, accounting unit must determine the cause and record the differences and treatment results in accounting books before preparing financial statements.
The inventory must recognize the actual assets, asset-forming sources. The person who prepares and signs the general reports on inventory results shall be responsible for the results of the inventory.
6. Disclosure of financial statement
The disclosures in the income statement of small and medium-sized enterprises should include:
- Assets, liabilities and equity;
- setting up and using of funds;
- Income summary;
- Income of workers.
Form and duration of disclosure of financial statements
Financial statement shall be disclosed under the following forms:
- Issuance of publications;
- Written notification;
- Listing;
- Other forms as prescribed by law.
A small and medium-sized enterprise which is a private enterprises or partnership must disclose its annual financial statement within 60 days from the end of accounting year; for other small and medium-sized enterprises, the disclosure period of their financial statements is within 120 days.
7. Preservation of accounting documents
Types of original accounting documents which must be preserved include:
- Accounting vouchers;
- Detailed accounting books, general accounting books;
- Financial statements, administrative accounting reports;
- Other related documents such as: All contracts; approval to convert profit to capital, approval to distribute dividends or to allocate profit to company reserves; decision on tax exemption, reduction, reimbursement, collection of overdue accounts, annual tax settlements; report on results of inventory and evaluation of assets; documents relating to inspection and auditing; documents relating to dissolution, bankruptcy, total division, partial division, acquisition, termination of operation, ownership transformation; documents which relate to the destruction of accounting documents and other documents relating to accounting.
Preservation of accounting documents
Accounting documents must be preserved fully and safely during use. Accountants are responsible for preserving their accounting documents during use.
Accounting documents that are preserved must be originals as prescribed by law for each type of accounting document. If any accounting document is temporarily seized, confiscated, lost or destroyed, a copy of such accounting document and a record of the seizure, confiscation, loss or destruction must be preserved... For an accounting document that has only one original but must be preserved in two places, one of the two places is allowed to preserve its copy. Copied accounting documents for preservation must be taken from the original and must be signed and stamped by the unit that preserves their original.
The Directors of small and medium-sized enterprises are responsible for preserving accounting documents and are responsible for safety, completeness and legality of accounting documents.
Accounting documents that are preserved must be complete, systematic and must be classified and sorted into separate sets of records chronologically and under accounting year.
Preservation place of accounting documents
Enterprises must preserve their accounting documents on their own storages. The storage room should meet conditions for equipment safety for preservation of documents as prescribed by law. An enterprise is permitted to hire a storage service provider. In this circumstance, there must be a signed contract between the enterprise and the storage service provider.
Accounting documents of an small and medium-sized enterprise that are dissolved or bankrupt include documents of the accounting year that are still in preservation period and documents relating to the dissolution, bankruptcy that are preserved in a place decided by the director of the enterprise.
Accounting documents of accounting years that are still in preservation period of an enterprise which is divided into two or more enterprises shall be processed/treated according to the following provisions: If the accounting documents are divisible to the new accounting unit, they shall be preserved in the new enterprise; if the accounting documents are indivisible, they shall be preserved in the dividing accounting unit or in a place decided by agencies that are competent in division of enterprises. Accounting documents relating to the division shall be preserved in the divided enterprise.
Accounting documents of the accounting year that are still in preservation period and accounting documents relating to acquisition of small and medium-sized enterprises shall be preserved in the acquired enterprise.
Preservation period of accounting documents
Accounting documents that must be preserved for 5 years include:
- Accounting documents which relate to management and administration, and which do not directly support book-entries nor elaborate upon financial reports such as note of receipts, note of payments, goods-received note, goods dispatch note shall not included in the file of accounting documents.
- Other accounting documents which relate to management and administration, and which do not directly support book-entries nor elaborate upon financial reports.
Accounting documents that must be preserved for 10 years include:
- Accounting documents which directly support book entries and which elaborate financial reports, detailed comprehensive sheets, detailed accounting books, general accounting books, annual financial statements, records of destruction of archived accounting documents and other documents relating to book entries and elaborating financial reports, audit reports and accounting inspection reports.
- accounting documents which relate to liquidation of fixed assets.
- accounting documents which relate to investment projects; including the accounting documents of the accounting year and accounting documents on settlement report of investment of completed project.
- accounting documents which relate to establishment, division, consolidation, acquisition, ownership transformation, dissolution, termination of operations and bankruptcy of an accounting unit.
Accounting documents that must be preserved indefinitely shall be stipulated as follows:
- Accounting documents that must be preserved indefinitely are ones that have historical or social significance in economy, security and national defense. The legal representative of an enterprise can himself decide which accounting documents must be preserved indefinitely based on the historical characteristics and long term significance of such documents, and he can assign accounting department or another department to preserve them in their original form or other forms.
- indefinite preservation period shall be over 10 years until the accounting documents are damaged naturally or are destroyed under the decision of the legal representative of the accounting unit.
Calculation of preservation period of accounting documents
Preservation period for documents specified in point 7.4 of general provision of this Decision shall be calculated from the end of the accounting year.
Chief accountant
Arrangement of chief accountant
Any small and medium-sized enterprise must appoint chief accountant or accountants. A small and medium-sized enterprise must immediately appoint chief accountants or accountants when it is established.
If the chief accountant or accountant position is vacant, competent persons must appoint immediately new chief accountant or accountant. An enterprise can appoint the chief accountant or accountants or hire chief accountant.
When changing the chief accountant or accountant, legal representative of the accounting unit must ask the former the chief accountant or accountant to transfer his/her work and accounting documents to the new chief accountant or accountant, and notify relevant departments and the bank where the account is opened of name and specimen signature of the Chief Accountant or new accountant. The new chief accountant shall be responsible for his/her work from the date of transfer. The former chief accountant or accountant is still responsible for the accuracy, completeness and objectivity of information and accounting documents during their working time in the accounting unit.
Standards and conditions of chief accountants
The person who is appointed to work as a chief accountant in small and medium-sized enterprises must have professional ethics, honesty and integrity; comply with the law; graduate from technical secondary school or more and have an actual working time in accounting for at least three years.
The person who is appointed to work as a chief accountant in small and medium-sized enterprises must satisfy the following conditions:
- not belong to any category of persons that are not permitted to act as accounting personnel prescribed in Article 51 of the Law on Accounting;
- Having taken chief accountant training course and being issued certificate of chief accountant retraining as prescribed by the Ministry of Finance.
Hiring accountants and chief accountants
- Small and medium-sized enterprises are allowed to hire accounting service providers or persons who have registered for providing accounting service to work as accountants or chief accountants.
- Hired accountant or chief accountant must satisfy professional standards stipulated in Articles 51, 55, 56 and 57 of the Law on Accounting and the documents guiding the implementation of the Law on Accounting.
- Hired chief accountants must meet the following conditions:
Have accounting practice certificate as prescribed in Article 57 of the Law on Accounting;
Have certificate of Chief accountant retraining as prescribed of the Ministry of Finance;
Have registered for providing accounting service or registered for accounting practice in accounting service providers.
- Hired accountants shall have responsibilities and rights as prescribed in Clause 2, Clause 3 of Article 50 of the Law on Accounting. Hired chief accountants shall have responsibilities and rights as prescribed in Article 54 of the Law on Accounting.
- The legal representative of the accounting unit shall be responsible for the hiring of accountants and chief accountants.
Part 2:
SYSTEM OF ACCOUNTS
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Accounts are used for classification and systematization of financial-economic transactions according to economic contents.
System of accounts of small and medium-sized enterprises includes level-1 accounts and level-2 accounts, accounts in the Balance sheet and accounts off-Balance sheet as prescribed in this accounting policy .
Small and medium-sized enterprises should base on the system of accounts defined in accounting Policy for small and medium-sized enterprises to conduct research, apply and elaborate system of accounts in consistence with the characteristics of production, business, management requirements of each unit and contents, structures and accounting methods of the respective control accounts.
If small and medium-sized enterprises need to supplement level-1 accounts or modify level-1 accounts and level-2 accounts in the system of accounts prescribed by the Finance Ministry on description, code, content and accounting method of particular economic transactions, they must gain a written approval from the Ministry of Finance.
Small and medium-sized enterprises may open subaccounts and sub-subaccounts for accounts that do not require subaccount or sub-subaccount in the Chart of accounts under accounting System of small and medium-sized enterprises specified in this Decision in service of the requirements of management of enterprises without requesting the Ministry of Finance for approval.
CHART OF ACCOUNTS UNDER ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
|
No |
Code |
Description |
NOTE |
||
|
Level-1 account |
Level-2 account |
Level-3 account |
|||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 1 CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
1 |
111 |
|
|
Cash on hand |
|
|
|
|
1111 |
|
Vietnam Dong |
|
|
|
|
1112 |
|
Foreign currencies |
|
|
|
|
1113 |
|
gold, silver, precious metals and jewels |
|
|
2 |
112 |
|
|
Cash in banks |
Details for each bank |
|
|
|
1121 |
|
Vietnam Dong |
|
|
|
|
1122 |
|
Foreign currencies |
|
|
|
|
1123 |
|
gold, silver, precious metals and jewels |
|
|
3 |
121 |
|
|
short-term financial investments |
|
|
4 |
131 |
|
|
Trade receivables |
Details for each customer |
|
5 |
133 |
|
|
Deductible VAT |
|
|
|
|
1331 |
|
VAT on purchase of goods and services |
|
|
|
|
1332 |
|
VAT on purchase of fixed assets |
|
|
6 |
138 |
|
|
Other receivables |
|
|
|
|
1381 |
|
Shortage of assets awaiting resolution |
|
|
|
|
1388 |
|
Other receivables |
|
|
7 |
141 |
|
|
Advances |
Details for each object |
|
8 |
142 |
|
|
short-term prepaid expenses |
|
|
9 |
152 |
|
|
raw materials, materials |
Details for management requirement |
|
10 |
153 |
|
|
Instruments, tools |
Details for management requirement |
|
11 |
154 |
|
|
Work in progress |
Details for management requirement |
|
12 |
155 |
|
|
Finished goods |
Details for management requirement |
|
13 |
156 |
|
|
Merchandise inventories |
Details for management requirement |
|
14 |
157 |
|
|
Outward goods on consignment |
Details for management requirement |
|
15 |
159 |
|
|
Provisions |
|
|
|
|
1591 |
|
Provision for short-term investments |
|
|
|
|
1592 |
|
provision for uncollectible receivables |
|
|
|
|
1593 |
|
provision against devaluation of goods in stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 2 NON- CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
16 |
211 |
|
|
fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2111 |
|
Tangible fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2112 |
|
Finance lease fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2113 |
|
Intangible fixed assets |
|
|
17 |
214 |
|
|
Depreciation of fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2141 |
|
Depreciation of tangible fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2142 |
|
Depreciation of finance lease fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2143 |
|
Depreciation of intangible fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2147 |
|
Depreciation of investment properties |
|
|
18 |
217 |
|
|
investment properties |
|
|
19 |
221 |
|
|
Long-term financial investments |
|
|
|
|
2212 |
|
contributed capital in joint venture |
|
|
|
|
2213 |
|
investment in associate companies |
|
|
|
|
2218 |
|
Other long-term financial investments |
|
|
20 |
229 |
|
|
Provision for long-term investments |
|
|
21 |
241 |
|
|
Construction in progress |
|
|
|
|
2411 |
|
purchase of fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
2412 |
|
Construction in progress |
|
|
|
|
2413 |
|
Major repairs of fixed assets |
|
|
22 |
242 |
|
|
Long-term prepaid expenses |
|
|
23 |
244 |
|
|
Long-term deposits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 3 LIABILITIES |
|
|
24 |
311 |
|
|
short-term loans |
|
|
25 |
315 |
|
|
Long-term liabilities at maturity |
|
|
26 |
331 |
|
|
Trade payables |
Details for each object |
|
27 |
333 |
|
|
Taxes and other payables to State Budget |
|
|
|
|
3331 |
|
Value Added Tax (VAT) |
|
|
|
|
|
33311 |
Output VAT |
|
|
|
|
|
33312 |
VAT on imported goods |
|
|
|
|
3332 |
|
Special consumption tax |
|
|
|
|
3333 |
|
Import and export tax |
|
|
|
|
3334 |
|
Corporate income tax |
|
|
|
|
3335 |
|
Personal income tax |
|
|
|
|
3336 |
|
Tax on use of natural resources |
|
|
|
|
3337 |
|
Land and housing tax, and rental charges |
|
|
|
|
3338 |
|
Other taxes |
|
|
|
|
3339 |
|
Fees, charges and other payables |
|
|
28 |
334 |
|
|
Payables to employees |
|
|
29 |
335 |
|
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
30 |
338 |
|
|
Other payables |
|
|
|
|
3381 |
|
Surplus of assets awaiting resolution |
|
|
|
|
3382 |
|
Trade union fees |
|
|
|
|
3383 |
|
Social insurance |
|
|
|
|
3384 |
|
Health insurance |
|
|
|
|
3386 |
|
Short-term deposits received |
|
|
|
|
3387 |
|
Unearned revenue |
|
|
|
|
3388 |
|
Other payables |
|
|
31 |
341 |
|
|
Long-term loans and liabilities |
|
|
|
|
3411 |
|
Long-term loans |
|
|
|
|
3412 |
|
Long-term liabilities |
|
|
|
|
3413 |
|
Issued bonds |
|
|
|
|
|
34131 |
Par value of bonds |
|
|
|
|
|
34132 |
Bond discounts |
|
|
|
|
|
34133 |
Bond premiums |
|
|
|
|
3414 |
|
Long-term deposits received |
|
|
32 |
351 |
|
|
Provision fund for severance allowances |
|
|
33 |
352 |
|
|
Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 4 OWNER’S EQUITY |
|
|
34 |
411 |
|
|
Stockholders' equity |
|
|
|
|
4111 |
|
Owner’s invested equity |
|
|
|
|
4112 |
|
share premium |
(joint-stock company ) |
|
|
|
4118 |
|
Other capital |
|
|
35 |
413 |
|
|
Exchange rate differences |
|
|
36 |
418 |
|
|
Other equity funds |
|
|
37 |
419 |
|
|
Treasury shares |
(joint-stock company ) |
|
38 |
421 |
|
|
Undistributed profit |
|
|
|
|
4211 |
|
Undistributed profit of previous year |
|
|
|
|
4212 |
|
Undistributed profit of current year |
|
|
39 |
431 |
|
|
Bonus and welfare fund |
|
|
|
|
4311 |
|
Bonus fund |
|
|
|
|
4312 |
|
Welfare fund |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 5 REVENUE |
|
|
40 |
511 |
|
|
Revenues from sales and service rendered |
|
|
|
|
5111 |
|
Revenue from sales of merchandises |
|
|
|
|
5112 |
|
Revenue from sales of finished goods |
Details for management requirement |
|
|
|
5113 |
|
Revenue from services rendered |
|
|
|
|
5118 |
|
Other revenue |
|
|
41 |
515 |
|
|
Financial income |
|
|
42 |
521 |
|
|
Revenue deductions |
|
|
|
|
5211 |
|
Trade discounts |
|
|
|
|
5212 |
|
Sales returns |
|
|
|
|
5213 |
|
Sales rebates |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
COSTS OF PRODUCTION AND BUSINESS
|
|
|
43 |
611 |
|
|
Purchases |
used for periodic inventory systems |
|
44 |
631 |
|
|
Production costs |
used for periodic inventory systems |
|
45 |
632 |
|
|
Costs of goods sold |
|
|
46 |
635 |
|
|
Financial expenses |
|
|
47 |
642 |
|
|
Business administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
6421 |
|
Selling expenses |
|
|
|
|
6422 |
|
General administration expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 7 OTHER INCOME |
|
|
48 |
711 |
|
|
other income |
Details for operation |
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 8 OTHER EXPENSES |
|
|
49 |
811 |
|
|
other expenses |
Details for operation |
|
50 |
821 |
|
|
Corporate Income tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 9 INCOME SUMMARY |
|
|
51 |
911 |
|
|
income summary |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TYPE 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BALANCE SHEET ACCOUNTS |
|
|
1 |
001 |
|
|
Leasehold assets |
|
|
2 |
002 |
|
|
Materials, goods kept for processing |
Details for management requirement |
|
3 |
003 |
|
|
Goods received for sale , deposit |
|
|
4 |
004 |
|
|
Bad debts treated |
|
|
5 |
007 |
|
|
Foreign currencies |
|
Part 3:
FINANCIAL REPORTING SYSTEM
GENERAL PROVISIONS
1. The purpose of financial reporting
The purpose of financial reporting is to:
(1) Summarize and present generally and comprehensively situation of assets, capital that forms of assets, situation and results of operation of an enterprise in a financial year.
(2) Provide essential economic-financial information for assessing the situation and results of operations, financial situation of an enterprise in the last financial year and forecast for the future.. Information of financial statements is an important basis for owners, investors, current and potential creditors of enterprises to reach decisions on management of operation or investment in enterprises as well as provide information for the macro-management of the State
2. Regulated entities
Financial reporting system is applied to all small and medium –sized enterprises in all economic sectors in the whole country which are limited liability companies, joint-stock companies, partnerships and private enterprises. Cooperatives are also allowed to apply system of annual financial statements defined in this accounting policy.
This system of annual financial statements does not apply to state-owned enterprises, state-owned one-member limited liability companies, joint-stock company listed on securities market, agricultural cooperatives and credit cooperatives.
The preparation and presentation of financial statements of small and medium-sized enterprises in particular sectors shall comply with provisions of accounting policy issued or approved for issuance by the Ministry of Finance.
3. Financial reporting system of small and medium-sized enterprises
(1) Financial statements provided for small and medium-sized enterprises include:
Mandatory reports
- Balance sheet: Form B 01 - DNN
- Income statement: Form B 02 - DNN
- Note to financial statement: Form B 09 - DNN
The financial statement submitted to tax authority must be enclosed with the following table:
- Account balance sheet: Form F 01- DNN
Optional reports (enterprises are encouraged to prepare):
- Cash flow statement: Form B03-DNN
In addition, enterprises may prepare other detailed financial statement to meet requirements for management and direction of their operation.
Financial statements provided for cooperatives include:
- Account balance sheet: Form B01- DNN/HTX
- Income statement: Form B02 - DNN
- Note to financial statement: Form B09- DNN/HTX
Contents, calculation methods and presentation forms of items in each report specified in this policy are applied uniformly to small and medium-sized enterprises subject to this financial reporting system.
During the application, if necessary, enterprises are allowed to supplement items in accordance with each area of operation and management requirements of enterprises; In case of any amendment, it must be approved in writing by the Ministry of Finance.
4. Responsibility, period of preparation and submission of financial statements
Responsibility, deadline of preparation and submission of financial statements:
a. All small and medium-sized enterprises subject to this financial reporting system must prepare and submit annual financial statements in accordance with the provisions of this policy.
b. For limited liability companies, joint stock companies and cooperatives, the deadline to submit annual financial statements is within 90 days from the end of fiscal year.
b. For private enterprises and partnerships, the deadline to submit annual financial statements is within 30 days from the end of fiscal year.
Enterprises may prepare monthly, quarterly financial statements to meet requirements for management of their operations.
Recipient of annual financial statements is defined as follows:
|
|
Recipient of annual financial statements |
||
|
Types of enterprise |
Tax authority |
business registration agency |
statistics agency |
|
limited liability company, joint-stock company, partnership, private enterprise cooperative |
x
x |
x
x |
x |
II. LIST AND FORM OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES
Balance sheet - Form B01-DNN
Account balance sheet - Form F01-DNN
Income statement- Form F02-DNN
Cash flow statement - Form B03-DNN
Note to financial statement - Form B09-DNN
LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT OF COOPERATIVES
1. Account balance sheet - Form B01-DNN/HTX
2. Income statement- Form F02-DNN
3. Note to financial statement - Form B09-DNN/HTX
FORMS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT
1. Balance sheet
|
Unit:.................. Address:................ |
|
Form B 01 - DNN (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
BALANCE SHEET
Date..................
Unit:..................
|
ASSET |
Code |
Note |
Ending |
Beginning |
|
A |
B |
C |
1 |
2 |
|
CURRENT ASSETS (100=110+120+130+140+150) |
100 |
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
110 |
(III.01) |
|
|
|
Short-term financial investments |
120 |
(III.05) |
|
|
|
1. short-term financial investments |
121 |
|
|
|
|
2. Provision for short-term investments |
129 |
|
(…) |
(...) |
|
III. Short-term receivables |
130 |
|
|
|
|
1. Trade receivables |
131 |
|
|
|
|
2. prepayments to suppliers |
132 |
|
|
|
|
3. Other receivables |
138 |
|
|
|
|
4. Provision for uncollectible short-term receivables (*) |
139 |
|
(…) |
(...) |
|
IV. Inventories |
140 |
|
|
|
|
1. Inventories |
141 |
(III.02) |
|
|
|
2. provision against devaluation of goods in stock (*) |
149 |
|
(…) |
(...) |
|
V. Other current assets |
150 |
|
|
|
|
1. Deductible VAT |
151 |
|
|
|
|
2. Taxes and other revenues of the State |
152 |
|
|
|
|
3. Other current assets |
158 |
|
|
|
|
B-NON- CURRENT ASSETS (200 = 210+220+230+240)
|
200 |
|
|
|
|
iI. Fixed assets |
210 |
(III.03.04) |
|
|
|
1. Cost |
211 |
|
|
|
|
2. Value of accumulated depreciation(*) |
212 |
|
(....) |
(.....) |
|
3. Cost of construction in progress |
213 |
|
|
|
|
II. investment properties |
220 |
|
|
|
|
1. Cost |
221 |
|
|
|
|
2. Value of accumulated depreciation(*) |
222 |
|
(....) |
(.....) |
|
III. long-term financial investments |
230 |
(III.05) |
|
|
|
1. Long-term financial investments |
231 |
|
|
|
|
2. Provision for long-term investments(*) |
239 |
|
(....) |
(.....) |
|
IV. Other non-current assets |
240 |
|
|
|
|
1. long-term receivables |
241 |
|
|
|
|
2. Other non-current assets |
248 |
|
|
|
|
3. Provision for uncollective long-term(*) |
249 |
|
(....) |
(.....) |
|
TOTAL ASSETS (250 = 100 + 200)
|
250 |
|
|
|
|
CAPITAL |
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES (300 = 310 + 320)
|
300 |
|
|
|
|
short-term liabilities |
310 |
|
|
|
|
1. short-term loans |
311 |
|
|
|
|
2. Trade payables |
312 |
|
|
|
|
3. deferred revenues |
313 |
|
|
|
|
4. Taxes and other payables to State Budget |
314 |
III.06 |
|
|
|
5. Payables to employees |
315 |
|
|
|
|
6. Accrued expenses |
316 |
|
|
|
|
7. Other short-term payables |
318 |
|
|
|
|
8. Provision for short term payables |
319 |
|
|
|
|
II. Long-term liabilities |
320 |
|
|
|
|
1. Long-term loans and liabilities |
321 |
|
|
|
|
2. Provision fund for severance allowances |
322 |
|
|
|
|
3. Other long-term payables, receivables |
328 |
|
|
|
|
4. Provision for long- term payables |
329 |
|
|
|
|
B- OWNER’S EQUITY (400 = 410+430) |
400 |
|
|
|
|
I. Owner’s equity |
410 |
III.07 |
|
|
|
1. Owner’s invested equity |
411 |
|
|
|
|
2. share premium |
412 |
|
|
|
|
3. Other capital of owners |
413 |
|
|
|
|
4. Treasury shares (*) |
414 |
|
(....) |
(....) |
|
5. Exchange rate differences |
415 |
|
|
|
|
6. Other equity funds |
416 |
|
|
|
|
7. undistributed post-tax profits |
417 |
|
|
|
|
II. Bonus and welfare fund |
430 |
|
|
|
|
TOTAL RESOURCES (440 = 300 + 400 ) |
440 |
|
|
|
OFF BALANCE SHEET ITEMS
|
Item |
Ending |
Beginning |
|
Leasehold assets |
|
|
|
Materials, goods kept for processing |
|
|
|
Goods received for sale , deposit |
|
|
|
Bad debts treated |
|
|
|
Foreign currencies |
|
|
Date..................
|
Prepared by (signature, full name) |
Chief accountant (signature, full name) |
Director (signature, full name, stamp) |
Note:
(1) The figures in the items with an asterisk (*) are recorded in negative numbers and in parentheses (...).
(2) The items without figures are not required to report but are not permitted to change the “code”.
(3) The enterprise whose annual accounting period is calendar year (X), the "Ending" can be recorded "31.12.X"; the "Beginning" can be recorded "01.01.X".
2. Account balance sheet:
Unit:.................. Address:........................ |
|
Form F01 - DNN (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
STATEMENT OF ACCOUNTS (*)
Year…
Unit:..................
|
Code |
Description |
Beginning balance |
Balance during year |
Ending balance |
|||
|
TK |
|
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
|
A |
B |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
(*) It may be used for level-1 account or both level-1 account and level-2 account and shall be only submitted to tax authority
|
|
|
Date……………. |
|
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Director |
|
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Income statement
Unit:.................. Address:........................ |
|
Form B 02 - DNN (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
INCOME STATEMENT
Year…
Unit:..................
|
Item |
Code |
Note |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
A |
B |
C |
1 |
2 |
|
1. Revenues from sales and service rendered |
01 |
IV.08 |
|
|
|
2. Revenue deductions |
02 |
|
|
|
|
3. Net revenues from sales and service rendered(10 = 01 - 02) |
10 |
|
|
|
|
4. Costs of goods sold |
11 |
|
|
|
|
5. Gross revenues from sales and service rendered (20 = 10 - 11) |
20 |
|
|
|
|
6. Financial income |
21 |
|
|
|
|
7. Financial expenses |
22 |
|
|
|
|
- In which: Interest expenses |
23 |
|
|
|
|
8. Business administrative expense |
24 |
|
|
|
|
9. Net profit from trading(30 = 20 + 21 - 22 – 24) |
30 |
|
|
|
|
10. other income |
31 |
|
|
|
|
11. other expenses |
32 |
|
|
|
|
12. Other profits (40 = 31 - 32) |
40 |
|
|
|
|
13. Total profit before tax (50 = 30 + 40) |
50 |
IV.09 |
|
|
|
14. Corporate Income tax expense |
51 |
|
|
|
|
15. Profits after corporate income tax (60 = 50 – 51) |
60 |
|
|
|
Date…………….
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Director |
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
4. Cash flow statement
|
Unit:.................. |
|
Form B03-DNN |
|
Address:........................ |
|
(Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
(Under direct method) (*)
Year…
Unit:.................. ...........
|
Item |
Code |
Note |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
A |
B |
C |
1 |
2 |
|
Cash flows from operation |
|
|
|
|
|
1. revenues from sales and service rendered and other revenues |
01 |
|
|
|
|
2. Amounts paid to suppliers of goods and services |
02 |
|
|
|
|
3. Amounts paid to employees |
03 |
|
|
|
|
4. Interest payments |
04 |
|
|
|
|
5. Payments of corporate income tax |
05 |
|
|
|
|
6. Other revenues from operation |
06 |
|
|
|
|
7. Other payments for operation |
07 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows from operation |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
II. Cash flows from investment |
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for purchase of fixed assets, investment property and other non-current assets |
21 |
|
|
|
|
Cash received from liquidation, transfer of fixed assets, investment property and other non-current assets |
22 |
|
|
|
|
Loans, purchase of debt instruments of other entities |
23 |
|
|
|
|
Collections from borrowers and proceeds from disposal of debt instruments of other entities |
24 |
|
|
|
|
payments for investments in other entities |
25 |
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from disposal of investments in other entities |
26 |
|
|
|
|
Interests and dividends received |
27 |
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities |
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
III. Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from share issuance, capital contribution |
31 |
|
|
|
|
Capital redemption and payments for purchase of treasury shares |
32 |
|
|
|
|
Drawdown of borrowings |
33 |
|
|
|
|
Repayments of borrowings |
34 |
|
|
|
|
Repayments of finance lease liabilities |
35 |
|
|
|
|
6. Dividends paid to shareholders |
36 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows from financial activities |
40 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows during the year (50=20+30+40) |
50 |
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year |
60 |
|
|
|
|
Effect of fluctuations in foreign exchange rates |
61 |
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year (70 = 50+60+61) |
70 |
V.11 |
|
|
Date…………….
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Director |
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
Note: *The items without figures are not required to report but are not permitted to change the “ code”.
|
Unit:.................. |
|
Form B 03 - DNN |
|
Address:........................ |
|
(Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
CASH FLOW STATEMENT
(Under indirect method) (*)
Year…
Unit:.................. ...........
|
Item |
Code |
Note |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
Cash flows from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
1. Profit before tax |
01 |
|
|
|
|
2. Adjustments for |
|
|
|
|
|
- Depreciation of fixed assets |
02 |
|
|
|
|
- Provisions |
03 |
|
|
|
|
- Unrealized foreign exchange gain/ loss |
04 |
|
|
|
|
- Profits/losses from investing activities |
05 |
|
|
|
|
- Interest expenses |
06 |
|
|
|
|
3. Operating income before changes in working capital |
08 |
|
|
|
|
- Increase/ decrease in receivables |
09 |
|
|
|
|
- Increase/ decrease in inventories |
10 |
|
|
|
|
- Increase/decrease in payables (other than interest, corporate income tax) |
11 |
|
|
|
|
- Increase/Decrease in prepaid expenses |
12 |
|
|
|
|
- Interest paid |
13 |
|
|
|
|
- Corporate income tax paid |
14 |
|
|
|
|
- Other proceeds from operating activities |
15 |
|
|
|
|
- Other payments for operating activities |
16 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows from operating activities |
20 |
|
|
|
|
II. Cash flows from investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for purchase of fixed assets, investment property and other non-current assets |
21 |
|
|
|
|
Cash received from liquidation, transfer of fixed assets, investment property and other non-current assets |
22 |
|
|
|
|
Loans, purchase of debt instruments of other entities |
23 |
|
|
|
|
Collections from borrowers and proceeds from disposal of debt instruments of other entities |
24 |
|
|
|
|
5. Payments for investments in other entities |
25 |
|
|
|
|
6. Proceeds from disposal of investments in other entities |
26 |
|
|
|
|
7. Interests and dividends received |
27 |
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities |
30 |
|
|
|
|
III. Cash flows from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from share issuance, capital contribution |
31 |
|
|
|
|
Capital redemption and payments for purchase of treasury shares |
32 |
|
|
|
|
3. Drawdown of borrowings |
33 |
|
|
|
|
4. Repayments of borrowings |
34 |
|
|
|
|
5. Repayments of finance lease liabilities |
35 |
|
|
|
|
6. Dividends paid to shareholders |
36 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows from financial activities |
40 |
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows during the year (50=20+30+40) |
50 |
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year |
60 |
|
|
|
|
Effect of fluctuations in foreign exchange rates |
61 |
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year (70 = 50+60+61)
|
70 |
V.11 |
|
|
Date…………….
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Director |
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
Note: (*) The items without figures are not required to report but are not permitted to change the “code”.
5. Notes to financial statement
|
Unit: Address: |
|
Form B 09 - DNN (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENT(*)
Year…
Operation features
Investment form
Operating field
Total number of workers
Operation features in the fiscal year that affect the financial statements
II. Accounting policies
Accounting year (starting on ... / ... / ... ending on ... / ... / ...)
Standard currency unit used in accounting
Accounting system
Accounting form
Method of inventory accounting
- Recognition of inventories;
- Method of calculating the value of inventories at the end of period;
- Method of accounting for inventories (perpetual inventory method or periodical inventory method)
Method of applicable fixed asset depreciation
Recognition of borrowing costs
Recognition of accrued expenses
Principles and method of recognition of payable provisions
Recognition of exchange rate differences
Principles and methods of revenue recognition
III. Additional information on the items of balance sheet
Unit:
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
Closing balance |
Beginning balance |
|
- Cash - Cash in banks - cash equivalents |
.... .... .... |
.... .... .... |
|
Total
|
|
|
|
02. Inventories |
Closing balance |
Beginning balance |
|
- - raw materials, materials - Instruments, tools - Work in process - Finished goods - Merchandise - Outward goods on consignment |
.... .... .... .... .... .... |
.... .... .... .... .... .... |
|
Total |
|
|
* Note of other figures and explanations (if any).............................................................
03- Increases /decreases of tangible fixed assets:
|
Item |
Building and structures |
Machinery and equipment |
Vehicles |
...
|
Other tangible fixed assets |
Total |
|
Cost of tangible fixed assets - Beginning balance - Increase in year In which: + New purchases + Construction - Decrease in year In which: + disposal +transfer + Transfer to investment property
- Closing balance (2) accumulated depreciation - Beginning balance - Increase in year - Decrease in year - Closing balance Net book values of tangible fixed assets(1-2) - Beginning balance - Closing balance In which: + Fixed assets used as pleaged loans +Temporarily unused fixed assets +Fixed assets awaiting liquidation
|
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....)
(.....) |
* Note of other figures and explanations:
- Fully depreciated fixed assets that are still in use: ........................................ ...................................
- Reasons for increase or decrease: .....................................................................................................
04. 04. Increases /decreases of intangible fixed assets
|
Item |
land use right |
Copyright |
Licence |
... |
Other intangible fixed assets |
Total |
|
(1)Cost of intangible fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Beginning balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Increase in year In which +Purchase +Internally generation from the enterprise - Decrease in year In which: + disposal, transfer + Other decreases |
(…)
(…) (…) |
(…)
(…) (…) |
(…)
(…) (…) |
(…)
(…) (…) |
(…)
(…) (…) |
(…)
(…) (…) |
|
- Closing balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) Accumulated depreciation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Beginning balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Increase in year - Decrease in year |
(... ) |
(... ) |
(... ) |
(... ) |
(... ) |
(... ) |
|
- Closing balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(3) Net book values of intangible fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Beginning balance - Closing balance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Note of other figures and explanations (if any) ..................................... ........................
|
05 – increase/decrease of investments in other entities: |
Closing balance |
Beginning balance |
|
(1) Short-term financial investments: - Short-term investment securities - Other short-term financial investments (2) Long -term financial investments: - Investments into jointly controlled entities - Investments into associates - Other long-term financial investments |
..... ...... ...... ..... ...... ...... ...... |
...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... |
|
Total |
|
|
* Reasons for increase or decrease: ....................................................................................................
|
06- Taxes and other payables to the State Budget: |
Closing balance |
Beginning balance |
|
- payable VAT |
..... |
..... |
|
- Special consumption tax |
..... |
..... |
|
- Import-export duties |
..... |
..... |
|
- Corporate income tax |
..... |
..... |
|
- personal income tax |
..... |
..... |
|
- severance tax |
..... |
..... |
|
- Land tax, land rents |
..... |
..... |
|
- Other taxes |
..... |
..... |
|
- Charges, fees and other payables |
..... |
..... |
07- Increase/ decreases of owner’s equity:
|
Item |
Beginning balance |
Increase in year |
Decrease in year |
Closing Balance |
|
A |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Owner’s capital share premium Other capital of owners Treasury shares (*) Exchange rate differences Other equity funds undistributed post-tax profits |
(.....) |
(.....) |
(.....) |
(.....) |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
* Reasons for increase or decrease: .........................................................................................
IV. Additional information on the items of income statement
Unit:..................
|
08. Revenues and other income |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
- Revenue from sales of merchandises In which: Revenue from merchandise exchange |
..... ..... |
..... ..... |
|
- Revenue from service provisions In which: revenues from service exchange |
..... ..... |
..... ..... |
|
- Financial income |
..... |
..... |
|
In which: |
|
|
|
Interests and dividends received |
...... |
...... |
|
+realized foreign exchange gains + Unrealized foreign exchange gains |
...... ...... |
...... ...... |
|
+ .... |
...... |
...... |
|
09. Adjustments of increase/ decrease of income subject to Corporate Income Tax |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
Total profit before tax |
...... |
...... |
|
(2) income which is not included in income subject to Corporate Income Tax (3) Expenses which are not deducted from income subject to Corporate Income Tax (4) unused losses (loss of the previous year which is deducted from pre-tax profit) |
...... ......
|
...... ......
|
|
(5) income subject to Corporate Income Tax during year (5 = 1- 2+3-4) |
...... |
...... |
|
10. Operating expenses: |
Current year |
Previous year |
|
raw material, material costs Labor costs fixed asset depreciation cost Outside service cost Other costs in cash |
..... ..... ..... ..... ...... |
...... ...... ...... ..... ..... |
|
Total |
....... |
....... |
V. Additional information on the items of cash flow statement (unit….)
11. Information on non-cash transactions arising during reporting year
|
|
Current year |
Previous year |
|
- purchase of assets by receiving liabilities which are directly related to or through finance lease transaction; |
….... |
......... |
|
- Transfer liabilities into owner’s equity |
….... |
......... |
12 - Cash and cash equivalents that the enterprise holds but is not permitted to use
|
|
Current year |
Previous year |
|
- Sums received from deposit; |
….... |
......... |
|
Other sums... |
….... |
......... |
VI. Other information
- Contingent liabilities
- Events arising after the end of the annual accounting period
- Comparative information
- Other information (2)
VII-Overall assessment of items and recommendations:
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
|
|
|
Date……………. |
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Director |
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
Note:
The items without figures are not required to report but are not permitted to change the ordinal number of the items.
The enterprise is allowed to present other information, if it deems necessary for the users of financial statements.
6. Account balance sheet (applied to cooperatives)
Unit: Address: |
|
Form B01- DNN/HTX (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
ACCOUNT BALANCE SHEET (*)
Year…
Unit:
|
Code |
Description |
Beginning balance |
Balance during year |
Closing balance |
|||
|
|
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
|
|
A |
B |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note:
(*) It may be used for level-1 account or both level-1 account and level-2 account
|
|
|
Date……………. |
|
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Chairman of cooperative |
|
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
|
7. Income statement (applied to cooperatives)
The form of this income statement shall comply with the Form B02-DNN, part A - List of financial statement of small and medium-sized enterprises
8. Notes to financial statement (applied to cooperatives)
|
Cooperative: Address: |
|
Form B09- DNN/HTX (Issued under the Minister of Finance’s Decision No. 48/2006 / QD-BTC dated September 14, 2006) |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENT(*)
Year…
I-Operation features of the cooperative
Operating field: ..............................................................................................
Total members: .....................................................................................................
Operation features of the cooperative in the fiscal year that affect the financial statements:
II. Accounting system in the cooperative
Accounting year (starting on ... / ... / ... ending on ... / ... / ...)
Standard currency unit used in accounting
Accounting system
Accounting form
Method of applicable fixed asset depreciation ...................................................................
III- Details some items: (Unit...)
01- Increases /decreases of fixed assets of the cooperative:
|
Item |
Building and structures |
Machinery and equipment |
Vehicles |
...
|
Other fixed assets |
Total |
|
Cost of fixed assets - Beginning balance - Increase in year In which: + Contribution of members +New purchases + Construction - Decrease in year In which: + disposal +transfer + ..... - Closing balance (2) accumulated depreciation value - Beginning balance - Increase in year - Decrease in year - Closing balance (3)Net book values of fixed assets(1-2) - Beginning balance - Closing balance In which: + Fixed assets used as pleaged loans
+Temporarily unused fixed assets +Fixed assets awaiting liquidation
|
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
(.....) (.....) (.....) (.....)
(.....) |
* Note of other figures and explanations:
- Fully depreciated fixed assets that are still in use: ........................................ ...................................
- Reasons for increase or decrease: ...........................................................................................................
02- Debts receivable, liabilities of the cooperative:
|
Item |
Amount |
condition |
Note |
|
A |
1 |
2 |
B |
|
Debts receivable: |
|
|
|
|
I. Receivable from members - ... - ... - ... |
|
|
|
|
II. Trade receivables - ... - ... - ... |
|
|
|
|
III. Other debts receivable - ... - ... - ... |
|
|
|
|
B-LIABILITIES: |
|
|
|
|
Trade payables: - ... - ... - ... |
|
|
|
|
II. Payables for members: - ... - ... - ... |
|
|
|
|
III. III. loans payable: |
|
|
|
|
1. Bank loans short-term loans Long-term loans |
|
|
|
|
2. Borrowings from other entities short-term loans - Long-term loans |
|
|
|
|
IV. Other payables |
|
|
|
03- Increase/ decrease of owner’s equity:
|
Item |
Beginning balance |
Increase in year |
Decrease in year |
Closing Balance |
|
A |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
I. contributed capital of members 1. contributed capital as stipulated 2. Capital contributed by members outside the specified level 3. Joint venture, associate capital contribution of other organizations II. accumulative capital 1. Other equity funds - - - 2. undistributed post-tax profits
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total (I+II) |
|
|
|
|
04. Revenues, other income and expenses
|
Item |
Activities of the cooperative |
Total |
|||||
|
..... |
..... |
..... |
.... |
.... |
.... |
||
|
A |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
... |
10 |
|
I. Revenues II. other income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
III. Costs 1. Cost for work in process at the beginning of period 2. Costs arising in the period - raw material, material cost - cost for employees - fixed asset depreciation cost - Other costs in cash 3. Cost for work in process at the end of year IV. Cost price of products, goods sold in year V. Business administrative expense VI. Profit before tax (VI = I + II – IV – V) VII. Corporate income tax expense |
x
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
x
|
|
|
VIII. post-tax profits of current year (VIII = VI – VII) |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
IX. Undistributed profit of previous year |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
X. Total profit used for distribution |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
1. Expenditures for capital contributors |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
2. Setting up fund |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
3. Distribution to its members |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
|
4. Undistributed profit |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
VII-Overall assessment of items and recommendations:
..........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
|
|
|
Date……………. |
|
|
Prepared by |
Chief accountant |
Chairman of cooperative |
|
|
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name) |
(signature, full name, stamp) |
|
Part 4:
REGULATIONS ON ACCOUNTING VOUCHERS
I-GENERAL PROVISIONS
Accounting vouchers are papers and information carriers recording completed economic, finance transactions as the basis for accounting entries..
All economic, finance transactions arising in production and business in units must be recorded in vouchers and recorded fully, truthly and objectively in accounting vouchers.
Forms of accounting vouchers include:
a) Forms of mandatory accounting vouchers include special ones that are valuable as money such as: note of receipts, note of payments, checks, receipts, charge/ fee tickets, bonds, treasury bills, government bonds , sales invoices and other mandatory vouchers. Forms of mandatory accounting vouchers are stipulated by competent State agencies. Accounting units must comply with forms, contents and methods of recording items which apply uniformly to accounting units or to each specific accounting unit.
b) Guiding forms of accounting vouchers are the ones stipulated by competent State agencies; in addition to the contents specified in the form, accounting units may add items or change the form in accordance with the recording and management requirements of the units.
System of forms of accounting vouchers
System of accounting voucher forms applicable to small and medium-sized enterprises include:
- Accounting vouchers issued under the accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises, including 5 items:
+ Labor and wage;
+inventory;
+sales;
+currency;
+Fixed assets.
- Accounting vouchers promulgated in other legal documents (form and guideline are under documents that have been issued)
An accounting voucher must contain all the following details:
- Name and serial number of the vouchers;
- Day, month, year of the vouchers;
- Name and address of the unit or individual that has made the voucher;
- Name and address of the unit or individual that receives the voucher;
- Content of the arising economic and financial transaction;
- Quantity, unit price and amount in figures of economic and financial transaction; total amount in figures and words of the voucher used for collecting and paying money;
- The signature of the voucher maker, approver and persons related to the voucher;
Vouchers used as a direct basis for accounting entries must be added the item of determination of accounts
The accounting vouchers must be made in full copies as prescribed. The vouchers must be recorded clearly, truthfully, fully with all details, and the unfilled-in blanks must be crossed out. There must be no erasion or correction in vouchers. In case of wrong inscription, the wrongly inscribed copy must be deleted but must not be torn away from the counterfoils.
The following acts shall be strictly prohibited:
- signing in blank vouchers and pre-printed forms (Director and Chief accountant of the units).
- Signing blank checks (account holder and chief accountant);
- Distorting the economic content of the voucher;
- Rectifying or erasing accounting vouchers;
- Annulment of vouchers without permission;
- Legalization of accounting vouchers.
Signing accounting vouchers;
All vouchers are valid only when they must be fully signed under the title defined in the vouchers. Electronic vouchers must have electronic signature in accordance with the law. All signatures in accounting vouchers must be signed using a ballpoint pen or pens, must not be signed in red ink or using pencil, signatures in accounting vouchers used for payment must be signed in each copy. The signature on the accounting vouchers of a person must be consistent and must match the signature that was registered under the regulations, if such person did not register for his signature, the signature of current time must match the signature of previous times.
Enterprises which do not appoint chief accountants must appoint an accountant to deal with customer, bank, the signature of chief accountant is replaced by such accountant’s signature. The accountant must comply with tasks, responsibilities and rights prescribed for a chief accountant.
The signature of the head of an enterprise (director) or an authorized person, chief accountant (or an authorized person) and the stamp on the vouchers must match the valid stamp and signature’s sample which is registered at the bank.
The accountant's signature in the voucher must match the signature registered in the "Register of specimen signatures of the enterprise".
Chief accountant (or authorized person) is not allowed to sign the word "authorized" of the head of the enterprise. The authorized person is not allowed to authorize to other people.0}
Enterprises must open the register of specimen signatures of cashiers, storekeepers, accountants, chief accountants (and their authorized persons), directors (and their authorized persons). The register of specimen signatures must be paginated, stamped and managed by the head of the enterprise (or authorized person) in order to facilitate inspection. Each person must sign three specimen signatures in the register.
They are not allowed to sign vouchers when they have not recorded or record insufficiently contents of the voucher under the responsibility of the signatories.
The decentralization of signing in vouchers is stipulated by the Director of enterprise in conformity with the law, requirements for management, ensuring strict control, asset security.
Order for circulation of accounting vouchers
- The order and time limit for circulating the accounting vouchers shall be stipulated by the chief accountant. The accounting vouchers made by the units or sent from outside must all be concentrated at the unit’s accounting department. The accounting department shall have to examine carefully such accounting vouchers which shall be used for making entries in the accounting books only after being examined and verified as true.
- The order for circulation of accounting vouchers shall include the following steps:
+ Making accounting vouchers and recording the arising economic and/or financial transaction in the vouchers;
+ Inspecting the vouchers;
+ Making entries in accounting books;
+ Retaining and preserving accounting vouchers.
The inspection of accounting vouchers shall cover the following contents:
- Inspecting the transparency, truthfulness, adequacy of the items recorded in the vouchers;
- Inspecting the legality, validity of the arising economic and financial transactions;
- Inspecting the accuracy of data and information in the vouchers;
- Inspecting the compliance with the regulation on internal control by the voucher makers, inspectors and approvers for each type of economic and financial transaction.
If acts of violating the unit and State’s economic and financial policies and regulations are detected, upon the inspection of accounting vouchers, the implementation of such accounting vouchers (fund deductions, payment, dispatching…) must be rejected and the violations must be immediately reported to the directors and chief accountants of the units for timely handling according to the current regulations.
For accounting vouchers made not according to the prescribed procedures, contents and/or with unclear figures, the persons responsible for inspection or for book entries must return them or notify such to the units where the vouchers have been made for refilling in or supplementing the procedures and adjustment before they are used as basis for book entries.
Translations vouchers into Vietnamese
The accounting vouchers which are written in a foreign language, when being used to record the accounting books in Vietnam must be translated into Vietnamese. The vouchers that rarely arise or repeatedly arise which have different contents must be translated their entire contents. For vouchers that repeatedly arise and have the same content, the first copy must be translated its entire contents, from the second copy, only main contents such as: name of the vouchers, name of unit or individual making the vouchers, name and individual receiving the vouchers, economic content of the vouchers and titles of the persons signing the vouchers are translated ... The translators must sign and write their full name and must be responsible for the content translated into Vietnamese. The Vietnamese translation must be accompanied with the original in foreign language.
Retaining accounting vouchers
- Accounting vouchers that were used must be sorted, classified , preserved and retained according to regulations on retaining accounting vouchers and documents of the State.
Period of retaining vouchers (See provisions in point 8.4, Part I - General Provisions)
- Losses of original vouchers must be reported to the Director and the chief accountant of the unit for timely handling measures. Particularly for the loss of sales invoices, receipts and blank checks, number of lost invoices, loss circumstances must be reported to the tax authorities or local police security agencies for measures to verify and handle according to the law. Simultaneously measures to notify and neutralize the lost vouchers must be taken.
Regulation on use and management of accounting vouchers
- The small and medium-sized enterprises must apply this regulation on accounting vouchers. During the implementation process, for mandatory accounting vouchers, units are not allowed to remove or rectify the vouchers. If they wish to rectify, they are required to gain the written agreement with the Ministry of Finance and must be approved the Ministry of Finance.
- Pre-printed voucher forms must be preserved carefully must not be damaged or rotten. The vouchers of the sales item such as VAT invoices, sales invoices, goods dispatch and internal transport note ... must be managed under the regulation on management and use of the prints.
- Enterprises that use electronic vouchers for economic, financial transactions and accounting entries must comply with the provisions of the legal documents on electronic vouchers.
Printing and issuing accounting vouchers
- Enterprises that print mandatory vouchers are required to comply with the design set in this policy.
Accounting vouchers such as invoices, dispatching notes, statements, ... relating to tax calculation approved to issue by the Ministry of Finance. Unit that wishes to print itself must gain a written approval from the Ministry of Finance (General Department of Taxation) and must register the number of vouchers according to the series of the Finance Ministry.
- Accounting vouchers can be printed in two languages: Vietnamese and foreign language. The printing-houses are not allowed to automatically change the content of the vouchers or to print accounting vouchers contrary to the provisions in this policy
II. LIST OF ACCOUNTING VOUCHERS
|
No |
Name of voucher |
Code |
PROPERTY |
|
|
|
|
|
BB (*) |
HD (*) |
|
|
A- ACCOUNTING VOUCHERS ISSUED UNDER THIS DECISION |
|
||
|
|
I-Labor and wage |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Employee timesheet |
01a-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
2 |
overtime record sheet |
01b-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
3 |
Wage payment sheet |
02-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
4 |
Reward payment sheet |
03-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
5 |
Travel ticket |
04-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
6 |
certification note of finished product or work |
05-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
7 |
Overtime payment sheet |
06-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
8 |
Outsourcing payment sheet |
07-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
9 |
package contract |
08-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
10 |
Report of liquidation/acceptance of package contract |
09-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
11 |
list of deductions from salary amounts |
10-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
12 |
Allocation list of salary and social insurance |
11-LĐTL |
|
x |
|
|
II- Inventories |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Goods-received note |
01-VT |
|
x |
|
2 |
Goods dispatch note |
02-VT |
|
x |
|
3 |
Report of testing materials, tools, products, goods |
03-VT |
|
x |
|
4 |
Report on remaining materials at the end of period |
04-VT |
|
x |
|
5 |
Report of inventory of materials, tools, products, goods |
05-VT |
|
x |
|
6 |
List of purchased goods |
06-VT |
|
x |
|
7 |
Allocation table of raw materials, materials, tools, instruments |
07-VT |
|
x |
|
|
III-Sales |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Payment sheet of goods consigned for agency or deposited |
01-BH |
|
x |
|
2 |
counter card |
02-BH |
|
x |
|
3 |
List of repurchased shares |
03-BH |
|
x |
|
4 |
A list of sold shares |
04-BH |
|
x |
|
|
IV- Currency |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Note of receipts |
01-TT |
x |
|
|
2 |
Note of payments |
02-TT |
x |
|
|
3 |
written request for advance |
03-TT |
|
x |
|
4 |
written payment for advance |
04-TT |
|
x |
|
5 |
written request for payment |
05-TT |
|
x |
|
6 |
receipts |
06-TT |
x |
|
|
7 |
List of gold, silver, precious metals and jewels |
07-TT |
|
x |
|
8 |
List of inventory of funds (used for VND) |
08a-TT |
|
x |
|
9 |
List of inventory of funds (used for foreign currency, gold, silver, precious metals and jewels) |
08b-TT |
|
x |
|
10 |
list of payment |
09-TT |
|
x |
|
|
V-fixed assets |
|
|
|
|
1 |
Report of transfer and receipt of fixed assets |
01-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
2 |
Report of liquidation of fixed assets |
02-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
3 |
transfer note of fixed assets of completed great repair |
03-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
4 |
Report of revaluation of fixed assets |
04-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
5 |
Report of inventory of fixed assets |
05-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
6 |
Sheet of calculation and allocation of fixed asset depreciation |
06-TSCĐ |
|
x |
|
|
B- VOUCHERS ISSUED UNDER OTHER LEGAL DOCUMENTS |
|||
|
1 |
Certificate of sick leave subject to society insurance allowance. |
|
|
x |
|
2 |
List of workers taking leave with sickness/ maternity allowance. |
|
|
x |
|
3 |
Value-Added Invoice |
01GTKT-3LL |
x |
|
|
4 |
Ordinary sales invoices |
02GTGT-3LL |
x |
|
|
5 |
Internal transport and goods dispatch note |
03 PXK-3LL |
x |
|
|
6 |
dispatch note of goods on consignment for agency |
04 HDL-3LL |
x |
|
|
7 |
finance lease service invoice |
05 TTC-LL |
x |
|
|
8 |
list of goods purchased without invoices |
04/GTGT |
x |
|
|
9 |
.......................... |
|
|
|
Note:
(*)BB: mandatory form
(*)HD: guidance form
Part 5:
REGULATIONS ON ACCOUNTING BOOKS
GENERAL PROVISIONS
1. Accounting books
Accounting books are used to record, systematize and retain all of economic and financial transactions having arisen under economic content and time order relating to enterprises.
Enterprises must comply with regulations on accounting books in the Law on Accounting, the Government's Decree No. 129/2004 / ND-CP dated May 31, 2005 providing instructions on the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Accounting in business, documents providing guidance on the Law on Accounting and this accounting policy.
2. Types of accounting books
Each enterprise has only one accounting book system for an accounting year. Accounting books include general accounting books and detailed accounting books.
The general accounting books include: The ledger, the journal.
The detailed accounting books include: detailed accounting books and cards.
The State prescribes compulsory book forms, contents and methods of making entries for ledgers and journals; prescribes oriented guidance on detailed accounting books and cards.
General accounting books
(a) The Journal is used to record economic and financial transactions arising in each accounting period and in an accounting year according to the time order and reciprocal relations between accounts of such transactions. The accounting data on the Journal must be recorded the total amount arising on the Debit side and the total amount arising on the Credit side of all accounting accounts used at the enterprise.
The Journal must be fully recorded the following factors:
- Day, month of book entry;
- Serial number and date of issuance of accounting vouchers used as basis for book entries;
- Summary of contents of the arising economic, financial transactions;
- Amount of the arising transactions;
(b)The Ledger is used to record economic and financial transactions arising in the accounting period and an accounting year (according to accounting accounts prescribed in the accounting account system applicable to small and medium-sized enterprises). The accounting data on the Ledger must be recorded the situation on assets, capital sources, situation and results of production and business operation of the enterprise. The Ledger must be fully recorded the following factors:
- Day, month of book entry;
- Serial number and date of issuance of accounting vouchers used as basis for book entries;
- Summary of contents of the arising economic, financial transactions;
- Amount of the arising economic, financial transactions, inscribed on the Debit side or the Credit side of the account.
Detailed accounting books
The detailed accounting books are used to record arising economic, financial transactions relating to accounting objects that need to be monitored in detail according to managerial requirements. The data on detailed accounting books supply information in service of the management of each kind of asset, capital sources, revenue and expenditure that have not been recorded in the Journal and the Ledger.
The quantity and structure of the detailed accounting books are not compulsorily prescribed. Enterprises shall have to base themselves on the guiding provisions of the State on detailed accounting books and their managerial requirements of enterprises to open necessary and appropriate books of detailed accounting.
3. Accounting book system
Each accounting unit only has one official and unique accounting book system for an accounting year. Enterprises must base on accounting account system applied in the enterprises and their own management requirements to open enough necessary general accounting books and detailed accounting books.
4. Responsibilities of individuals assigned to keep and record accounting books
The accounting books must be strictly managed, with the book-keeping and entering responsibility being assigned to individuals. Employees assigned the accounting books shall have to bear responsibility for things inscribed therein and to keep the books during the time of using them.
In case of change of the accounting book keepers and inscribers, the chief accountant shall have to organize the transfer of responsibility to manage and enter accounting books between the out-going accountants and the in-coming accountants. The transfer note must be signed for certification by the chief accountant.
5. Recording accounting books using hand or computer
Accounting units are allowed to record accounting books using hand or computer.
In case of recording accounting books using hand, accounting units must follow one of the accounting forms and forms of accounting books as prescribed in Section II - accounting forms. Accounting units are allowed to open more detailed accounting books according to their management requirement.
In case of recording accounting books using computer, enterprises are allowed to choose either purchase or design accounting software accordingly. Forms of accounting on computer applied in enterprises must meet the following requirements:
- Have all necessary general accounting books and detailed accounting books to meet the accounting requirements as prescribed. The general accounting books must contain all the contents prescribed by regulations on accounting books.
- Strictly comply with the regulations on opening, recording, closing and rectifying the accounting books as prescribed by the Law on Accounting, the documents guiding the implementation of the Law on Accounting and the provisions of this accounting policy.
- Enterprises must base on the standards and conditions of accounting software prescribed by the Ministry of Finance in Circular No. 103/2005 / TT-BTC dated November 24, 2005 to choose accounting software suitable to their management requirements and conditions.
6. Opening, recording and closing accounting book
Opening accounting books
The accounting books must be opened at the beginning of an accounting year. For a newly-established enterprise, accounting books must be opened from the date of its establishment. The legal representative and chief accountant of an enterprise shall have to sign for approval of these accounting books recorded by hand before they are used, or sign for approval of official accounting books after they are printed from computer.
The accounting books must be used pre-printed forms which may be bounded into volume or may be in loose sheets. These sheets should be bounded into a volume after use for retention.
Before the accounting books are used, the following procedures must be completed:
For accounting books in form of volume:
The first page of a book must be clearly written with the name of the enterprise, the book title, the date of book opening, the accounting year and book- entry period, the full name of the book keeper , inscriber, chief accountant and legal representative, the date of ending book entry or the date of transferring the book to another person.
Pages must be numbered from the first to the last page and stamped with the seal of the accounting unit at places between two pages (called the overlapping stamp).
For books in loose sheets:
The top of each loose sheet must be clearly inscribed with the name of the enterprise, the ordinal number of each book sheet, the book title, the date of use, the full name of the book keeper and inscriber.
The loose sheets, before being used, must be signed for certification by the director or authorized person, stamped and recorded in the register for use of loose-sheeted books. The loose-sheeted books must be arranged in a accounting account order to ensure safety and easy access.
Recording books
Recording books must necessarily be based on the accounting vouchers which were inspected and meet regulations on accounting vouchers. All data recorded on accounting books are required to have legal and reasonable accounting vouchers.
Closing books
At the end of the accounting period, accounting books must be closed before the financial statement is prepared. In addition, accounting books must be closed in the inventory or other cases as prescribed by law.
7. Correction of accounting books
When accounting books which are recorded using hand are detected errors during book-entry, it is prohibited to erase untraceably wrong information and data. Correction must be made using one of the following methods:
(a) The method of correction (also called method of wiping out):
This method is used to correct errors on accounting books, the wrongly inscribed figures shall be crossed out with a straight line so that the wrongly inscribed content which has been crossed out can still be seen. Above the crossed-out place, the correct figure shall be inscribed in common ink. The corrected figures should be certified to their sides with the signature of the Chief accountant or accountant. This method is used in case:
- Errors are made in the explanation and not related to the reciprocal relationships between accounts;
- Errors do not affect the total money amounts.
(b) The method of negative figure inscription (also called the method of red inscription)
This method is used to correct errors as follows: all the wrong entries must be re-written in red ink (negative figure inscription) to cancel these entries, then later the correct entries shall be written in common ink in replacement thereof.
This method is used in case:
- Errors relate to the reciprocal relations between accounts due to wrong determination of amounts, which have already been inscribed in the accounting books and cannot be corrected by the method of correction;
- Errors are detected after financial statements have been submitted to competent agencies; In this case, the correction of errors in the accounting books in the year of detection of errors under the prospective or retroactive method is permitted under the provisions of Accounting Standard No. 29, "Changes in accounting policies, accounting estimates and errors ";
- Errors are made when the amounts of money in accounts have been inscribed time and again or the wrongly inscribed figures are bigger than the correct figures.
When using the method of negative figure inscription to correct errors, a "corrected book entry voucher" must be made and signed for certification by the chief accountant.
(c)the method of additional inscription:
This method shall apply to cases where the entries are inscribed correctly for the reciprocal relations between accounts but the inscribed money amounts are smaller than the money amounts on the vouchers or the money amounts inscribed on vouchers are omitted and not fully added up. In case of correction by this method, the "corrected book entry voucher" must also be made to additionally record in normal ink the difference amount..
Correction of book entries which are computerized
- If errors are detected before annual financial statements are submitted to competent State agencies, the correction can be made directly in accounting books of such year on the computers;
- If errors are detected after annual financial statements are submitted to competent State agencies, the correction can be made directly in accounting books of the year in which errors are detected on the computers and noted in the last line of the accounting books of year in which errors are made;
- Cases of correction of book entries which are computerized are made according to the “method of negative figure inscription” or “ method of additional inscription ".
When the annual settlement report is approved or when the inspection and auditing have been completed and an official conclusion is given, if there is a decision to correct the figures in the financial statements relating to figures that were recorded in accounting books, the unit must correct the accounting books and the balance of the relevant accounts under the prescribed method. The correction is made directly in the accounting books of the year in which errors are detected , and taken notes on the last page (last line) of the accounting books of the year prior to the year of error (if errors are detected after the annual financial statements are submitted to the competent State agencies) for convenient comparison and inspection.
8. Adjustment of accounting books
Where enterprises must an make retroactive adjustment due to detecting material misstatements in the previous years under the provisions of Accounting Standard No. 29, "Changes in accounting policies, accounting estimates and errors", accountants must adjust beginning balance in general accounting books and detailed accounting books of relevant accounts.
9. Accounting book forms
(a) Enterprises are allowed to apply one in four following accounting forms:
- General journal;
- Journal- Ledger;
- Entry voucher;
- Computerized accounting.
In each form of accounting books, there are specific provisions on the amount, structure, form, order and method of recording and the relationship between the accounting books.
(b) enterprises must base on the size and characteristics of production and business operation, management requirements, professional qualifications of accounting personnel, technical equipment condition to calculate and choose a suitable accounting form, and must comply with the provisions of such accounting book form, including: Type and structure, comparison and inspection relation, order, recording method of accounting books.
II. ACCOUNTING FORM
1. Accounting form of general journal
Principles, basic features of the accounting form of General Journal.
Basic features of the accounting form of General Journal. All arising economic and financial transactions must be entered into the Journal, and the focus is General journal according to the time order of their arising and economic contents (determination of the accounting amount) of each transaction, then the figures in the General Journal shall be taken out for entering the Ledger according to each arising transaction.
Accounting book form of General Journal shall include the following types of accounting book:
- The General Journal, special journal;
- The Ledger;
- The detailed accounting books, cards.
The order of entering the accounting books in form of General Journal (Diagram 01)
(a) Daily, based on the accounting vouchers inspected and used as bases for book entry, the arising operations firstly are entered into the General Journal, then based on the figures on the General Journal, they are made entries into the Ledger according to appropriate accounting accounts. If the units opened the detailed accounting books or cards, alongside the entering of the General Journal, the arising operations are entered into the relevant detailed accounting books or cards.
If the units open the special Journal daily, based on the vouchers used as a basis for book entry, arising transactions are entered into relevant special Journals. Periodically (every 3, 5, 10 ... days) or at the end of a month, depending on the volume of arising transactions, each special Journal shall be summarized, figures are taken out to enter into the appropriate accounts in the Ledger, after duplicate numbers are eliminated because one transaction is recorded in many special Journal concurrently (if any).
(b) At the end of a month, quarter and year, the figures on the Ledger is added up, the account Balance sheet is made.
After the consistency inspection and comparison, the figures recorded on the Ledger and the Detail General Sheet (made from the detailed accounting books, cards) shall be used for making the financial reports.
On principle, the total arising Debit amount and the total arising Credit amount on the account Balance sheet must be equal to the total arising Debit amount and the total arising Credit amount on the General Journal( or the General Journal and special Journal after duplicate numbers in special Journal are deliminated) of the same period.
DIAGRAM NO.1
THE ORDER OF ENTERING THE ACCOUNTING BOOKS IN FORM OF GENERAL JOURNAL
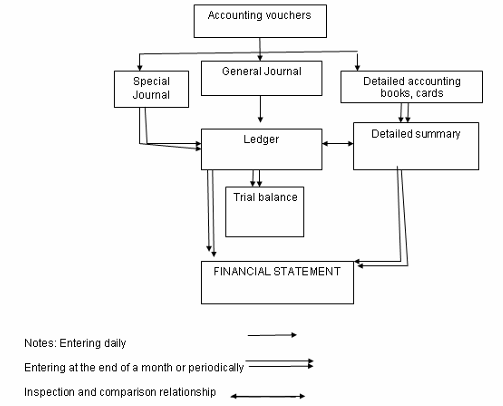
2. Accounting form of Journal- Ledger
Basic features of the accounting form of Journal- Ledger.
Basic features of the accounting form of Journal- Ledger: The arising economic, financial transactions are recorded according to the time order and economic contents (according to accounting accounts) on the same sole general accounting book being the Journal-Ledger. The bases for entering the Journal-Ledger accounting book are accounting vouchers or the general sheet of accounting vouchers of the same types.
The form of Journal-Ledger accounting shall include the following types of accounting book:
- Journal- Ledger;
- The detailed accounting books, cards.
The order of entering the accounting books in form of Journal- Ledger (Diagram 02)
(a) Daily, accountants base on the accounting vouchers or the general sheet of accounting vouchers of the same type which is used as the basis for entering the books, to determine Debit account, credit account to enter the Journal-Ledger. Figures of each voucher ( or general sheet of accounting vouchers of the same type) are entered in the same line in both Journal and Ledger . The general sheet of accounting vouchers are made for vouchers of the same types (receipt notes, payment notes, goods-dispatch notes, goods-receipt notes…) arising may times in one day or every 1, 2 or 3 days
The accounting vouchers and the general sheet of accounting vouchers of the same type after being entered the Journal-Ledger are used to enter relevant detailed accounting books, cards.
(b) At the month-end, after recording all arising accounting vouchers in the Journal-Ledger and detailed accounting books, cards, accountans add figures of arising amount column in the Journal and Debit column, credit column of each account in Ledger to enter in arising adding at the end of month. Based on the balance at the beginning of the month ( quarter) and arising one during the month (quarter), accountants calculate the balance at the end of the month (quarter) of each account in the Journal- Ledger.
(c) When inspecting and comparing the added number at the end of month (quarter) in the Journal – Ledger, the following requirements must be met:
|
total amount in “arising” column in Journal |
|
Total arising Debit amount of all accounts |
|
Total arising Credit amount of all accounts |
|
= |
= |
|||
|
|
|
|
Total Debit balance of accounts |
= |
Total Credit balance of accounts |
(D) Detailed accounting books and cards must also be closed to add arising Debit amount, arising Credit amount and calculate month-end balance of each object. Based on the book closing figures of objects, "Summary of Details" is made for each account. The figures in the "Summary of detail" are compared with arising Debit amount, arising Credit amount and the Balance at the end of month of each account in the Journal - Ledger.
Figures in the Journal - Ledger and in the "Summary of details" after the books are closed are checked, compared, if they are consistent, they shall be to prepare the financial statements.
DIAGRAM NO.02
THE ORDER OF ENTERING THE ACCOUNTING BOOKS IN FORM OF JOURNAL- LEDGER
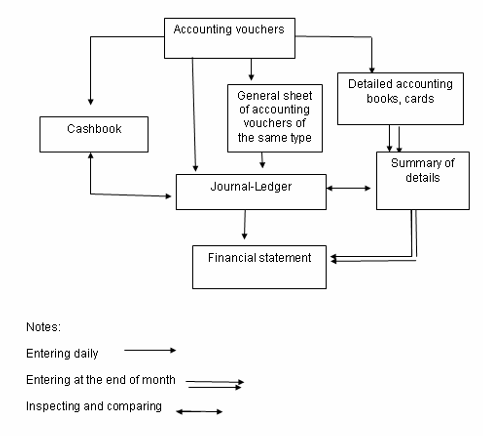
3. Form of book-entry voucher accounting book
Basic features of the accounting form of book-entry voucher
Basic features of the accounting form of book-entry voucher: The direct bases for entering the general accounting book is the "Entry Vouchers" The entering of general accounting books shall include:
+ Entering according to the time order on the entry voucher register.
+ Entering according to economic contents in the Ledger.
The entry vouchers shall be made by accountants on the basis of each voucher or the general sheet of original vouchers of the same type and the same economic content.
The entry vouchers are numbered continuously in each month or for the whole year (according to the ordinal number in the entry voucher register) and enclosed with original vouchers, and must be approved by the chief accountant before entering the accounting books.
Forms of Book-Entry Voucher accounting book shall include the following types of accounting book:
- The book-entry voucher;
- The entry voucher register;
- The Ledger;
- The detailed accounting books, cards.
The order of entering the accounting books in form of book –entry voucher (Diagram No. 02)
(a) Daily, accountants make the entry vouchers, based on the accounting vouchers or the general sheet of inspected accounting vouchers of the same type. Based on the entry Voucher, accountants enter the entry voucher register, which are later used for entering the Ledger. The accounting vouchers, after being used as bases for making the Entry Voucher, shall be used for entering the detailed accounting books and cards.0}
(b) At the month-end, accountants must close the book and calculate the total sum of money of the economic and financial operations arising in the month in the entry voucher Register, calculate the total arising Debit amount, the total arising Credit amount and the balance of each account in the Ledger. Based on the Ledger, accountants make the account balance sheet.
( c)After the comparison for consistency, the figures in the Ledger and the Summary of details (made from the detailed accounting books, cards) are used for preparing financial statement.
The relations of comparison and inspection must ensure that the total arising Debit amount and the total arising Credit amount of all accounts in the account Balance sheet are equal to each other and equal to the total arising amount in the Entry Voucher Register. The total Debit balance and the total Credit balance of all accounts in the account Balance sheet must be equal to each other, and the balance of each account in the Account Balance sheet must be equal to the balance of each corresponding account in the Summary of Details.
DIAGRAM NO.3
THE ORDER OF ENTERING THE ACCOUNTING BOOKS IN FORM OF BOOK –ENTRY VOUCHER
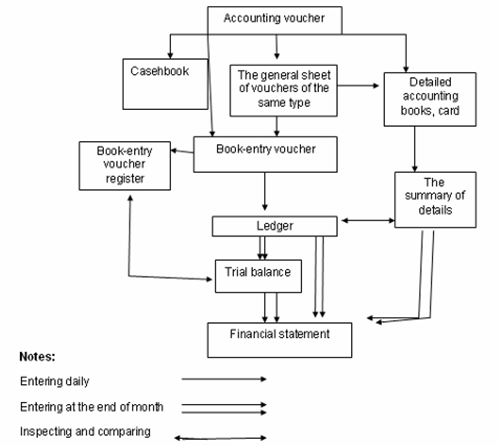
4. Computerized accounting form.
Basic features of computerized accounting form
The basic features of computerized accounting form :accounting work is carried out according to an accounting software program on the computer. The accounting software is designed on the principle of one of four accounting forms, or a combination of accounting forms prescribed above. The accounting software does not show the complete process of accounting entries, but must print fully the accounting books and financial statements as prescribed.
Computerized accounting form shall include the following types of accounting books: Each accounting software which is designed under one form of accounting shall have a type of accounting book of such form which is not required to be the same as accounting book forms recorded by hand.
The order of entering the accounting books in form of computerized accounting
(a) Daily, accountants base on accounting vouchers or the general sheet of inspected accounting vouchers of the same type which are used as the basis for book-entry, to determine the debit account, credit account to enter data into computers under the tables, forms designed in the accounting software.
According to the procedure of the accounting software, the information is automatically entered into the general accounting books (Ledger or Journal - Ledger ...) and the relevant detailed accounting books, cards.
(b) At the end of month(or any necessary time), accountants shall close (add) accounting books and prepare financial statement . The comparison between the figures summarized and the detailed figures is made automatically and ensures accuracy and truthfulness according to information that was entered during the period. Accountants may check and compare figures between the accounting books and the financial statement after they are printed out.
The printing of the financial statements shall comply with provisions.
At the end of each month, each year, general accounting books and detailed accounting books are printed out, bounded into books and undergone legal procedures under provisions of accounting books inscribed by hand.
DIAGRAM NO.4
THE ORDER OF ENTERING THE ACCOUNTING BOOKS IN FORM OF COMPUTERIZED ACCOUNTING
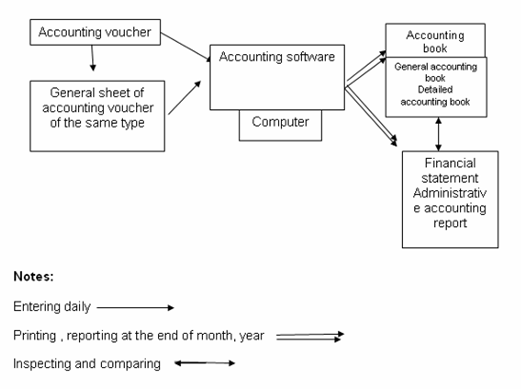
III. LIST OF ACCOUNTING BOOKS APPLIED TO SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES
1. List of books
|
No. |
Book’s title |
Code |
Accounting form |
||
|
General Journal |
Journal-Ledger |
Book-entry voucher |
|||
|
01 |
Journal-Ledger |
S01-DNN |
- |
x |
- |
|
02 |
Book-entry voucher |
S02a-DNN |
- |
- |
x |
|
03 |
Book-entry register |
S02b-DNN |
- |
- |
x |
|
04 |
Ledger (used for accounting form of book-entry voucher) |
S02c1-DNN S02c2-DNN |
- |
- |
x x |
|
05 |
General Journal |
S03a-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
06 |
Cash receipt journal |
S03a1-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
07 |
Cash payment journal |
S03a2-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
08 |
Purchase journal |
S03a3-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
09 |
Sales journal |
S03a4-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
10 |
Ledger (used for accounting form of General Journal) |
S03b-DNN |
x |
- |
- |
|
11 |
Account balance sheet |
S04-DNN |
x |
- |
x |
|
12 |
Cashbook |
S05a-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
13 |
Detailed accounting book of cash |
S05b-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
14 |
Bank deposit book |
S06-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
15 |
Detail book on materials, instrument, product, goods |
S07-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
16 |
Detailed summary of materials, instrument, product, goods |
S08-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
17 |
Warehouse card (or book) |
S09-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
18 |
fixed asset book |
S10-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
19 |
Monitoring book of fixed assets and tools, instruments in using place |
S11-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
20 |
Fixed asset card |
S12-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
21 |
Detail book on payment to buyers (sellers) |
S13-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
22 |
Detail book on payment to buyers (sellers) in foreign currency |
S14-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
23 |
Monitoring book of payment in foreign currency |
S15-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
24 |
Detailed book of borrowed money |
S16-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
25 |
Detailed book of sales |
S17-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
26 |
Operation cost book |
S18-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
27 |
Card of cost price of product, service |
S19-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
28 |
Detail book on accounts |
S20-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
29 |
Detailed book on issuing shares |
S21-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
30 |
Detailed book on treasury shares |
S22-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
31 |
Detailed book on securities investment |
S23-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
32 |
Working capital source detail book |
S24-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
33 |
construction cost book |
S25-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
34 |
VAT monitoring book |
S26-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
35 |
Detailed book on refundable VAT |
S27-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
36 |
Detailed book on VAT exemption |
S28-DNN |
x |
x |
x |
|
37 |
Other detailed books at the request of management requirements of enterprises |
|
|
|
|
The order and method of recording and the relationship among types of accounting books according to each accounting form are defined in Section II "Accounting Forms" above.
* * *
Notes:
(1) The document detailing "Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises" was circulated in book issued by the Ministry of Finance (the Department of Audit and Accounting Regulation)
(2) Detailed information and answers to questions about "Accounting policy for small and medium-sized enterprises" are on website: www.vacpa.org.vn.








