Circular 28/2011/TT-BTNMT technical procedures for ambient air noise monitoring đã được thay thế bởi Circular 24/2017/TT-BTNMT on environmental monitoring techniques và được áp dụng kể từ ngày 15/10/2017.
Nội dung toàn văn Circular 28/2011/TT-BTNMT technical procedures for ambient air noise monitoring
|
MINISTRY OF NATURAL
RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC
OF VIETNAM |
|
No.: 28/2011/TT-BTNMT |
Hanoi, August 01, 2011 |
CIRCULAR
TECHNICAL PROCEDURES FOR AMBIENT AIR AND NOISE MONITORING
MINISTER OF NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT
Pursuant to the Government's Decree No. 25/2008/ND-CP dated March 04, 2008 on defining the functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, amended and supplemented by the Government's Decree No.19/2010/ND-CP dated March 08, 2010 and Decree No. 89/2010/ND-CP dated August 16, 2010;
Pursuant to the Government's Decree No. 102/2008/ND-CP dated September 15, 2008 on collection, management and use of the natural resources and environment database;
Pursuant to the Prime Minister’s Decision No. 16/2007/QD-TTg dated January 29, 2007 on approval for the Master Plan for national monitoring network for natural resources and environment by 2020;
At the request of Director of Vietnam Environment Administration, Director of Department of Science and Technology, and Director of Legal Department,
HEREBY PRESCRIBES:
Chapter I
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1. Scope
This Circular provides for the technical procedures for ambient air and noise monitoring, including: determination of monitoring objectives, monitoring program design, and monitoring program execution.
Article 2. Regulated entities
1. This Circular applies to:
a) Central and local environment authorities; environmental monitoring stations and centers of the national environmental monitoring network and local environmental monitoring networks;
b) The organizations licensed or assigned to carry out environmental monitoring activities, provide environmental monitoring services, and submit reports to central and local environment authorities;
2. This Circular does not apply to the ambient air and noise monitoring using automatic or continuous devices.
Article 3. Interpretation of terms
In this document, these terms are construed as follows:
1. Ambient air refers to the outdoor air to which people, plants, animals or material may be exposed;
2. Dust is a fine dispersion in which dispersion medium is gas phase and dispersed phase is solid particles larger than molecular size and smaller than 100 mm in diameter.
Article 4. Rules for application of standards and citation methods
1. The application of standards and citation methods must comply with the monitoring and analytical methods and standards mentioned in Chapter II of this Circular;
2. If amendments to the monitoring and analytical standards and methods mentioned in Chapter II of this Circular occur, newly revised standards and methods shall come into force.
Chapter II
TECHNICAL PROCEDURES FOR AMBIENT AIR MONITORING
Article 5. Monitoring objectives
The major objectives for the ambient air monitoring are as follows:
1. Determine the air pollution status and its effects on the community health in conformity with currently permitted standards;
2. Determine effects of separate sources of waste or groups of waste sources on the quality of local air environment;
3. Provide information to the formulation of plans for pollution control and industrial development;
4. Evaluate the spatial and temporal variations of the air quality;
5. Issue warnings of pollution to the air environment;
6. Satisfy other requirements for central and local environment management.
Article 6. Designing a monitoring program
A monitoring program must be approved or accepted in writing by a competent authority or an agency in charge of monitoring programs. Designing the ambient air monitoring program is detailed as below:
1. Monitoring type
Depending on the monitoring objectives, the program designer must determine whether the monitoring is background monitoring or impact monitoring.
2. Monitoring location and points
a) The determination of monitoring locations and points depends on the monitoring objectives;
b) Before determining a monitoring location or point, a survey shall be conducted at the monitoring region to determine sources of waste causing the ambient air pollution. After conducting field surveys, location of monitoring points shall be marked on diagram or map;
c) While determining locations of ambient air monitoring points, the following matters should be considered:
- Weather conditions: wind direction, wind speed, solar radiation, air humidity and air temperature;
- Topographical conditions: the monitoring place must have convenient and clear topography with features representing the subject region. At places with complex topography, the monitoring location is determined according to local emission conditions.
3. Monitoring parameters
a) Typical and representative parameters for a monitoring region shall be selected depending on the data collection and field surveys which must be firstly conducted to collect information about the monitoring location (residential area, production area, etc.), production type, emission locations, and sources of waste generated thereto;
b) The following major parameters are selected to evaluate the ambient air quality:
- Parameters mandatorily monitored on the scene: wind direction, wind speed, temperature, relative humidity, pressure and solar radiation;
- Other parameters: sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrous oxide (NOx), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Ozone (O3), Total suspended particles (TSP), dust particles less than or equal to 10 µm in diameter (PM10), Plumbum (Pb);
c) Depending on objectives and requirements of the monitoring program, other parameters mentioned in the QCVN 06:2009/BTNMT may be additionally monitored.
4. Monitoring time and frequency
a) Monitoring time depends on the following elements:
- Monitoring objectives;
- Monitoring parameters;
- Operations generating waste in the monitoring region and surrounding regions;
- Meteorological factors;
- Monitoring equipment;
- Whether the applied monitoring approach is positive or negative;
- Data processing methods;
- Sensitivity of analytical methods.
b) Monitoring frequency
- Frequency of background monitoring: at least once every month;
- Frequency of impact monitoring: at least 06 times annually.
c) Notes to determine monitoring frequency:
When there are cyclical changes of air quality, the length of time between two times of sampling constantly which must be designed short enough to discover such changes;
5. Establishing a monitoring plan
A monitoring plan which is prepared according to the monitoring program includes the following contents:
a) The list of personnel performing the monitoring tasks and assignments for each participating person;
b) The list of organizations and individuals participating or cooperating in the monitoring of environment (if any);
c) The list of monitoring equipment, apparatus, and chemicals for field monitoring and laboratory analysis;
d) Labor safety tools and equipment for the monitoring of environment;
dd) Samples required, sample volume, and sample storage time;
e) Methods for laboratory analysis;
g) Environmental monitoring expenses;
h) The plan for environmental monitoring quality assurance and management.
Article 7. Implementing a monitoring program
The implementation of a monitoring program includes the following tasks:
1. Preparations
Following preparations shall be made prior to monitoring activities:
a) Prepare documents, maps, diagrams, and common data about the sampled regions;
b) Monitor the climate and weather variations;
c) Prepare necessary tools and instruments; check, clean, and calibrate the equipment and instruments for sampling, measuring, and testing before going to the scene;
d) Prepare chemicals, supplies, and instruments for taking and preserving samples;
dd) Prepare sample labels, forms, monitoring and analysis logs as prescribed;
e) Prepare instruments for taking and transporting samples;
g) Prepare labor safety tools and equipment;
h) Prepare funding and personnel for monitoring;
i) Prepare accommodation for personnel who work for many days;
k) Prepare other relevant documents and forms.
2. Sampling, measuring and analysis at field
a) At the sampling location, meteorological parameters (temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed and direction) shall be monitored at the field;
b) Basing on data quality objectives, the air sampling, measurement and analysis methods must comply with any of the methods mentioned in the following Table 1:
Table 1. Methods for field air sampling, measurement and analysis
|
No. |
Parameters |
Code of standard or method |
|
1 |
SO2 |
• TCVN 7726:2007 (ISO10498:2004); • TCVN 5971:1995 (ISO 6767:1990); • TCVN 5978:1995 (ISO 4221:1980); |
|
2 |
CO |
• TCVN 5972:1995 (ISO 8186:1989); |
|
3 |
NO2 |
• TCVN 6137:2009 (ISO 6768:1998); |
|
4 |
O3 |
• TCVN 6157:1996 (ISO 10313:1993); • TCVN 7171:2002 (ISO 13964:1998); |
|
5 |
Particulate lead |
• TCVN 6152:1996 (ISO 9855:1993); |
|
6 |
Dust |
• TCVN 5067:1995 |
|
7 |
Other meteorological parameters |
• Regulations on meteorological monitoring adopted by National Centre for Hydrometeorological Forecasting – NCHMF. • Manufacturers’ instructions for operation of meteorological monitoring equipment. |
b) If national standards for field air sampling, measurement and analysis mentioned in Table 1 hereto are not available, corresponding international standards mentioned in Table 1 or other international standards with equal or higher accuracy shall be applied;
c) Quality assurance and control tasks on the field shall comply with regulations on environmental monitoring quality assurance and control adopted by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
3. Preserving and transporting samples
a) Methods for sample storage must be conformable with monitoring parameters and methods for analyzing samples at the laboratory. Samples must be analyzed immediately after they are taken or stored at 5oC for a period of not exceeding 24 hours;
b) With regard to samples taken by employing the absorption method, the absorbing substances must be stored in vials with firm caps, placed on brackets and carefully arranged into cold storage box;
c) With regard to CO samples which are taken by employing the volume replacement method, sample storage devices must be arranged orderly, not be placed on each other or pressed by other things to avoid breaking and leaking;
d) Dust samples must be stored in dust sample storing bags which must be carefully closed, then put into sealed containers and maintained at room temperature;
4. Laboratory analysis
a) Basing on data quality objectives and laboratory conditions, the analysis of parameters must comply with any of the methods stated in the following Table 2:
Table 2. Methods for analysis of monitoring parameters at laboratories
|
No. |
Parameters |
Code of standard or method |
|
1 |
SO2 |
• TCVN 5971:1995 (ISO 6767:1990); • TCVN 5978:1995 (ISO 4221:1980); |
|
2 |
CO |
• TCVN 5972:1995 (ISO 8186:1989); • TCVN 7725:2007 (ISO 4224:2000); |
|
3 |
NO2 |
• TCVN 6137:2009 (ISO 6768:1998); • TCVN 6138:1996 (ISO 7996:1985); |
|
4 |
Particulate lead |
• TCVN 6152:1996 (ISO 9855:1993); |
|
5 |
Dust |
• TCVN 5067:1995 |
b) If national standards for determination of parameters mentioned in Table 2 hereto are not available, corresponding international standards mentioned in Table 2 or other international standards with equal or higher accuracy shall be applied;
c) Quality assurance and control tasks at laboratories shall comply with regulations on environmental monitoring quality assurance and control adopted by the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment.
5. Data processing and reporting
a) Data processing
- Data check: check the rationality of the environmental analysis and monitoring data. Data shall be checked according to documents of the samples (sampling record, field sampling logs, sample delivery record, field measurement/analysis result reports, laboratory analysis result reports, etc.), data of QC samples (blank samples, repeated samples, reference samples, etc.);
- Statistical processing: according to the quantity of samples and the reports, various methods and software programs may be used for statistical processing as long as the essential description (minimum value, maximum value, mean value, number exceeding standards, etc.) must be available;
- Comments on the data: comments on data must be given according to monitoring and analysis results that have been processed and verified, and relevant technical regulations and standards.
b) Reporting
After the monitoring program is completed, a monitoring result report shall be made and sent to a competent authority as prescribed.
Chapter III
TECHNICAL PROCEDURES FOR NOISE MONITORING
Article 8. Monitoring objectives
The major objectives for the noise monitoring are as follows:
1. Determine the levels of noise causing effects on the community health in conformity with currently permitted standards;
2. Determine effects of separate noise sources or groups of noise sources;
3. Provide information to the formulation of plans for noise control;
4. Evaluate the spatial and temporal variations of the noise pollution;
5. Issue warnings of the noise pollution;
6. Satisfy other requirements for central and local environment management.
Article 9. Designing and implementing a monitoring program
1. Noise monitoring location
a) The QCVN 26:2010/BTNMT - National Technical Regulation on Noise stipulates maximum levels of noise in areas where people live and work; the noise referred to in this Regulation is caused by human activities regardless noise sources or noise locations.
b) Regions requiring the measurement of noise include:
- Places needing special quiet: hospitals, libraries, sanitariums, kindergartens, and schools;
- Residential areas, hotels, dwelling houses, and administrative agencies;
- Commercial and service areas;
- Production factories located in residential areas.
c) Noise monitoring locations are selected in conformity with the national technical regulation TCVN 5964:1995, in which the following points should be carefully considered:
- Select a location which must have typical features of the monitoring region (with determined co-ordinates);
- Avoid obstacles which may cause the reflection of sound;
- Avoid man-made sources of noise such as music, clash made by hitting of metal objects, sounds of children frolicking, etc.);
- Select monitoring locations so as to ensure the most stable sound transmission with the unchanged wind components from the source to the monitoring location.
d) With regard to industrial manufacturing factories, the noise monitoring is conducted at the workplace as regulated in the National Technical Regulation TCVN 3985:1999.
2. Monitoring parameters
The noise monitoring parameters include:
a) LAeq: A-weighted equivalent sound level;
b) LAmax: maximum A-weighted sound level;
c) LAN,T : percentile level ;
d) Analyze noise at the one octave band (in industrial zones) ;
dd) Traffic intensity (for monitoring traffic noise).
3. Monitoring time and frequency
a) Monitoring frequency
The noise monitoring frequency depends on requirements of the agency in charge of the noise monitoring program, funding and purposes of the monitoring program provided that it shall not less than 04 times per year.
b) Monitoring time
- Noise at prescribed places and traffic noise must be continuously measured within 12, 18 or 24 hours depending on monitoring requirements.
- Noise at production factories must be measured within the working time;
- Because sound levels are influenced by weather conditions, the selection of noise monitoring time must pay attention to the following points:
+ Monitoring time must be selected so as to ensure that within the selected monitoring time, the average sound level is determined in a band of weather conditions appearing at monitoring locations;
+ Monitoring time is selected so as to ensure that measures are conducted within typical weather conditions.
4. Monitoring equipment
a) The noise monitoring equipment shall comply with the National Technical Regulation TCVN 5964:1995;
b) The equipment used in the noise monitoring includes integrating sound level meters with frequency analyzer. If the integrating sound level meter is not available, the sound exposure level meter shall be applied, in which monitoring times must be recorded and the statistical distribution method shall be employed to determine the LAeq,T value:
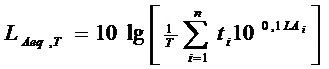
Where
- T = åti: total duration of sampling intervals;
- ti : time of exposure at the noise level LAi; (corresponding to the monitoring time i);
- LAi: A-weighted sound level during the ith time interval (ti);
- n: total times of noise level measurement.
c) For the purpose of assurance of monitoring quality, the sound level meters must be calibrated in conformity with applicable standards at the sound levels of 94 dBA and 104 dBA before each noise monitoring and periodically tested by competent calibration agencies.
5. Monitoring methods
Monitoring methods and time shall be selected in conformity with the national technical regulations coded TCVN 5964:1995 and TCVN 5965:1995.
a) Measurements
When conducting outdoor measurements, the reflection of sound must be minimized. Measurements must be taken at least 3.5m far away from the sound reflecting structures, excluding the ground. If other regulations are not applied, measurements are taken 1.2 - 1.5 m above the ground.
b) Outdoor measurements near multistoried buildings
These measurements shall be taken at the locations where the noise exposing on the multistoried building should be considered. Not otherwise provided for, measurements should be taken 1-2 m far away from the building and 1.2 – 1.5 m above the ground.
c) Traffic noise level measurements
- Measurements are taken 1.2 - 1.5 m above the ground;
- The reflection of sound must be minimized;
- Avoid sources of unwanted noise which may influence on measurements.
d) Indoor measurements
- These measurements shall be taken at the locations inside the fence where the noise should be considered. Not otherwise provided for, measurements must be taken at least 1 m far away from the walls or other reflecting surfaces, 1.2 – 1.5 m above the floor, 1.5 m far away from windows, and about 7.5 m far away from other sources of noise;
- Noise at the workplace caused by industrial machines must be measured at the 1:1 octave band frequency (as regulated in the National Technical Regulation TCVN 3985:1999).
dd) Notices
- Three measurements are taken within 1 hour, each of which is continuously taken within a 10-minute interval. Then, the mean value of such three measurements shall be taken. The achieved result shall be considered as the mean value of such measuring hour;
- For traffic noise caused by vehicle flow, besides measuring noise, it is necessary to determine the traffic intensity (vehicle/hour) by means of counting manually or automatic equipment. Type of vehicle in the vehicle flow must be classified, including:
+ Very large vehicles (containers and others with more than 10 wheels);
+ Trucks and coaches;
+ Cars (under 12 seats);
+ Motorbikes, mopeds.
- Similar steps shall be applied to measure the noise at 1:1 octave band provided that after setting time, measuring mode must be set up according to the 1:1 octave band frequency.
6. Data processing and reporting
a) Data processing
- Data check: check the rationality of the noise monitoring data. Checking data shall be based on monitoring documents (records, logs, field measuring results, etc.);
- Statistical processing: according to the quantity of measuring results and the reports, various methods and software programs may be used for statistical processing as long as the essential description (minimum value, maximum value, mean value, number exceeding standards, etc.) must be available;
- Comments on the data: comments on data must be given according to monitoring results that have been processed and verified, and relevant technical regulations and standards.
b) Reporting
After the monitoring program is completed, a noise monitoring result report shall be made and sent to a competent authority as prescribed.
Part IV
IMPLEMENTATION
Article 10. Implementation organization
1. The Vietnam Environment Administration shall instruct and inspect the implementation of this Circular;
2. Ministers, Heads of Ministerial-level Agencies, Heads of Affiliates of the Government, Chairpersons of the People's Committees at all levels, and other organizations and individuals involved shall assume responsible for implementing this Circular.
Article 11. Effect
1. This Circular shall come into force as from September 15, 2011.
2. Difficulties that arise during the implementation of this Circular should be reported to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (via Vietnam Environment Administration) for consideration./.
|
|
PP MINISTER
|






