Circular No. 21/2012/TT-BTNMT quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring đã được thay thế bởi Circular 24/2017/TT-BTNMT on environmental monitoring techniques và được áp dụng kể từ ngày 15/10/2017.
Nội dung toàn văn Circular No. 21/2012/TT-BTNMT quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring
|
THE MINISTRY OF
NATURAL RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT |
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF
VIETNAM |
|
No. 21/2012/TT-BTNMT |
Hanoi, December 19, 2012 |
CIRCULAR
REGULATIONS ON QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL IN ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
Pursuant to the Law on Environment protection dated November 29, 2005;
Pursuant to the Government's Decree No. 25/2008/NĐ-CP on March 04, 2008 on defining the functions, tasks, powers and organizational structure of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment amended and supplemented in the Government’s Decree No. 19/2010/NĐ-CP dated March 08, 2010 and Decree No. 89/2010/NĐ-CP dated August 16, 2010;
At the request of General Director of Vietnam Environment Administration, General Director of the Legal Department and General Director of Department of science and technology,
The Minister of Natural Resources and Environment promulgates the Circular regulating quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring.
Chapter I
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Article 1. Governing scope
1. This Circular regulates quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring.
2. Activities of environmental monitoring through automatic equipment are not regulated by this Circular.
Article 2. Regulated entities
This Circular applies to central and local environmental authorities; environmental monitoring stations and centers; organizations and individuals involved in environmental monitoring activities to provide data to central and local environmental authorities.
Article 3. Interpretation of terms
In this Circular, some terms are construed as follows:
1. Quality assurance (QA) in environmental monitoring means a system of integrating management and technical activities in an organization to ensure environmental monitoring activities meet prescribed quality standards.
2. Quality control (QC) in environmental monitoring means measures taken to assess, monitor and adjust precision of measurements to ensure activities of environmental monitoring meet prescribed quality standards.
3. Precision means level of concentration of duplicate measurement value on the same object.
4. Accuracy means measurement of reliability of the method, description of how closely a measurement comes to the true value of a physical quantity.
5. Sample batch means a group of samples treated and analyzed simultaneously and continuously under a process by an analyst in the same equipment calibration in a certain period of time.
6. Field blank sample means a sample of clean material used to control contamination during the process of sampling, measurement and testing at the site. Field blank sample is treated, stored, transported and used to analyze factors in the laboratory in almost the same way as real samples.
7. Duplicate sample includes at least two samples taken in the sample position and at the same time by the same equipment, treated, stored, transported and used to analyze factors in the laboratory as follows: Duplicate sample is used to control concentration of sampling, measurement and testing at the site.
8. Trip blank sample means a sample of clean material used to control contamination during the transport of samples. Trip blank sample is transported together with real samples under the same conditions, stored and used to analyze factors in the laboratory in almost the same way as real samples.
9. Equipment blank sample means a sample of clean material used to control level of contamination of sample-taking equipment, assess stability and interference of equipment. Equipment blank sample is treated in the same way as real samples by the sample-taking equipment, stored, transported and used to analyze factors in the laboratory in almost the same way as real samples.
10. Method blank sample means a sample of clean material, normally double-distilled water, used to inspect level of contamination of instruments, chemicals and reference materials during sample analysis.
11. Duplicate sample includes two or more components of the same sample to be prepared and analyzed independently under the same method. Duplicate sample is the sample used to assess precision of analysis results.
12. Certified reference materials means an amount of material or type of substance with adequate properties for the calibration of equipment, assessment of a test or determination of value for materials.
13. Quality assurance project plan means the plan describing all procedures on necessary quality assurance, quality control activities and other technical activities of the environmental monitoring program to ensure achieved results meet the requirements.
14. Method detection limit means lowest value of concentration of a substance in need of analysis with accuracy up to 99%, concentration of the substance for analysis greater than zero.
15. Instrument detection limit means lowest value of a substance to be analyzed found to be five times greater than interference signal of the equipment.
Chapter II
PARTICULAR PROVISIONS
Section 1. QUALITY ASSURANCE IN DESIGNING ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING PROGRAM (HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO AS 'THE PROGRAM')
Article 4. Quality assurance in the determination of the monitoring program’s targets
Based on state administration agencies’ requirements for environmental protection, environmental monitoring stations and centers, organizations and individuals shall participate in environmental monitoring to determine specific targets of the program. Determination of targets must be based on current policies and laws on environmental protection and demands for information that needs to be collected.
Article 5. Basic requirements for a monitoring program
1. Accord with national strategy, program and plan for environmental protection
2. Comply fully with regulations the program’s design;
3. Comply with regulations on processes and methods for each component and factor of the environment to be monitored.
4. Be checked, adjusted and supplemented on a regular basis;
Article 6. Design of the program
Designing the program is carried out as follows:
1. Determine targets of the program as prescribed in Article 4 hereof;
2. Carry out a survey of the area to be monitored;
3. Determine sources of impacts and main pollutants in monitoring areas; determine borders of monitoring areas and make forecasts about potential impacts or changes in monitoring areas;
4. Determine types of monitoring, components of the environment to be monitored;
5. Establish the list of monitoring factors for each environmental component: Factors measured and test at the site, factors analyzed in the lab;
6. Design sampling methods; determine lines and points to take samples and do markings on the maps; describe geographical positions, coordinates and symbols of monitoring points;
7. Determine monitoring frequency and time;
8. Determine methods of sampling, measurement and testing at the site and analytical methods in labs.
9. Determine sampling processes, volume of samples to be taken, types of sample containers, preservative chemicals, sample keeping time, types and quantity of quality control samples;
10. Make a list and plans for maintenance and calibration of site equipment and lab equipment including equipment, instruments and means for traffic safety assurance;
11. Determine vehicles serving activities of taking and transporting samples;
12. Make a plan for implementing quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring; Establishment of the quality assurance plan is subject to Appendix I enclosed herewith.
13. Establish plans for arrangement of personnel implementing monitoring of which specific duties of individual staff must be specified;
14. Establish cost estimates for implementing the program including expenses for quality control and quality assurance implementation in environmental monitoring;
15. Make a list of organizations and individuals participating in the program and responsibilities of relevant parties;
Section 2. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL IN MONITORING ON SITE
Section 7. Quality assurance in monitoring on site
1. Determine positions to take samples;
2. Determine factors to be monitored including names of the factors, measurement units and method of monitoring such factors;
3. Use monitoring methods in accordance with monitoring targets and factors; Monitoring method is implemented under applicable regulations on environmental monitoring or according to international standard method recognized by Vietnam’s competent state agencies. Information about monitoring factors and methods is prescribed in Table 1, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
4. Use facilities in accordance with determined monitoring method meeting requirements of the method in terms of techniques and measurement. Facilities must have use instructions, detailed information about dates for maintenance, inspection, calibration and operators of the monitoring equipment. Information about monitoring facilities is prescribed in Table 2, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
5. Sample storage method and manner must be in compliance with monitoring factors according to applicable regulations on environmental monitoring or according to international standard method recognized by Vietnam’s competent state agencies. Information about sample storage method is prescribed in Table 3, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
6. Chemicals and samples are fully prepared according to regulations of each monitoring method, contained appropriately with labels describing name or type of chemicals, standard sample; name of manufacturer; concentration, preparation date, person in charge; useful life and other information (if any);
7. Sample containers must meet following requirements:
a) Be consistent with each monitoring factor;
b) Ensure quality without affecting or changing sample quality;
c) Containers must be labeled throughout the existence of samples Labels must display information about monitoring factors, sample symbols, sampling time, used sample storage method and other information (if any);
8. Transport of sample must fully ensure quality and quantity; Transport time and temperature of samples are prescribed in applicable regulations on environmental monitoring for each monitoring factor.
9. Delivery and receipt of samples as follows:
a) Delivery and receipt of samples are carried out at the site. Staff that carry out monitoring on site shall make delivery to staff responsible for transport of samples;
b) Delivery and receipt of samples are carried out at the lab. Staff who carry out monitoring on site or are responsible for transport of sample shall make delivery to staff working in the lab;
c) Delivery and receipt of samples as prescribed in Points a, b, this Clause must be included with a written record fully describing names and signatures of relevant parties as prescribed in Table 4, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
10. Staff that carry out monitoring on site must be appropriately qualified. Assignment of duties to staff is prescribed in Table 5, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
11. Reports on sampling must be made right after the time of sample taking. Reports must include at least information prescribed in Table 6, Appendix II enclosed herewith.
Section 8. Quality control in monitoring on site
Upon implementing monitoring on site, quality control samples should be used to control quality. Quality control samples used must be in compliance with each monitoring factor Quantity of quality control samples is used as follows:
1. Do not exceed 10% of total quantity of samples that need monitoring;
2. In case actual quantity of samples to be monitored in a monitoring program is smaller than 30 samples, the quantity of samples to be used must be at least three.
Section 3. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL IN MONITORING ON SITE
Section 9. Quality assurance in labs
1. Lab staff
a) Have document specifying responsibility, authority of lab staff issued by the lab’s competent persons;
b) Management staff must acquire at least university degrees;
c) Staff shall be assigned to perform tests when they are recognized by the lab's heads as having achieved accuracy as required by internal standards.
2. Quality management system: The lab must establish and maintain a quality management system in accordance with scope of operation, ensure objectivity and accuracy of test results;
3. Control of documents and records: The lab must carry out classification, statistical work, storage, management and control of documents and records within the lab’s quality management system.
4. Internal assessment of the lab’s operation: Annually, the lab must make a plan and carry out self-assessment of its activities in order to ascertain compliance with requirements of the quality management system. After assessment, the lab must put forward measures to remedy and improve detected mistakes (if any)
5. Testing method:
a) Choice of testing method:
Testing methods to be used are promulgated standard methods: Vietnam's standards or international standards, regional standards with equivalent or higher accuracy; Use of latest standardized methods is prioritized. Internal methods established by the lab must be approved as prescribed in Point b, Clause 5, Article 9 hereof.
b) Approval for testing method:
The lab must make a plan for granting approval for testing method. The lab shall be responsible for assessing the plan, implementation and result of granting approval for the method, making submission to higher levels for promulgation and application of the method in the lab;
The lab must have written evidence of choice of the method, confirm value from use of the method.
6. Lab facilities: The lab must make a plan for inspection, maintenance and calibration of equipment on a periodical basis. Equipment failing to meet technical requirements of the manufacturer must be remedied and calibrated before being put into operation.
7. Lab conditions and environment: The lab must carry out control of the lab’s environmental conditions to ensure no adverse effects on test results or on quality of tests
8. Test sample management:
a) Sample management processes must be appropriate to each particular analysis factor:
b) The lab’s sample encryption system must be established and maintained during the period the sample is stored in the lab. Sample encryption system must ensure samples are not mistaken;
c) Upon receipt of samples, the lab must record deviations in comparison with sample storage conditions as prescribed. The lab must consult with clients upon notice of any suspicion of non-conformities;
d) Samples after analyzed must be kept and stored in a period of time as prescribed for later inspection or analysis (if need be).
9. Data quality assurance: The lab must establish procedures on quality control to inspect rightness and repetition of tests as well as proficiency of staff performing tests.
Section 10. Quality control in labs
1. The lab must use quality control samples such as equipment blank sample, method blank sample, duplicate sample, certified reference materials, spike samples, control standard sample or other quality control samples required by the program or set out by the lab’s quality management program.
2. Minimum quantity of quality control samples needed for each sample batch must be adequate for inspection of contamination of instruments, chemicals, reagents and for assessment of precision and accuracy of analysis results but not exceed 15% of total quantity of samples needed for analysis in a monitoring program.
Section 4. QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL IN DATA MANAGEMENT AND REPORTING
Article 11. Basic requirements for data management and establishment of reports on environmental monitoring
1. Data management and assessment:
a) Documents and records relating to monitoring on site and analysis in the lab must be established in an adequate and timely manner and must be kept and managed as prescribed;
Data from activities of monitoring on site must be adequate and consistent with monitoring documentation; appropriate and consistent with sampling time and positions, monitoring method and equipment;
Data from lab analysis must be adequate and consistent with lab analysis documentation; appropriate and consistent with analysis time and factors, types of samples, analytical methods and equipment.
b) Data from monitoring on site and lab analysis must be inspected, calculated and handled. If staff who conduct monitoring and analysis find faults or errors in monitoring activities, reports must be made immediately to higher levels for handling or destruction of such data. However, previous documents and data before being handled or destroyed must be still kept as original documents for later study;
c) Results of measurement and testing on site and results of lab analysis must be accurate, clear and unbiased. Upon detection or suspicion of monitoring results, monitoring and analysis may be conducted again and relevant staff must be responsible for recording in the monitoring documents and records and reporting to higher levels for consideration and handling.
2. Establishment of monitoring reports:
a) Organizations that carry out environmental monitoring must make reports on monitoring results after every phase of monitoring and make annual compilation of monitoring results; Reports on monitoring results must include results of implementation of quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring.
b) Reports on monitoring results must stick closely on and meet the program’s targets, ensure authenticity, timeliness, accuracy and objectivity;
Section 12. Quality control in handling of data
Quality of monitoring data must be inspected according to data quality objective; Assessment must include at least:
1. Assessment of precision of analysis
Duplicate samples are used to assess precision of analysis results. For two duplicates, precision is assessed on the basis of RPD assessment, calculated as follows:
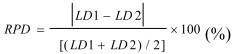
Where:
RPD: relative percent difference;
LD1: measured value of the first duplicate
LD2: measured value of the second duplicate
2. Assessment of completeness of data
a) Completeness of data is determined through full percentage of data, as measurement of quantity of samples to be monitored, compared with quantity of samples expected to take previously
b) Calculation: following formula is used to determine full percentage of data
![]()
Where:
C: Full percentage of data (%)
V: Number of measurements of monitoring samples accepted as eligible according to plan;
T: Total number of samples to be monitored as previously planned
C must achieve from 95% and over to ensure monitoring data meet demands for supply and use of information
Section 13. Quality assurance in establishment of reports
1. Reports on monitoring results must be signed and legally sealed by heads of environmental monitoring organizations before being submitted to competent agencies.
2. Reports on monitoring results must be established as prescribed in Point IV enclosed herewith.
Chapter III
IMPLEMENTATION
Article 14. Implementation
1. Vietnam Environment Administration shall be responsible for providing guidance and inspecting the implementation of this Circular.
2. Based on processes, methods, economic – technical norms and current expenditure regime, during the establishment of budget estimates for implementation of activities of monitoring, organizations participating in activities of environmental monitoring must establish budget estimates for implementation of quality assurance and quality control.
Article 15. Effect
1. This Circular takes effect since February 03, 2013.
2. The Minister of Natural Resources and Environment’s Circular No. 10/2007/TT-BTNMT dated October 22, 2007 providing guidance on quality assurance and quality control in environmental monitoring shall become invalid since this Circular takes effect.
3. Difficulties that arise during the implementation of this Circular should be reported to the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (via Vietnam Environment Administration) for consideration and handling./.
|
|
PP THE MINISTER |




